Citation: Erwin TL, Zamorano LS (2014) A synopsis of the tribe Lachnophorini, with a new genus of Neotropical distribution and a revision of the Neotropical genus Asklepia Liebke, 1938 (Insecta, Coleoptera, Carabidae). ZooKeys 430: 1–108. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.430.8094
Carabid beetles range in size from 0.6 mm to 90.2 mm and occur in nature in several fractal universes influencing life therein as predators, ectoparasitoids, seed eaters, and even fungal mycelia feeders in a multitude of ways. Understanding the impact of this beetle family’s importance across a multidimensional landscape in a cascade of fractal universes is our biodiversity challenge for the 21st century for one of insects’ most diverse families.
“So nat’ralists observe, a flea
Hath smaller fleas that on him prey;
And these have smaller fleas to bite ‘em.
And so proceeds Ad infinitum.”
Johnathan Swift
“Great fleas have little fleas upon their backs to bite ‘em,
And little fleas have lesser fleas, and so ad infinitum.
And the great fleas themselves, in turn, have greater fleas to go on,
While these again have greater still, and greater still, and so on.”
Augustus De Morgan
This synopsis provides an identification key to the genera of Tribe Lachnophorini of the Western and Eastern Hemispheres including five genera previously misplaced in carabid classifications. The genus Asklepia Liebke, 1938 is revised with 23 new species added and four species reassigned from Eucaerus LeConte, 1853 to Asklepia Liebke, 1938. In addition, a new genus is added herein to the Tribe: Peruphorticus gen. n. with its type species P. gulliveri sp. n. from Perú. Five taxa previously assigned to other tribes have adult attributes that make them candidates for classification in the Lachnophorini: Homethes Newman, Aeolodermus Andrewes, Stenocheila Laporte de Castelnau, Diplacanthogaster Liebke, and Selina Motschulsky are now considered to belong to the Lachnophorini as genera incertae sedis. Three higher level groups are proposed to contain the 18 recognized genera: the Lachnophorina, Eucaerina, and incertae sedis.
Twenty-three new species of the genus Asklepia are described and four new combinations are presented. They are listed with their type localities as follows: (geminata species group) Asklepia geminata (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Santarém, Rio Tapajós, Brazil; (hilaris species group) Asklepia campbellorum Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil, Asklepia demiti Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., circa Rio Demiti, Brazil, Asklepia duofos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil, Asklepia hilaris (Bates, 1871), comb. n., São Paulo de Olivença, Brazil, Asklepia grammechrysea Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., circa Pithecia, Cocha Shinguito, Perú, Asklepia lebioides (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Santarém, Rio Tapajós, Brazil, Asklepia laetitia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Leticia, Colombia, Asklepia matomena Zamorano & Erwin, sp.n., 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil; (pulchripennis species group) Asklepia adisi Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil, Asklepia asuncionensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Asunción, Río Paraguay, Paraguay, Asklepia biolat Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Perú, Asklepia bracheia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., circa Explornapo Camp, Río Napo, Cocha Shimagai, Perú, Asklepia cuiabaensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Cuiabá, Brazil, Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Limoncocha, Ecuador, Asklepia kathleenae Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Belém, Brazil, Asklepia macrops Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Concordia, Río Uruguay, Argentina, Asklepia marchantaria Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil, Asklepia marituba Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Marituba, Ananindeua, Brazil, Asklepia paraguayensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., San Lorenzo, Rio Paraguay, Paraguay, Asklepia pakitza Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Perú, Asklepia pulchripennis (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Santarém, Rio Tapajós, Brazil, Asklepia samiriaensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Boca del Río Samiria, Perú, Asklepia stalametlitos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Guayamer, Río Mamoré, Bolivia, Asklepia strandi Liebke, 1938, Guyana, Asklepia surinamensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., l’Hermitage, Surinam River, Surinam, Asklepia vigilante Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Boca del Río Samiria, Perú. Images of adults of all 18 genera are provided.
La presente sinopsis provee una clave dicotómica para todos los géneros del hemisferio oriental y occidental incluyendo cinco géneros anteriormente mal clasificados dentro de Carabidae. El género Asklepia Liebke, 1938 es revisado; 23 especies nuevas para la ciencia son incluídas, además de cuatro especies de Eucaerus LeConte, 1853, que son reasignadas dentro del género Asklepia Liebke, 1938. Adicionalmente, un nuevo género es asignado dentro de la tribu: Peruphorticus gen. n. y la especie tipo P. gulliveri sp. n. de Perú. Cinco taxones anteriormente asignados a otras tribus presentan atributos que los hacen buenos canditados para ser clasificados como Lachnophorini: Homethes Newman, Aeolodermus Andrewes, Stenocheila Laporte de Castelnau, Diplacanthogaster Liebke y Selina Motschulsky, son actualmente considerados como pertenecientes del complejo Lachnophorini como géneros incertae sedis. Se propone que los 18 géneros se distribuyen en tres taxones superiores: Lachnophorina, Eucaerina e incertae sedis.
Veinte y tres especies nuevas del género Asklepia son descritas y cuatro nuevas combinaciones son presentadas. Todas las especies y sus localidades tipo son enlistadas de la manera siguiente: (grupo de especies geminata) Asklepia geminata (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Santarém, Rio Tapajós, Brazil; (grupo de especies hilaris) Asklepia campbellorum Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil, Asklepia demiti Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., circa Rio Demiti, Brazil, Asklepia duofos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil, Asklepia hilaris (Bates, 1871), comb. n., São Paulo de Olivença, Brazil, Asklepia grammechrysea Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., circa Pithecia, Cocha Shinguito, Perú, Asklepia lebioides (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Santarém, Rio Tapajós, Brazil, Asklepia laetitia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Leticia, Colombia, Asklepia matomena Zamorano & Erwin, sp. nov., 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil; (grupo de especies pulchripennis) Asklepia adisi Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil, Asklepia asuncionensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Asunción, Río Paraguay, Paraguay, Asklepia biolat Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Perú, Asklepia bracheia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., circa Explornapo Camp, Río Napo, Cocha Shimagai, Perú, Asklepia cuiabaensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Cuiabá, Brazil, Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Limoncocha, Ecuador, Asklepia kathleenae Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Belém, Brazil, Asklepia macrops Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Concordia, Río Uruguay, Argentina, Asklepia marchantaria Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil, Asklepia marituba Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Marituba, Ananindeua, Brazil, Asklepia paraguayensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., San Lorenzo, Río Paraguay, Paraguay, Asklepia pakitza Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Perú, Asklepia pulchripennis (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Santarém, Rio Tapajós, Brazil, Asklepia samiriaensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Boca del Río Samiria, Perú, Asklepia stalametlitos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Guayamer, Río Mamoré, Bolivia, Asklepia strandi Liebke, 1938, Guyana, Asklepia surinamensis sp. n., l’Hermitage, Surinam River, Surinam, Asklepia vigilante Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Boca del Río Samiria, Perú. Imágenes de los adultos de los 18 géneros son proporcionadas.
Amazon Basin, Australia, Nearctic, Neotropics, Paleotropics, Eucaerina, Lachnophorina, Odacanthitae, Odacanthini, Calophaenini, new taxa, new distribution records
Cuenca Amazónica, Australia, Neárctico, Neotrópico, Paleotrópico, Eucaerina, Lachnophorina, Odacanthitae, Odacanthini, Calophaenini, nuevos taxones, nuevos reportes de distribución
One of the major lacunae in our knowledge of tropical Carabidae is the Tribe Lachnophorini whose 15 Western Hemisphere genera (mostly Neotropical) and three Eastern Hemisphere genera (Paleotropical and Australian) have never been fully revised, nor have two of the Eastern Hemisphere genera been associated formally with the Tribe, until now. Lachnophorini is a tribe known mostly from 19th century isolated species descriptions and lists, or a general coverage in papers of broader scope (
The larva of only one species of the tribe has been described (
We were intrigued that
With the discovery of the minute species Gehringia olympica Darlington, 1933 and its later southern counterparts, the explosion of discovery of new species of anillines in the Western Hemisphere (
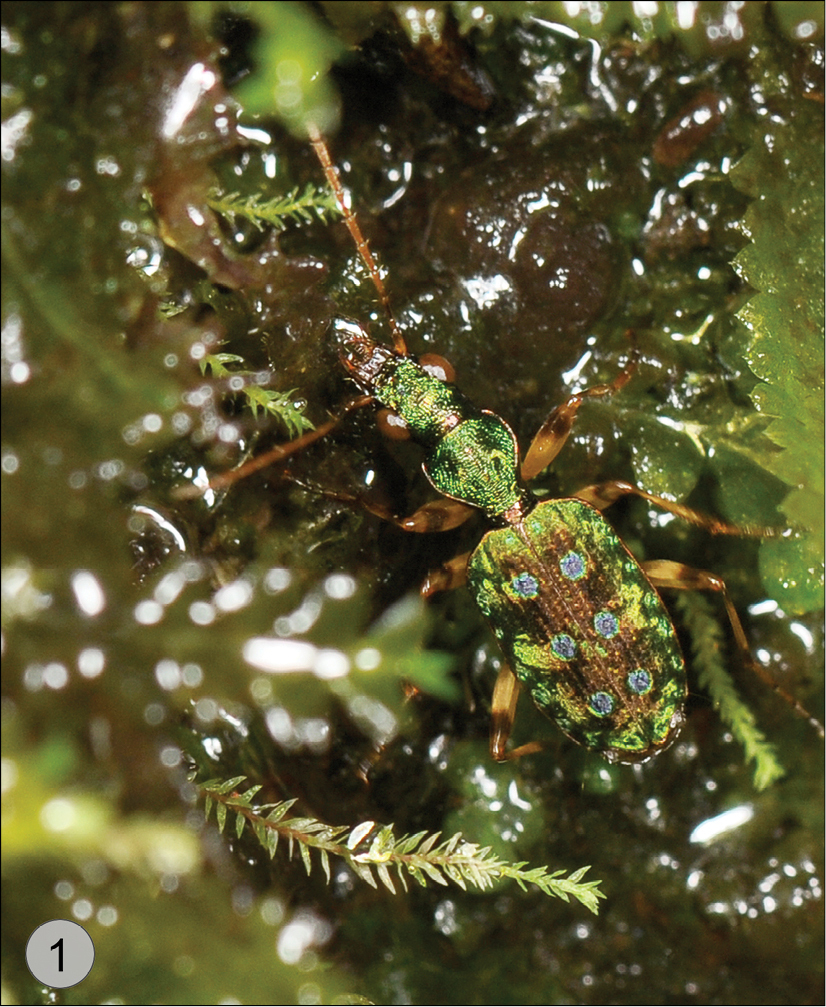
Quammenis spectabilis Erwin. Live individual in its natural hygropetric habitat in Costa Rica. Photo credit: K. Taro Eldredge, University of Kansas.
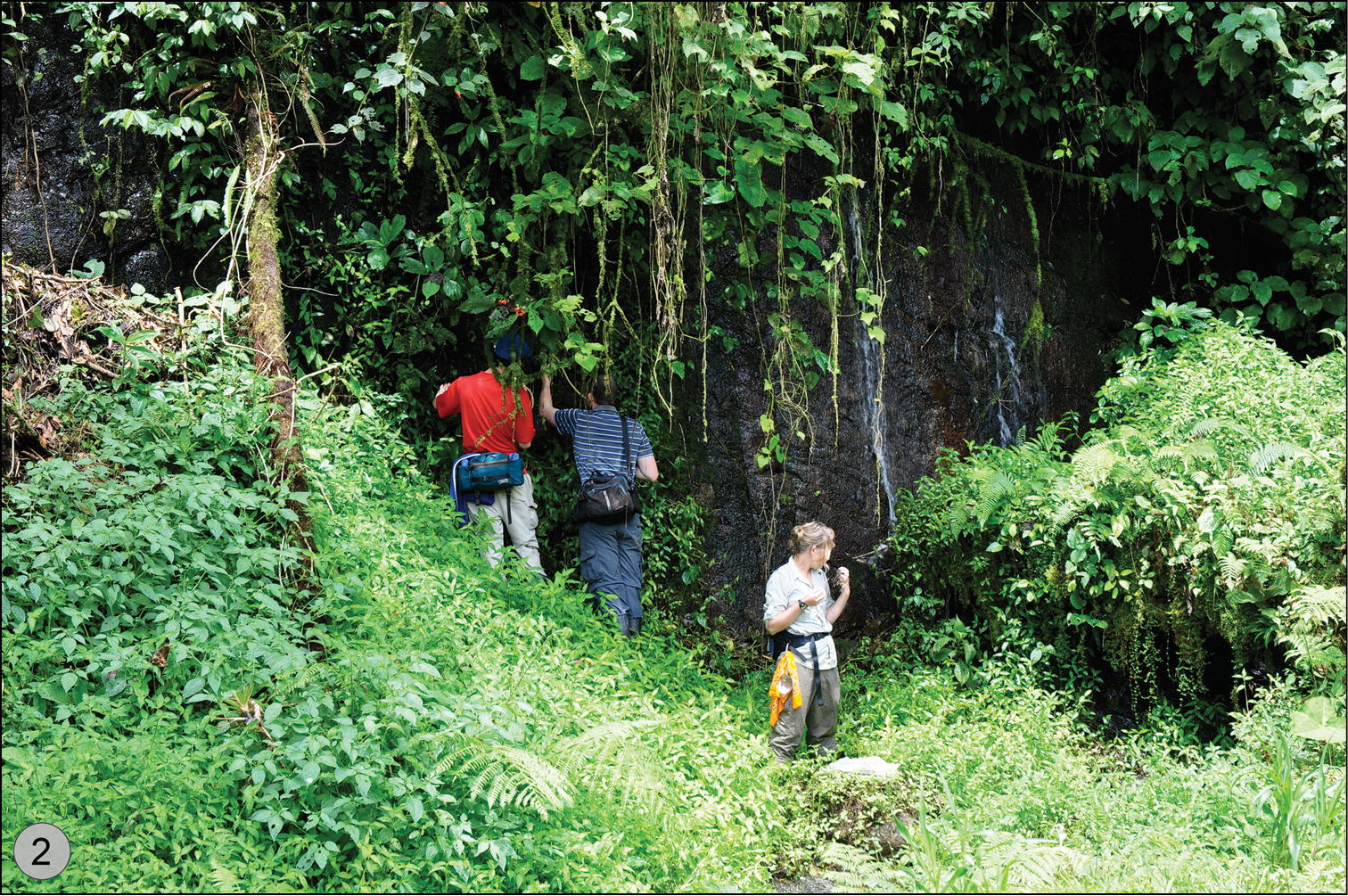
Natural hygropetric habitat in Costa Rica of Quammenis spectabilis Erwin with Andrew Short and his University of Kansas grad students Crystal Maier and Clay McIntosh. Photo credit: K. Taro Eldredge, University of Kansas.
As noted in several past contributions, methods and species concepts follow those previously described (
For measurements, an image of the specimens was obtained using a Leica M420 stereoscope coupled to an EntoVisionTM system. The resulting image was processed using the software Cartograph version 7.2.5 by Microvision Instruments. The magnification on the zoom was set to calibrate the system and it is embedded into the file of the image. The image was opened with the software program Archimed version 6.1.4 also by Microvision and the Measure tool, was then used to determine the lengths of the various parts. A total of 419 images were obtained.
Measurements of length (ABL, SBL) and width (TW) follow those of
Attributes of the abdominal ventral sterna are referred to using the numbering system generally accepted in carabid studies, i.e., the sternum divided medially by the hind coxae is sternum II (the first being hidden) and the last visible is sternum VII (
In a revision of the genus Pericompsus (
The same problem exists for the proximal end of the median lobe of the male genitalia. In
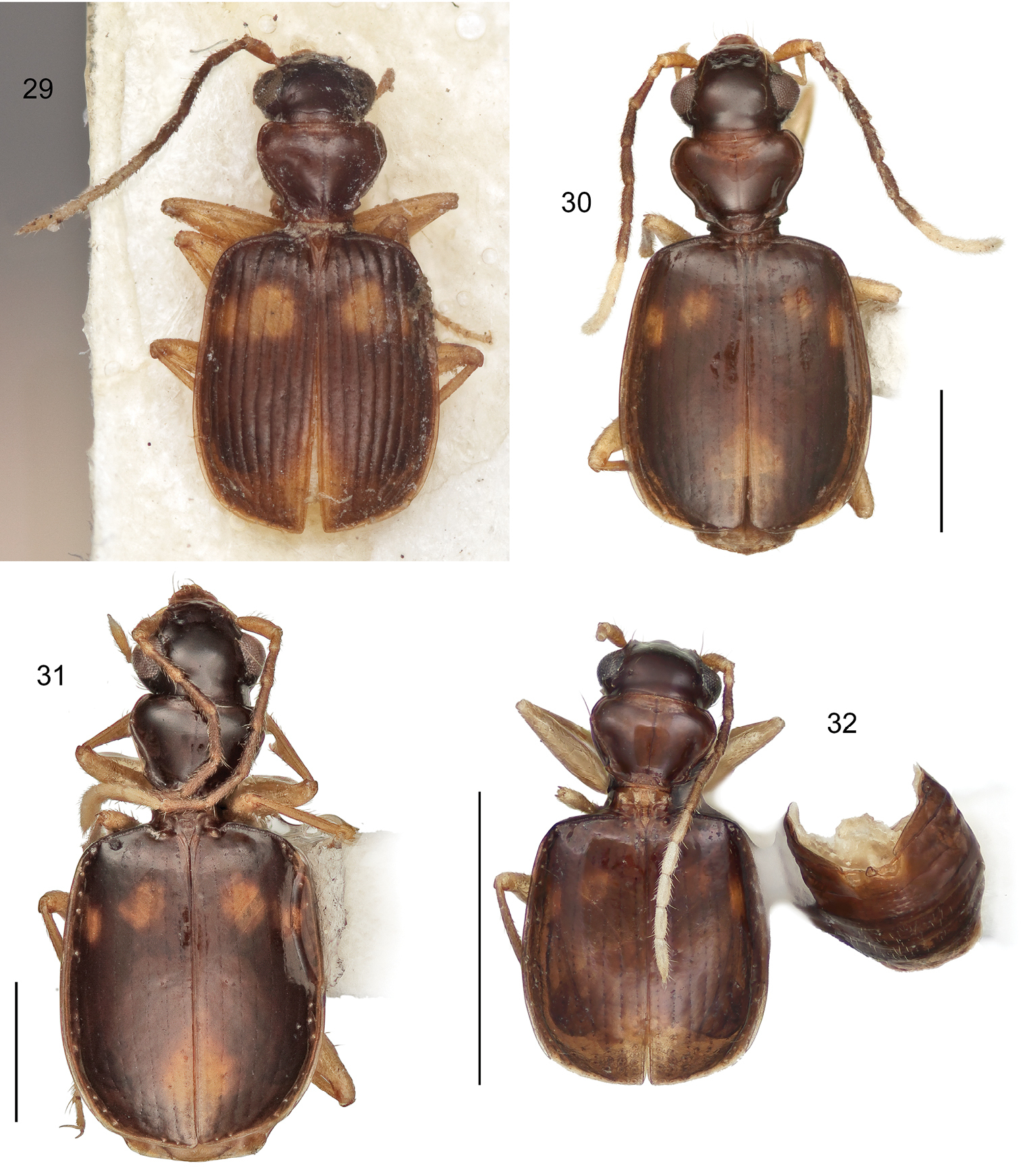
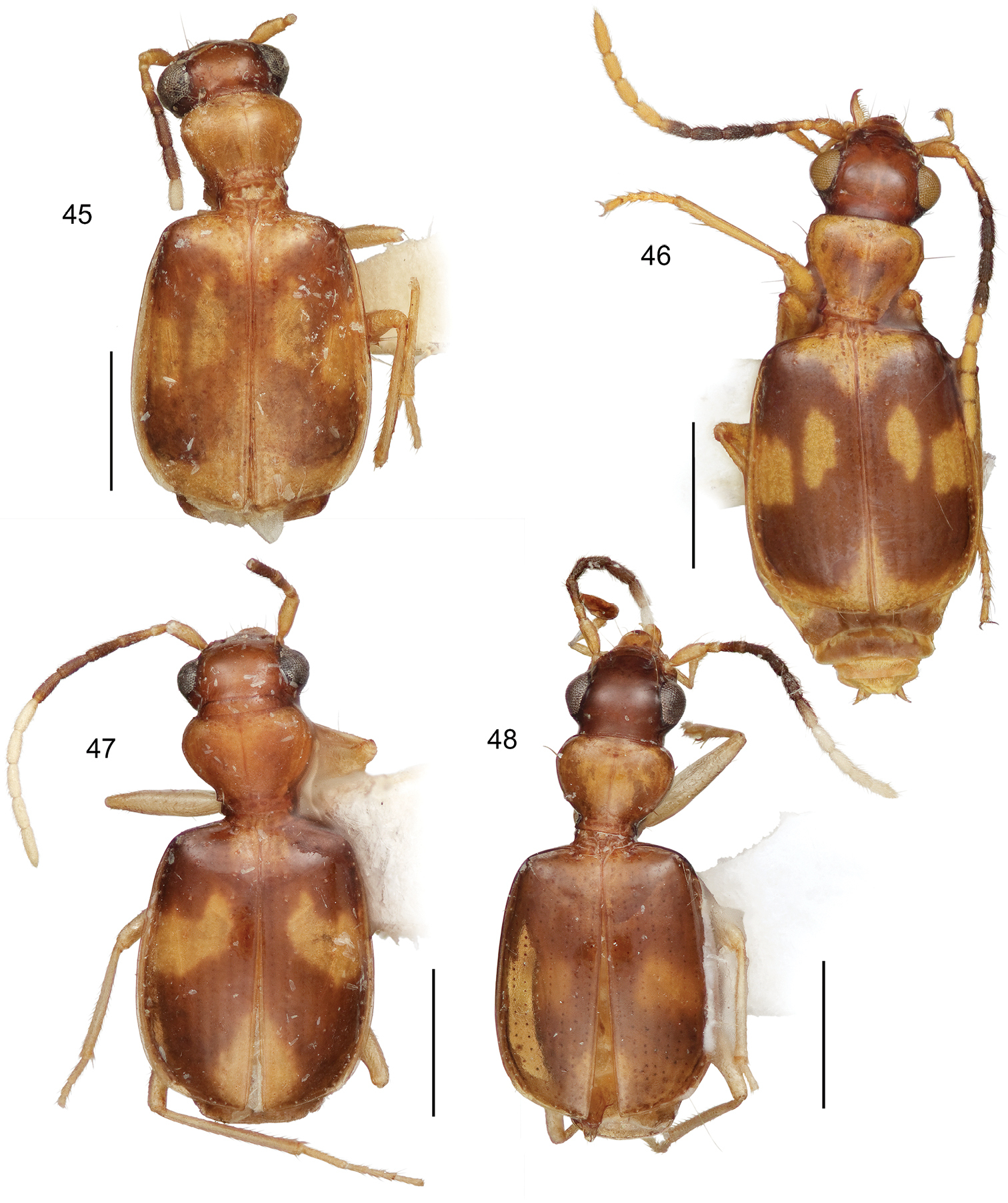
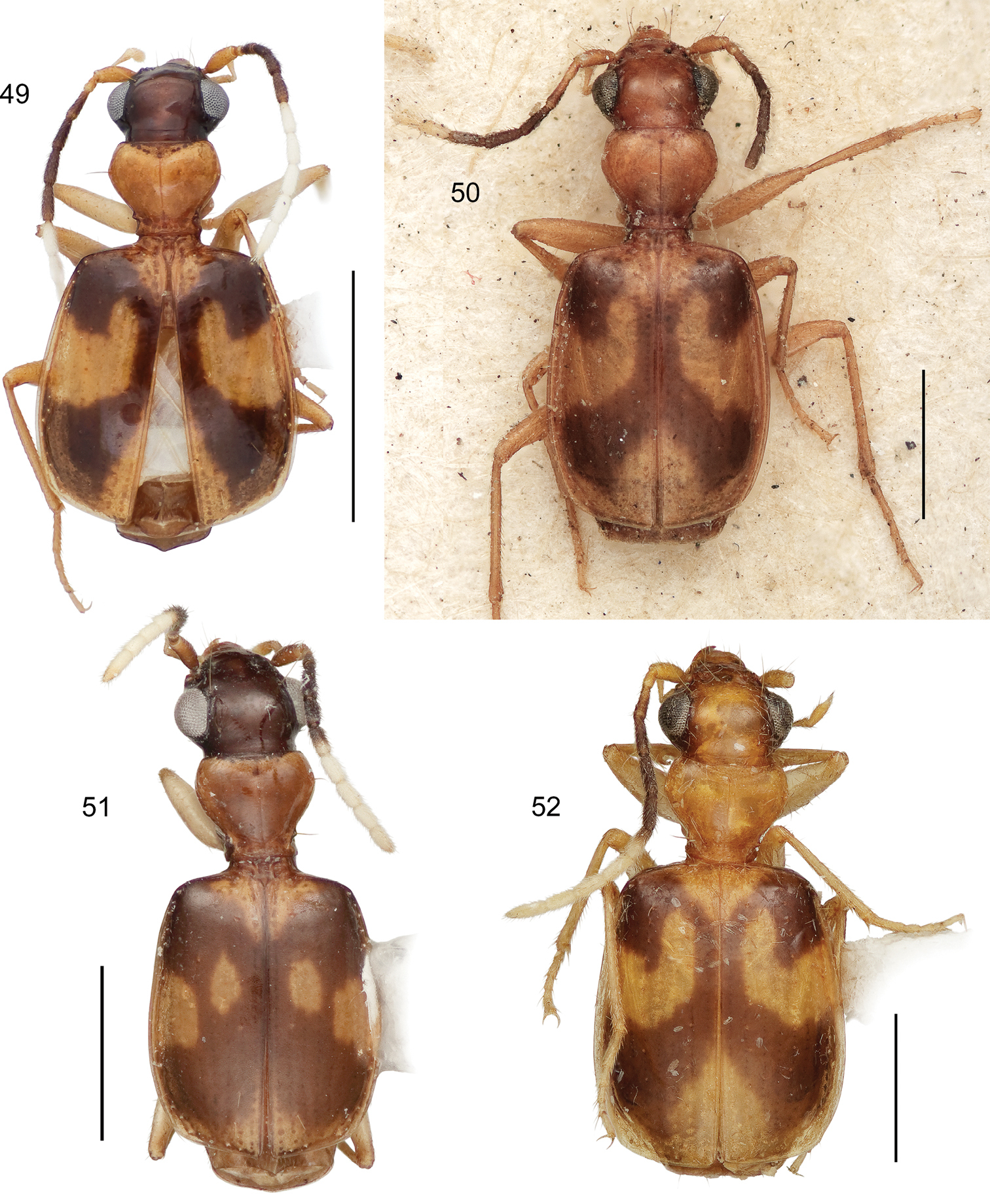
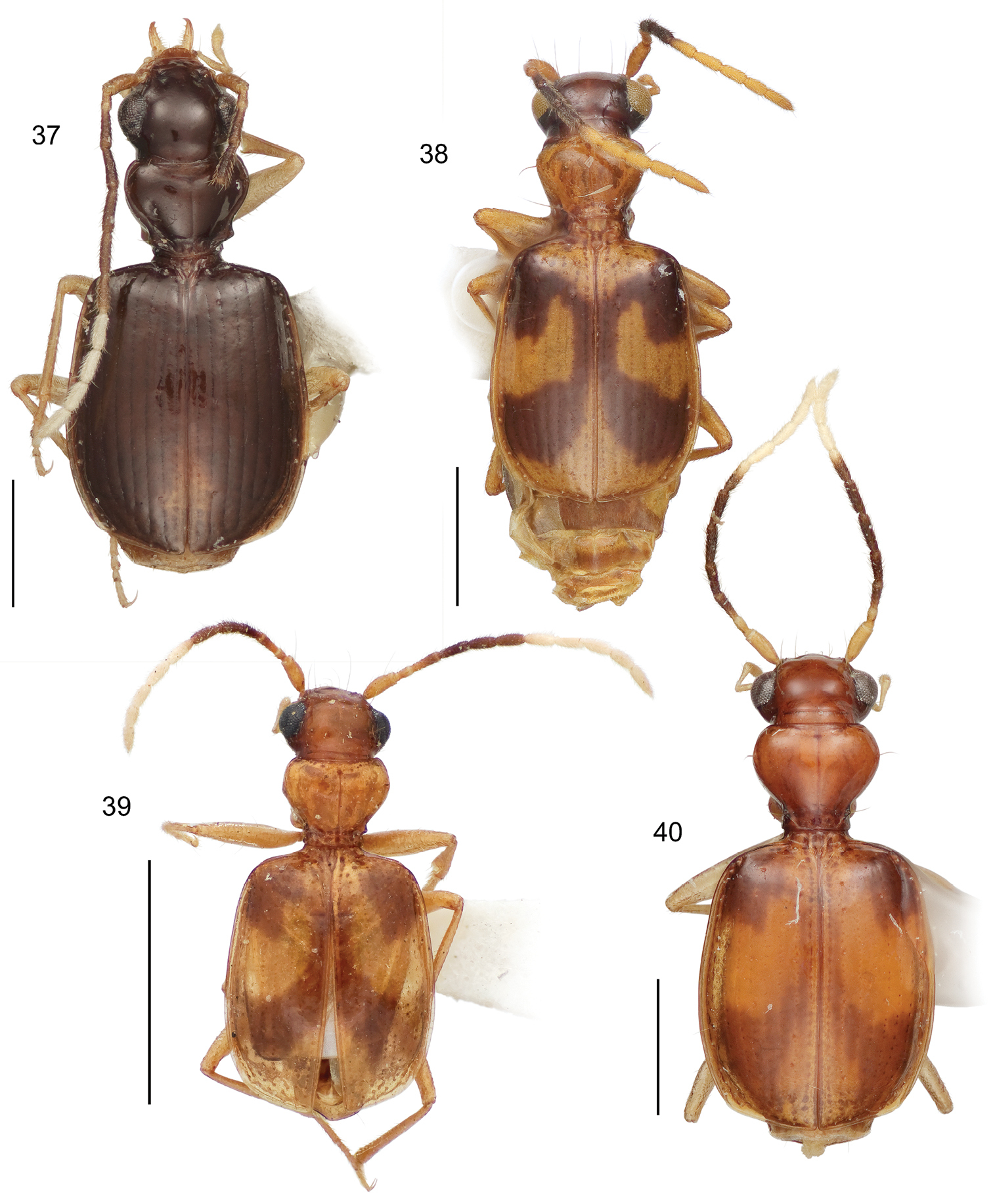
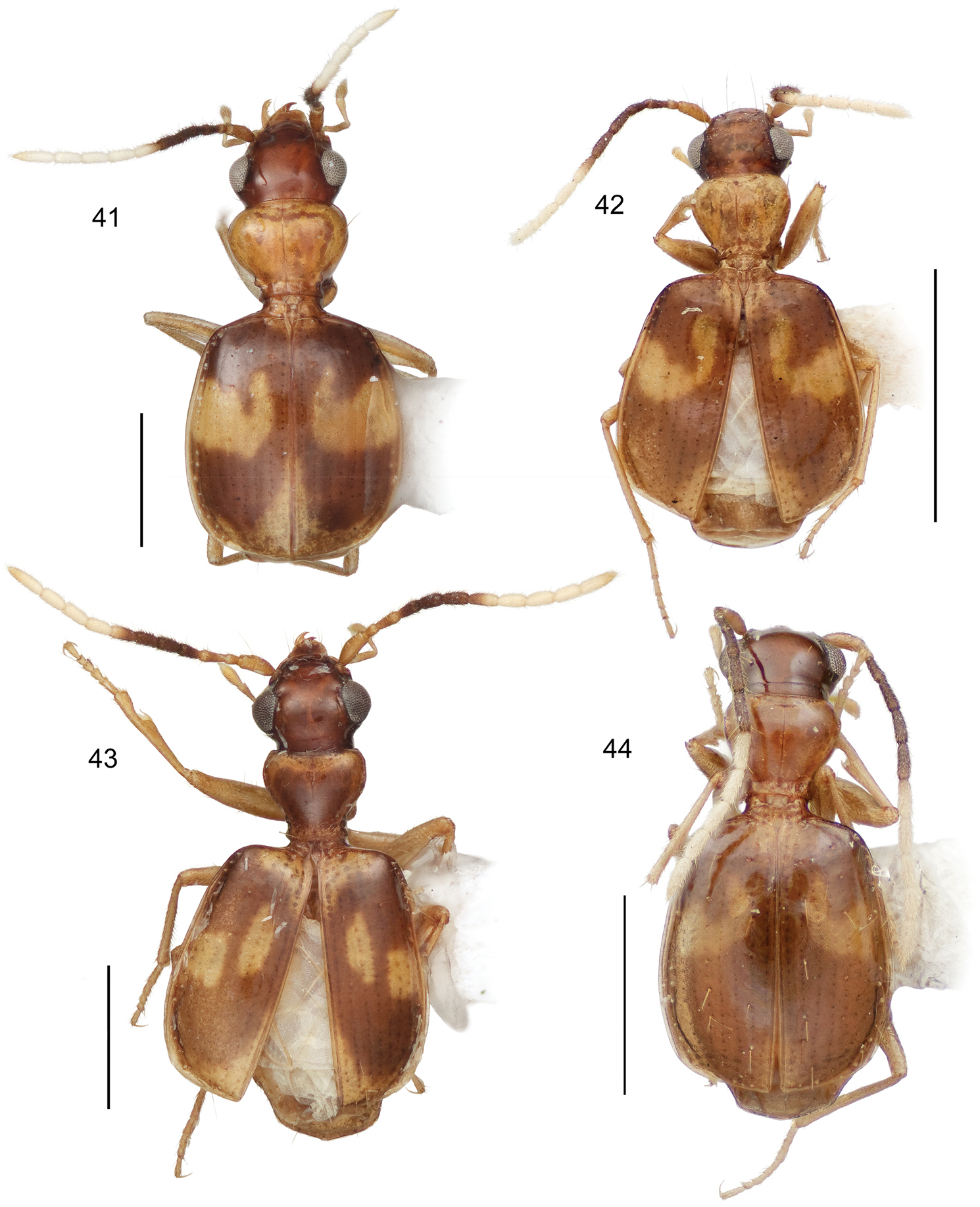
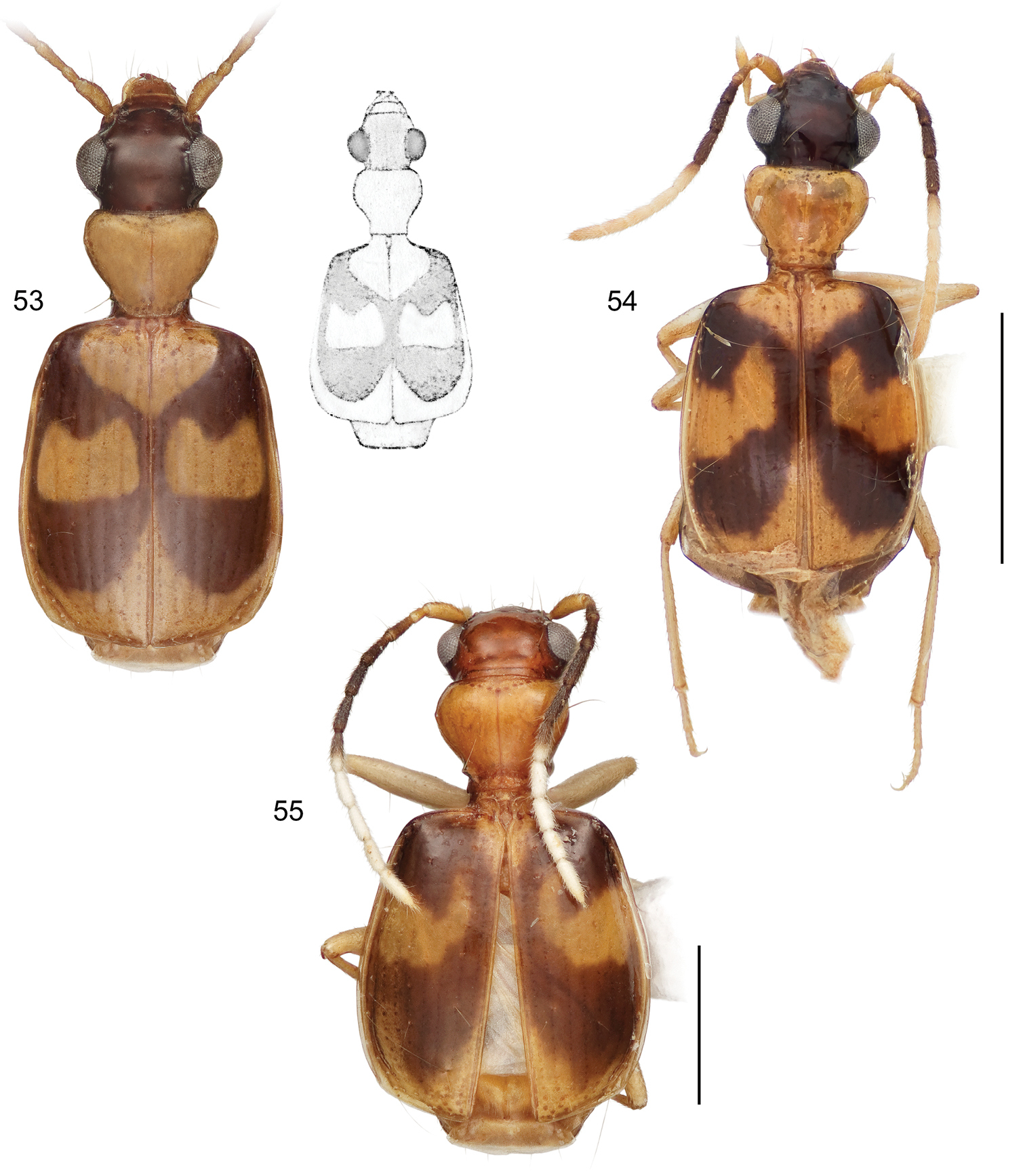
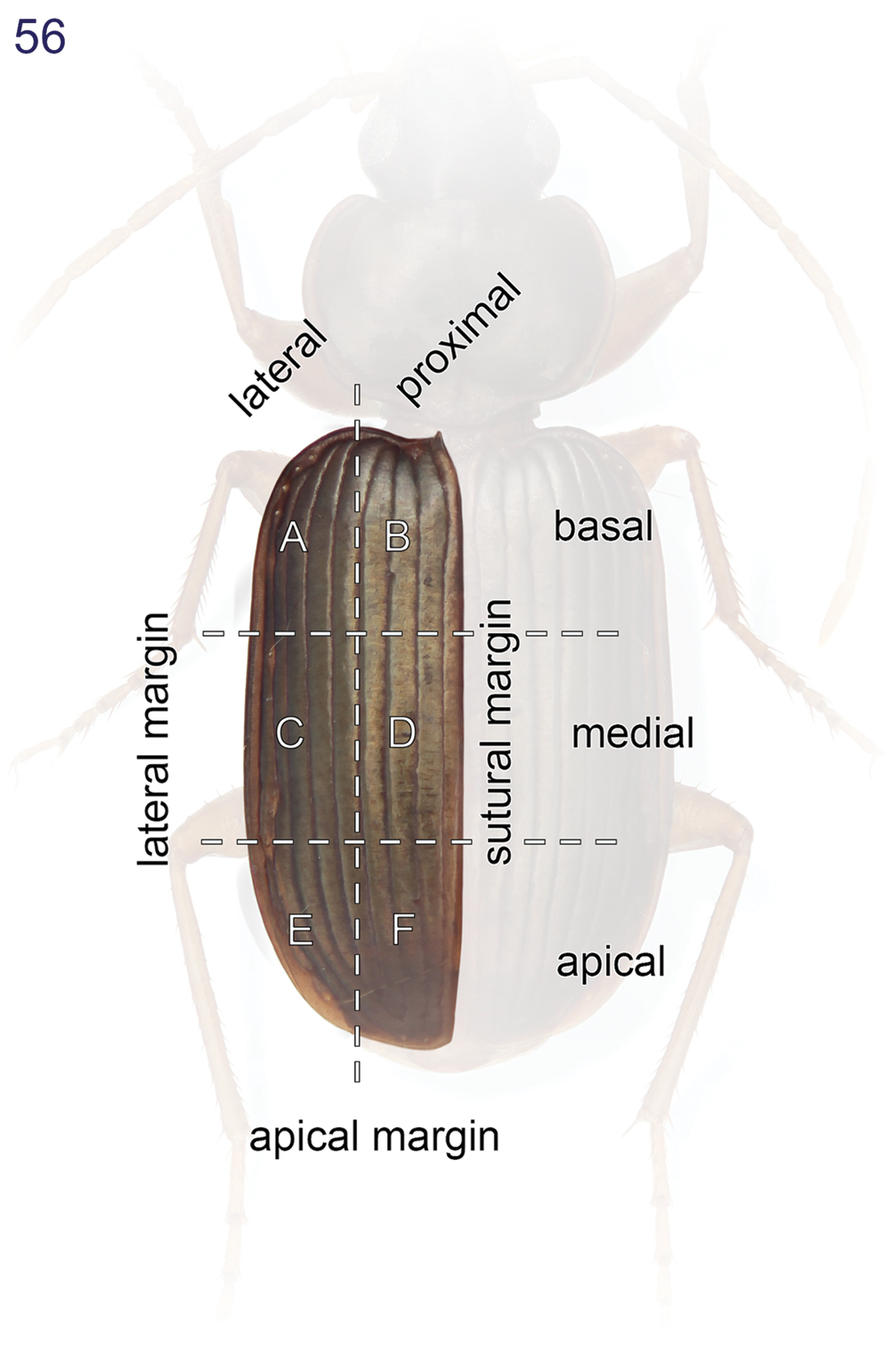
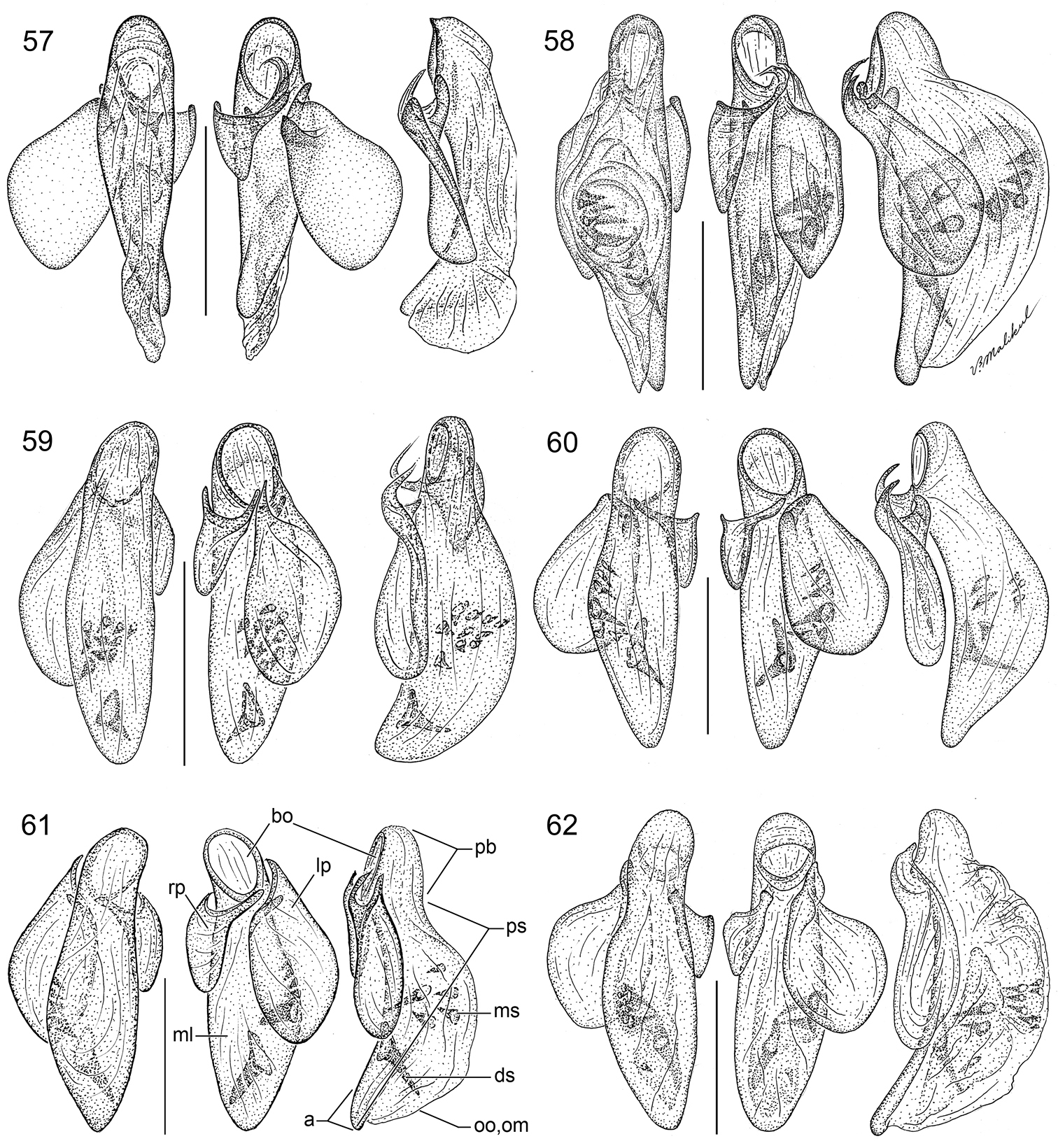
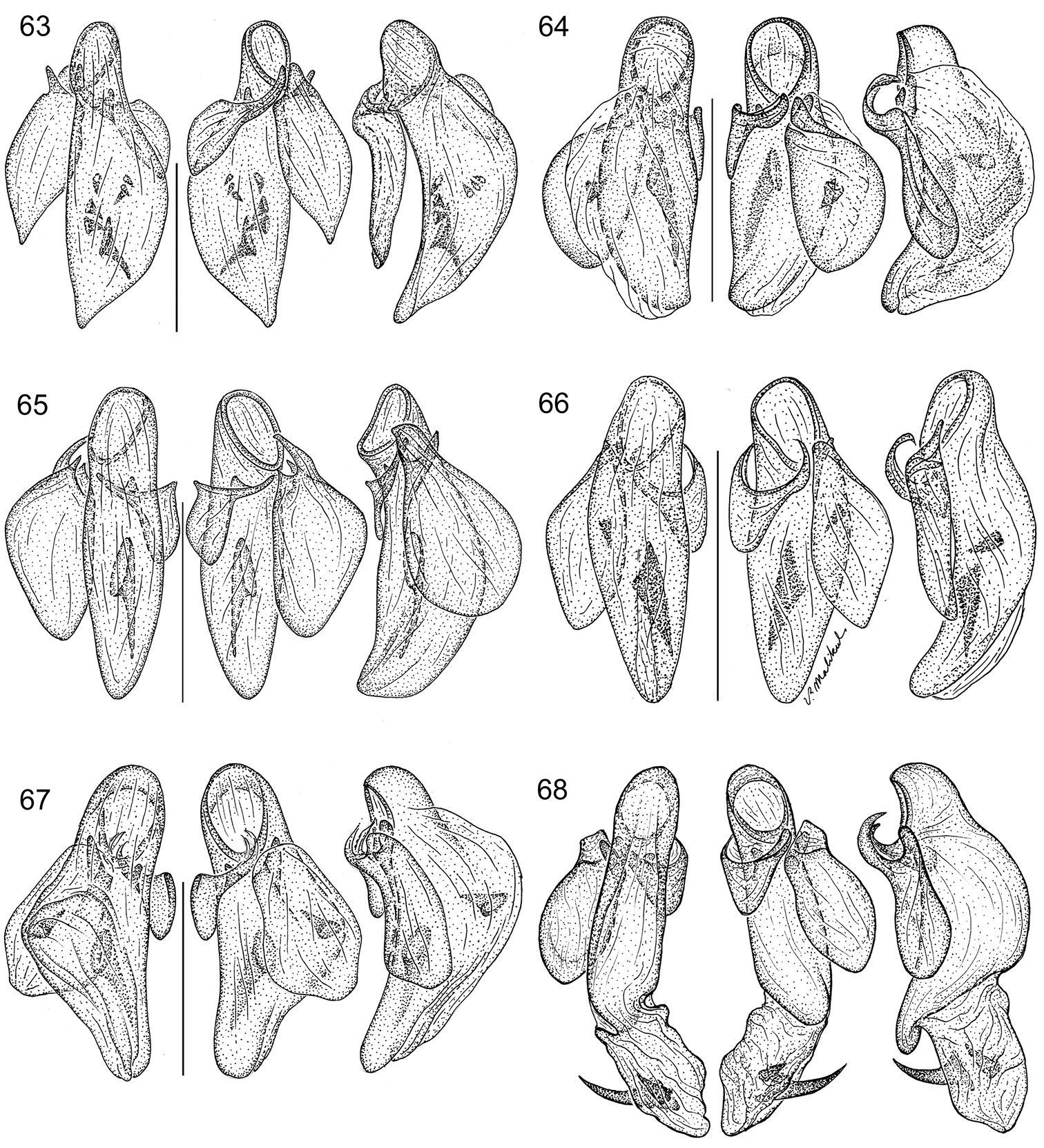
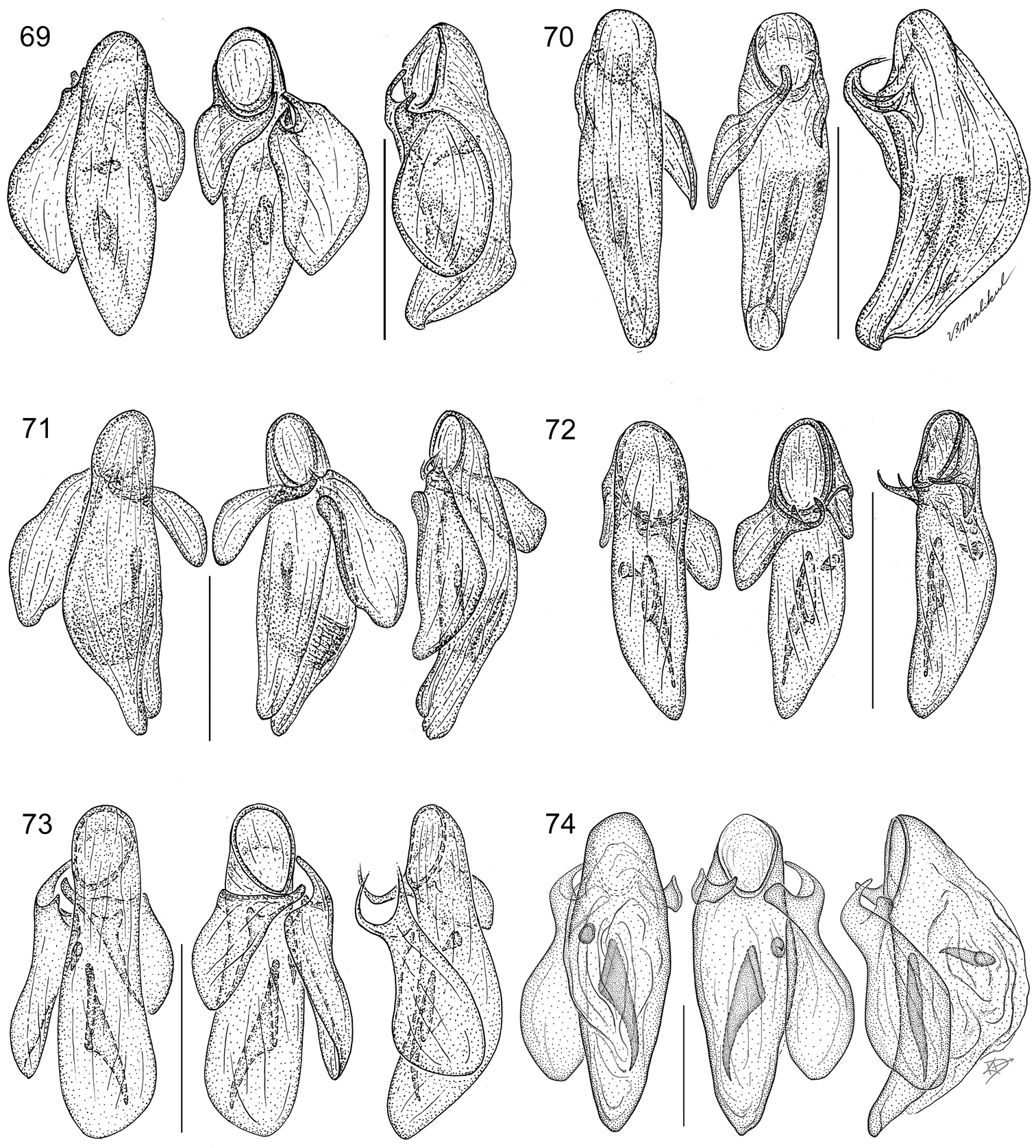
This study includes a total of thousands of specimens of Lachnophorini, and 383 adult specimens of Asklepia, all currently at the National Museum of Natural History, Washington, DC (NMNH). Among the Asklepia, three specimens were received from the AMNH (Lee Herman, Curator); 31 specimens from the University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada (UASM) collected in Brazil and sent to us by George E. Ball; 14 specimens from the Carnegie Museum of Natural History (CMNH) (Robert L. Davidson, Collection Manager); and ten specimens from the Museum of Zoology at the University of São Paulo, Brazil (MZUSP) (Dra. Sônia Casari, Curator). Also studied were the lectotype of Asklepia lebioides Bates and holotypes of Asklepia pulchripennis, Asklepia geminata, and Asklepia hilaris from the Muséum National d‘Histoire Naturelle, Paris (MNHP, Azadeh Taghavian, Collection Manager) and a paralectotype of Asklepia lebioides from the Natural History Museum in London (BMNH, Beulah Garner, Curator). Primary type specimens of new species will be deposited in their countries of origin if required by legal agreements, or museums of ownership at the conclusion of our studies on this tribe. The habitus images of the adult beetles portray most of the character states referred to in the keys provided. Illustrations of male genitalia are standard for descriptive taxonomy of carabid beetles in both preparation and aspects presented, as is the presentations of the female genitalia. The habitus images of the adults were made with a Visionary DigitalTM high resolution imaging system rendered using Photoshop to become “Digital Photo-illustrations.” Figure 56 demonstrates an elytron divided into six quadrants that we use to describe color patterns. Figure captions include an ADP number, which is a unique identification number for the specimen that was illustrated or imaged and links the specimen and associated illustrations and/or images to additional information, such as collecting notes, in electronic databases at the NMNH.
Geographical data are presented for species based on all known specimens available at the time of manuscript preparation, including those in the literature. Geo-referenced data have been determined from locality information provided on specimen labels; only those exact georeferences reported in decimal degrees that are provided on the label are placed in quotes. Otherwise, we have estimated others as closely as possible from places, mileage, or other locality data listed on the label and searched with Google Earth Pro. Latitude and longitude for those are reported in decimal degrees and have been corrected from those reported on the labels, if necessary; our bottom line is that georeferences locality data reported herein are far more accurate than those provided on specimens labels.
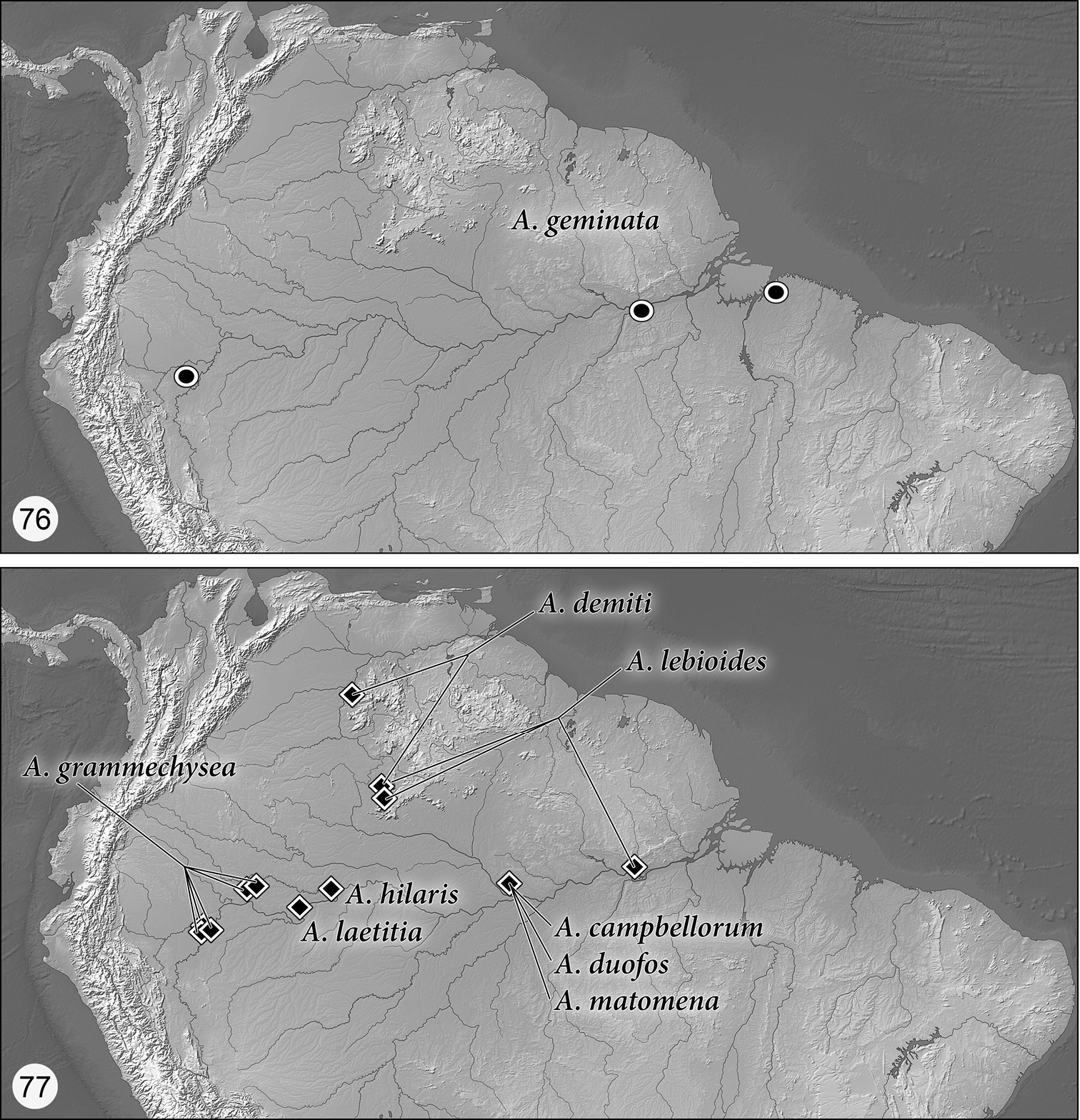
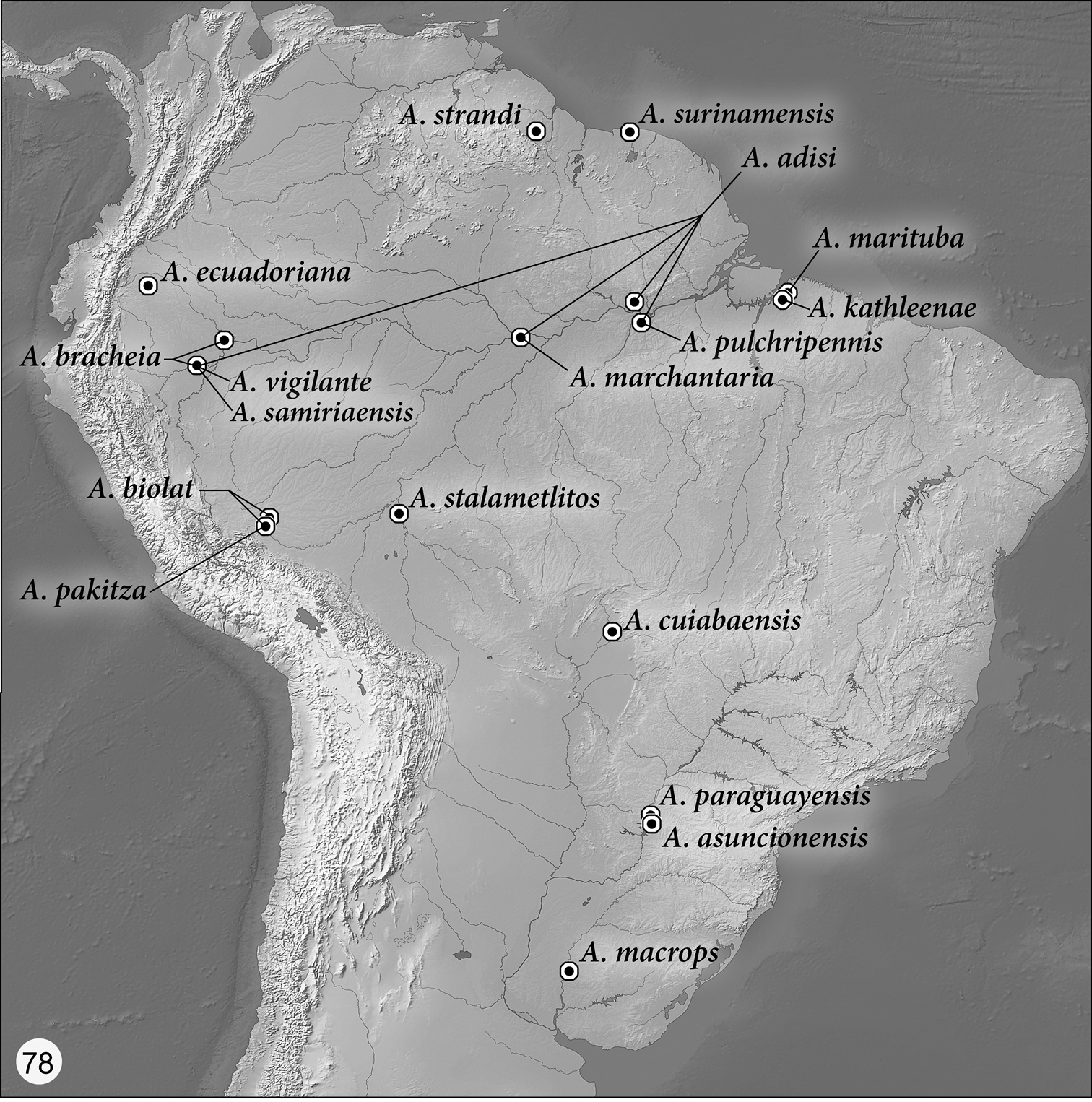
Distribution maps are provided for the species of Asklepia (Figs 76–78). Here, vernacular names in English are proposed, as common names are becoming increasingly needed in conservation reports and studies, and/or agricultural and forestry applications. These names are based on criteria set forth in
| 1 | Antennal scape very long and apically swollen, at least 1 ½ times longer than antennomere 3 | Calophaenini Jeannel, 1942 |
| 1 | Antennal scape short and robust, shorter than or about coequal in length with antennomere 3 | 2 |
| 2 (1’) | Pronotum elongate and cylindrical, often bulbous at basal third | Odacanthini Laporte de Castelnau, 1834 |
| 2’ | Pronotum not elongate and cylindrical, normally subquadrate or cordate with explanate, or beaded margins and usually well-defined hind angles | Lachnophorini LeConte, 1853 |
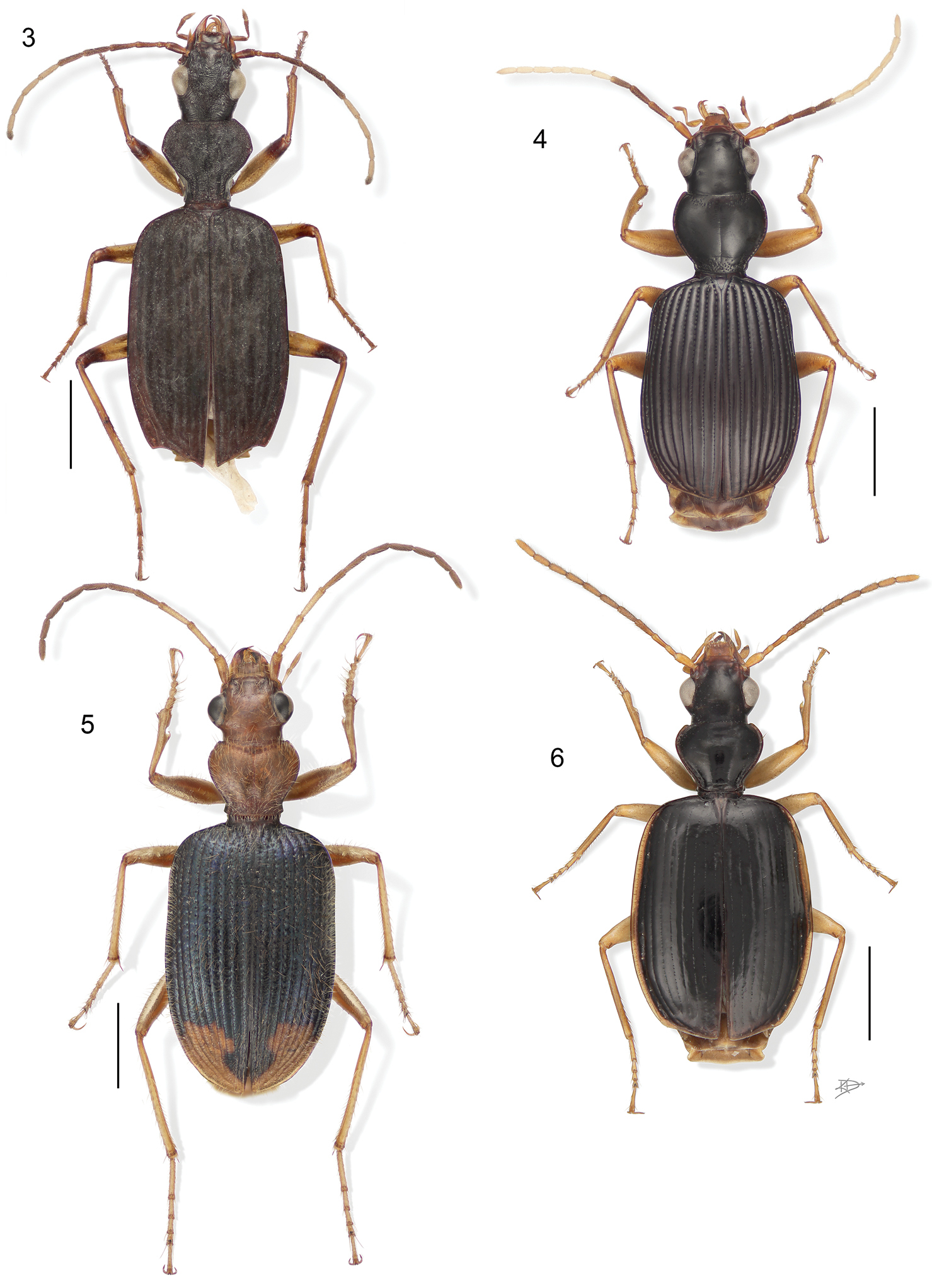
Body form ranges from Agonum-like in Anchonoderus Reiche adults (Fig. 52) to ant-like in those of Ega Laporte de Castelnau (Fig. 56), Selina Motschulsky (Fig. 20), and Stenocheila Laporte de Castelnau (Fig. 21). Mandibles are markedly falciform (subfalciform in Anchonoderus). Subgena with patch of setae ventrad the eye, or entire venter of head with sparse short vestiture (except in Amphithasus, Aporesthus, Diplacanthogaster, Guatemalteca, Homethes, Lachnaces, and Quammenis); antennomeres 2 and 3 fully setose (except in Aporesthus, Diplacanthogaster, Guatemalteca, Homethes, and Quammenis); apical palpomeres inflated or fusiform; apical labial palpomere with short setae (except in Anchonoderus, Aporesthus, Guatemalteca, Homethes, Peruphorticus, and Pseudophorticus); elytra obliquely truncate (and deeply sinuate in Aeolodermus, Quammenis, and Stenocheila); abdominal sterna with scattered setae (except in Aporesthus, Diplacanthogaster, and Quammenis); spermatheca bipartite, or derivable from a bipartite ground plan (cf.
We have arrayed the lachnophorine genera in two subtribes based on vestiture and body form: Eucaerina LeConte contains Amphithasus, Aporesthus, Asklepia, Eucaerus, Guatemalteca, and Lachnaces, all of which have adults with little, or no general setation and except for Amphithasus are of planate body form; and Lachnophorina LeConte contains Anchonoderus, Calybe, Ega, Euphorticus, Lachnophorus, Pseudophorticus, Peruphorticus, and Selina, adults of which are richly invested with setae and/or pubescence and of a medium to markedly convex body form. Given that Selina is the only Eastern Hemisphere taxon in this group, its adult similarity to Ega adults may be convergence.
We note that Amphithasus is somewhat “forced” into the Eucaerina herein provisionally until such time that a major phylogenetic analysis can be undertaken either by a detailed morphological analysis, a molecular analysis, or desirably both. Attributes of the rarely collected adults of this genus are sufficiently distinctive that they may deserve a subtribe of their own (and that subtribe may also include three undescribed genera of which we have only six specimens and are reluctant to describe at present – one of these, with three species, has evolved somewhat parallel to the members of Rhadine LeConte, 1848, a platynine genus). In regard to Quammenis, we believe it to be closely associated with Diplacanthogaster Liebke, 1932 and Stenocheila Laporte de Castelnau, 1832 of South America; and if so, then both Homethes Newman, 1842 and Aeolodermus Andrewes, 1929 of the Old World need to be reconsidered because adults of Aeolodermus have much in common with adults of Quammenis. For the present, we treat these five genera as incertae sedis within the Lachnophorini.
| 1 | Specimens from Australia, the Malay Archipelago, and/or the Philippines | 17 |
| 1’ | Specimens from Africa, Vietnam, and the Indian subcontinent (Habitus, Fig. 20) | Selina Motschulsky, 1858 |
| 1’’ | Specimens from the Western Hemisphere | 2 |
| 2(1’’) | Antennomeres 3 and 4 markedly elongate, length more than combined length of scape and pedicel combined and testaceous, antennomeres 5-11 markedly broad, flattened, and black (Habitus, Fig. 21) | Stenocheila Laporte de Castelnau, 1832 |
| 2’ | Antennomeres 3 and 4 moderately elongate or not, length coequal to, or less than combined length of scape and pedicel, antennomeres 5-11 not broadened, cylindrical and color various | 3 |
| 3(2’) | Pronotum with transverse rugae on disc and laterally with a setiferous dentiform projection; elytron with sutural apex obliquely truncate (Habitus, Fig. 8) | Diplacanthogaster Liebke, 1932 |
| 3’ | Pronotum without transverse rugae on disc, or if so then laterally without a setiferous tooth; elytron with sutural apex rounded or acute | 4 |
| 4(3’) | Elytron with 3 large ocellate fossae; apex deeply sinuate. Dorsal surface matte metallic green, fovea purple. Head and pronotum with numerous micro-rugosities (Habitus, Fig. 22) | Quammenis Erwin, 2000 |
| 4’ | Elytron without ocellate fossae; apex obliquely truncate. Dorsal surface not green. Head and pronotum not rugose, but may be densely punctate | 5 |
| 5(4’) | Elytron glabrous, with few fixed setae | 6 |
| 5’ | Elytron pubescent or densely setigerous | 9 |
| 6 (5) | Elytron with dorsal surface dull or shiny – no trace of iridescence | 7 |
| 6’ | Elytron with dorsal surface moderately to markedly iridescent | 14 |
| 7(6) | Form robust and convex. Elytral interneurs striate, or striatopunctate. Ultimate labial palpomere glabrous, fusiform, pointed, not acuminate (Habitus, Fig. 4) | Amphithasus Bates, 1871 |
| 7’ | Form planate. Elytral interneurs punctate, punctures without connecting striae | 8 |
| 8(7’) | Elytron bicolored, Pattern with dark pattern. Interneurs of discontinuous punctures, shallowly impressed; punctures slightly more impressed in basal and apical third of elytron. Ultimate labial palpomere pubescent, globose, subulate. Abdomen finely setose (Habitus, Figs 29–56) | Asklepia Liebke, 1938 |
| 8’ | Elytron concolorous, black or infuscated, or with paler sutural interval. Interneurs of continuous punctures to apex, markedly impressed, “appearing” striatopunctate but fine punctures not connected with striations. Palpomeres fusiform, glabrous. Abdomen with only fixed ambulatory setae (Habitus, Fig. 6) | Aporesthus Bates, 1871 |
| 9(5’) | Pronotal disc with scattered supplemental robust black setae | 10 |
| 9’ | Pronotal disc without supplemental robust setae (Habitus, Fig. 5) | Anchonoderus Reiche, 1843 |
| 10(9) | Elytron with deep transverse depression across basal third; pronotum cylindrical with barely developed lateral bead | 11 |
| 10’ | Elytron without transverse depression, but disc may be broadly fossate at basal third | 12 |
| 11(10) | Neck markedly constricted, narrower than dorsal diameter of eye from a dorsal aspect. Pronotum and head smooth and glabrous with few fixed setae, surface shiny and smooth (Habitus, Fig. 9) | Ega Laporte de Castelnau, 1835 |
| 11’ | Neck not much constricted, broader than dorsal diameter of eye from a dorsal aspect. Pronotum and head pubescent, surface dull (Habitus, Fig. 7) | Calybe Laporte de Castelnau, 1834 |
| 12(10’) | Head and pronotum multipunctate, these markedly impressed and dense. Elytron with interneurs striatopunctate, rows of punctures markedly impressed, and with three shallow fossae in third interval (Habitus, Fig. 16) | Peruphorticus Erwin & Zamorano, gen. n |
| 12’ | Head and pronotum smooth, with scattered punctures or densely pubescent; intervals with fossae or not | 13 |
| 13(12’) | Ultimate palpomeres fusiform, pointed (Fig. 28), not acuminate or subulate. Pronotum surface densely pubescent, feebly rugose and punctate (Habitus, Fig. 19) | Pseudophorticus Erwin, 2004 |
| 13’ | Ultimate labial palpomeres basally globose, apically acuminate or subulate. Pronotum smooth, surface densely and finely pubescent, or with scattered long setae | 16 |
| 14(6’) | Pronotum broad, rectangulate, apical and basal margin as wide as base of elytron, lateral margins slightly rounded. Maxillary palpus elongate, basal palpomere slim, longer than scape (Fig. 26). Ultimate labial palpomere acuminate (Habitus, Fig. 14) | Lachnaces Bates, 1872 |
| 14’ | Pronotum narrowed at the base, more or less trapezoidal. Maxillary palpus not elongate, basal palpomere robust, about coequal in length with scape. Ultimate labial palpomere fusiform or subulate | 15 |
| 15(14’) | Pronotum surface iridescent and smooth. Ultimate labial palpomere fusiform (Fig. 25) (Habitus, Fig. 12) | Guatemalteca Erwin, 2004 |
| 15’ | Pronotum surface with numerous micro-punctures densely distributed; dull. Ultimate labial palpomere globose, subulate (Fig. 23) (Habitus, Fig. 10) | Eucaerus LeConte, 1853 |
| 16(13’) | Elytron with three fossae, basal fossa larger and spread across interneurs 2 and 3, mid and apical fossae centered on interneur 2. Ultimate labial palpomere subulate (Fig. 27) (Habitus, Fig. 15) | Lachnophorus Dejean, 1831 |
| 16’ | Elytron without fossae. Ultimate labial palpomere acuminate (Fig. 24) (Habitus, Fig. 11) | Euphorticus Horn, 1881 |
| 17(1) | Abdominal sterna and dorsal surface of tarsomeres glabrous (Habitus, Fig. 13) | Homethes Newman, 1842 |
| 17’ | Abdominal sterna and dorsal surface of tarsomeres with fine vestiture (Habitus, Fig. 3) | Aeolodermus Andrewes, 1929 |
Fig. 3
Homethes emarginatus Chaudoir, 1872:389
Size range – 7.5 mm to 8.0 mm; adults of this genus are active in May (1 ex. CAS) and have been found at lights (
Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
Fig. 4
Amphithasus truncatus Bates, 1871:32
Size range – 3.5 mm to 6.0 mm; adults of this genus are found singly at night on wet leaf litter at the margins of swamps and medium-sized rivers, and on dry trails in primary rainforest.
Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Perú.
Currently, two described species are assigned to this genus, however, there are five species represented in the NMNH collection. There is a need for a taxonomic revision of the group. Anchomenus elegans Dejean, 1831:725, was placed in “Amphithasus” by
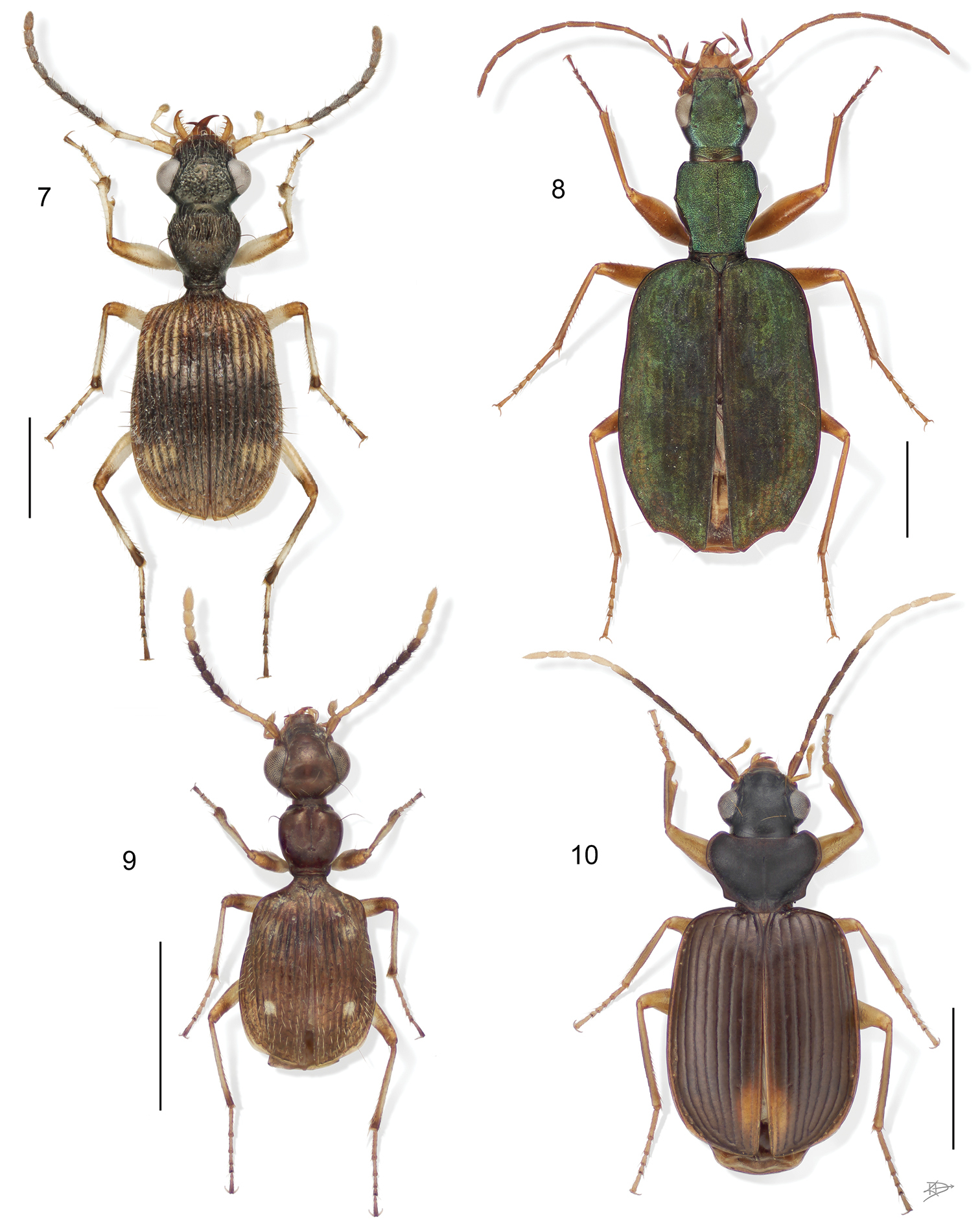
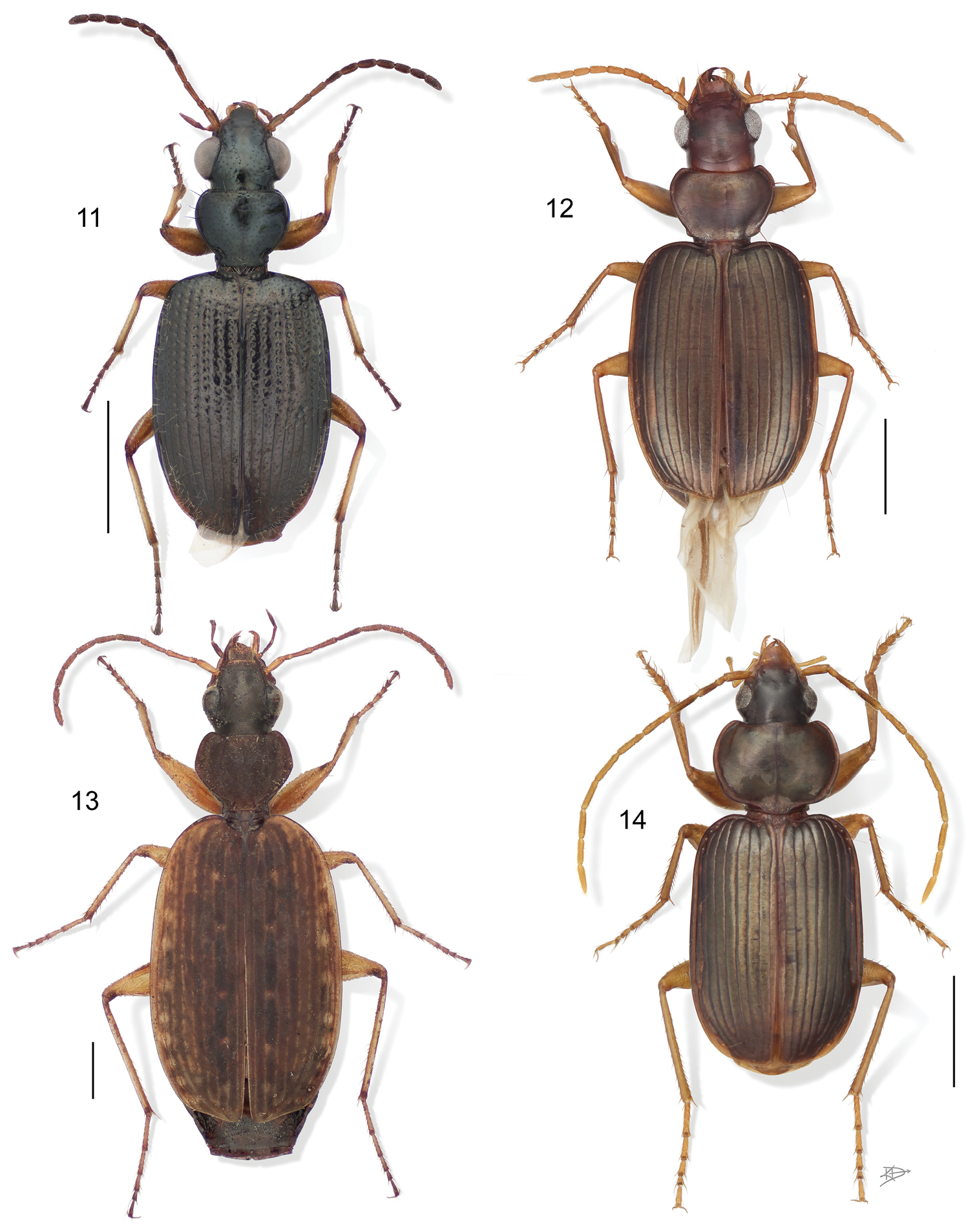
3 Aeolodermus emarginatus Chaudoir. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP133799 from Mabatobato, Luzon, Philippines 4 Amphithasus sp. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP023719 from Rio Sucusari, Perú 5 Anchonoderus apicalis Reiche. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132554 from nr. Atalaya, Perú 6 Aporesthus sp. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132542 from Tena, Ecuador.
Fig. 5
Platynus elegans Brullé, 1838:25 [=Anchonoderus eximius (Audouin), 1836:34]
Size range – 4.5 mm to 8.5 mm; adults of this genus are found on the muddy banks of rivers and streams where they run in the sun from crack to crack in the baked mud. Other ubiquitous species are found throughout the forest where there is sandy soil and thin dry leaf litter, as well as on upper parts of river banks in thin layers of leaf litter. However, most species occur at stream margins among small stones and gravel and in flood debris along upper stream margins. The fact that only 27 species are described from the Neotropics and 11 occur at a single locality at Pakitza, Perú indicates the identification of species is impossible without recourse to types. A taxonomic revision of the group is need.
Arizona and Texas south to Argentina, including many of the Caribbean islands.
Currently, 27 described species are assigned to this genus.
Fig. 6
Aporesthus anomalus Bates, 1871:103
Size range – 4.0 mm to 5.5 mm; these very interesting small beetles occur on the underside of suspended logs and branches that straddle small to medium sized streams in the rainforest. They run to the top when the underside is splashed with water and when the streams rise due to heavy rainfall. Nothing more has been published about species of this genus.
Bolivia, Brazil, Guyana, Guyane, Ecuador, Paraguay, Perú, Surinam.
Currently, three described species are assigned to this genus; however, ten species are represented in the NMNH collection. A taxonomic revision of the group is needed. Identification of species is impossible without recourse to types.
Fig. 7
Calybe leprieuri Laporte de Castelnau, 1834:92
Size range – 3.1 mm to 4.9 mm; species of this genus not only have color patterns and movements like ants, but also have body constrictions giving them near ant-like proportions. They live near water bodies usually on steep slopes just above the margin on damp clay soils.
Northwestern México south to Argentina.
Currently, eight described species are assigned to this genus; however, many more species are represented in the NMNH collection. There is a need for a taxonomic revision of the group. Identification of species is impossible without recourse to types.
7 Calybe sp. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132561 from Pakitza, Perú 8 Diplacanthogaster bicolor Liebke. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP133817 from Ouro Preto, Brazil 9 Ega sp. (no described species of this genus is known from Perú). Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132560 from Pakitza, Perú 10 Eucaerus sp. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132552 from Pakitza, Perú.
Fig. 8
Diplacanthogaster bicolor Liebke, 1932
Size range – 7.0 mm to 9.0 mm; the single species of this genus is active in April, July, and August, and probably in proximity of water.
Brazil.
Fig. 9
Ega formicaria Laporte de Castelnau, 1835: 93
Size range – 2.8 mm to 4.7 mm; species of this genus not only have color patterns and movements like ants, they have body constrictions, giving them ant-like proportions, even more so than their probable adelphotaxon, Calybe. They live near water bodies usually on steep slopes above the water on damp clay soils, in the company of similar-sized ants. They catch small arthropod prey on the run much like tiger beetles. Identification is very difficult without recourse to types; the genus is in need of a taxonomic revision.
Southern USA (CA to GA, FL) south to Argentina. Not known from the Caribbean islands.
Currently, 17 described species are assigned to this genus, some of which are likely Calybe species; however, many more true Ega species are represented in the NMNH collection. A taxonomic revision of the group is needed. Identification of species is impossible without recourse to types.
Figs 10, 23
Eucaerus varicornis LeConte, 1853:387
Size range – 2.4 mm to 5.5 mm; these species are all hygrophilous, occurring in rotting leaf litter in densely shaded wet situations, stream sides, or swamps, and at margins of open marshes. They are common in some places; however, they run fast and it is difficult to obtain series without a lot of work. The opposite is true at other places where 100 or more individuals will flush together from a third of a square meter of wet leaf litter. Their way of life is unknown, but they likely are predatory on small arthropods.
Maryland, USA south through Texas and Florida to Brazil, including the larger Caribbean islands, México, and Central America.
Currently, 10 described species are assigned to this genus; however, several more species are represented in the NMNH collection. A taxonomic revision of the group is needed. Identification of species is impossible without recourse to types.
Figs 11, 24
Lachnophorus pubescens Dejean, 1831:30
Size range – 4.0 mm to 4.9 mm; these beetles are somewhat ubiquitous. They occur near water or at damp places, on a variety of soil types. Adults of all species are dark, often black, and one new species from Paraguay is vividly metallic. Adults of another new species from Perú was found readily under clumps of cut grass in an open field, as well as on algae covered sandy clay running in the bright sunshine. Adults are attracted to lights.
Southern United States south to southern Brazil, including some Caribbean islands.
Currently, four described species are assigned to this genus; however, two additional new species are represented in the NMNH collection. A taxonomic revision of the group is needed. Identification of species is impossible without recourse to types.
11 Euphorticus sp. (only Euphorticus pubescens (Dejean) is known from México and this is not that species). Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132558 from Tapilulu, México 12 Guatemalteca virgen Erwin. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132546 from nr. La Virgen, Costa Rica 13 Homethes sp. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP133797 from Australia 14 Lachnaces sp. (at present this genus has three described species, all from the upper Amazon Basin). Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132578 from Tambopata Reserved Zone, Explorer’s Inn, Perú.
Figs 12, 25
Guatemalteca virgen Erwin, 2004:12
Size range – 4.3 mm to 5.2 mm; these small beetles occur along small rocky streams in the highlands and in wet leaf litter in the lowlands; they take cover in the day time under stones or stream side debris. Many adults have been collected in Guyane with flight intercept traps (FITs).
Costa Rica; Guatemala; Guyane; México; Perú.
Currently, one described species is assigned to this genus; however, two additional new species are represented in the NMNH collection, one from Guyane and another from Perú. A taxonomic revision of the group is needed.
Fig. 13
Homethes elegans Newman, 1842:402
Size range – 8.5 mm to 9.0 mm; these small beetles, at least in some species, are known to fly. According to
Australia, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
Nine species are known to occur in Australia (
Figs 14, 26
Lachnaces sericeus Bates, 1872:202
Size range – 3.2 mm to 5.4 mm; these small beetles occur in Amazonian inundation forests of the Varzea and Igapó systems. Adults occur in very wet leaf litter and in rotten wood in swampy areas. One adult was found by insecticidal fogging of the suspended fronds of an Astrocaryum palm; no doubt it was seeking refuge from inundation.
Brazil, Perú.
Currently, three described species are assigned to this genus: however, eight species are represented in the NMNH collection. A taxonomic revision of the group is needed.
Figs 15, 27
Lachnophorus pilosus Dejean, 1831:29
Size range – 4.0 mm to 6.3 mm; these small beetles are found on bare sandy stream banks in shady forests, or on sand in sunny areas along rivers. Their coloration pattern makes them appear like ants, and movements are ant-like, but they do not necessarily occur with ants. They catch small arthropod prey on the run much like tiger beetles.
Southern United States south to Uruguay, including the larger Caribbean islands.
Currently, 42 described species are assigned to this genus. A taxonomic revision of the genus is needed. Identification is very difficult without recourse to types.
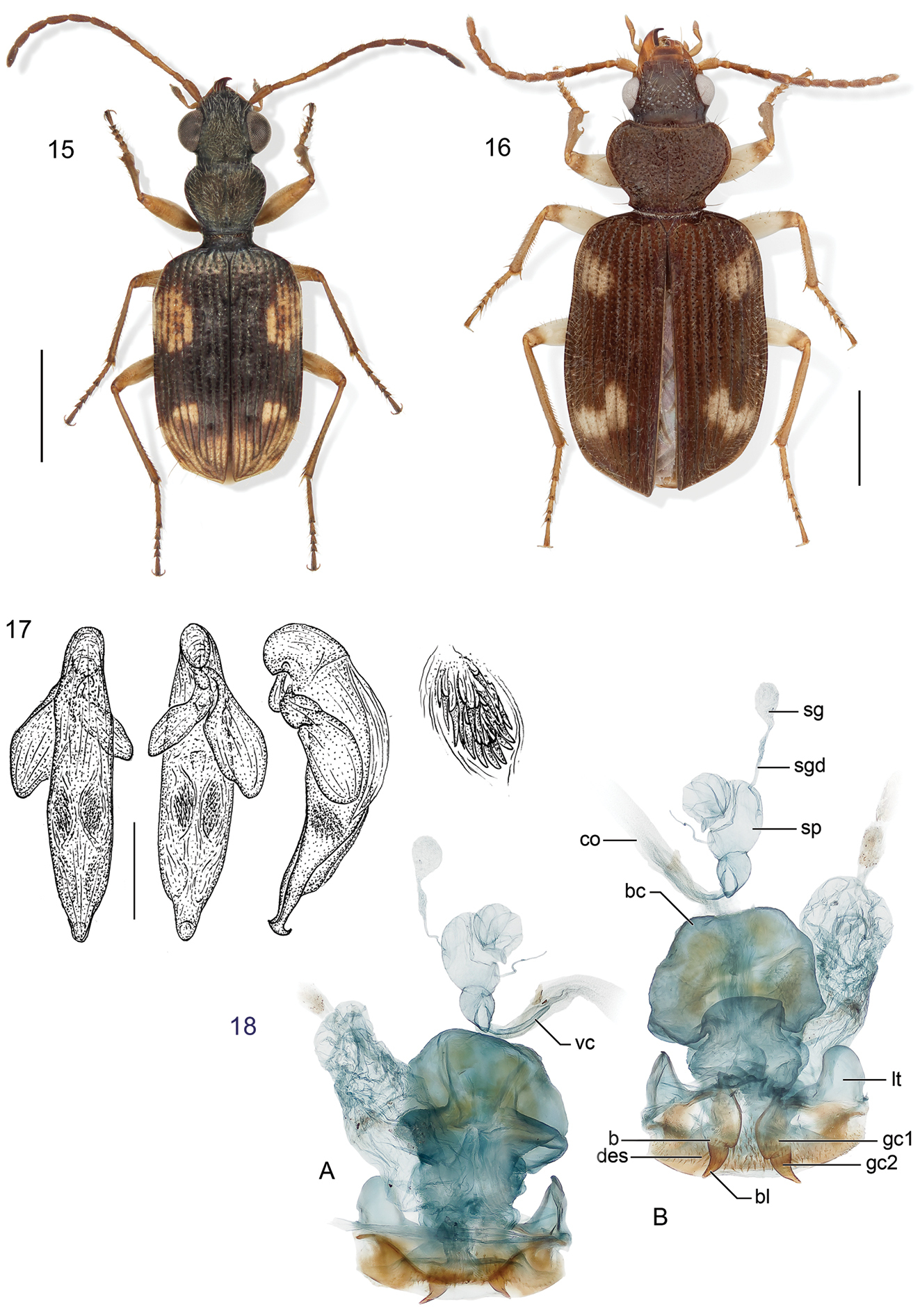
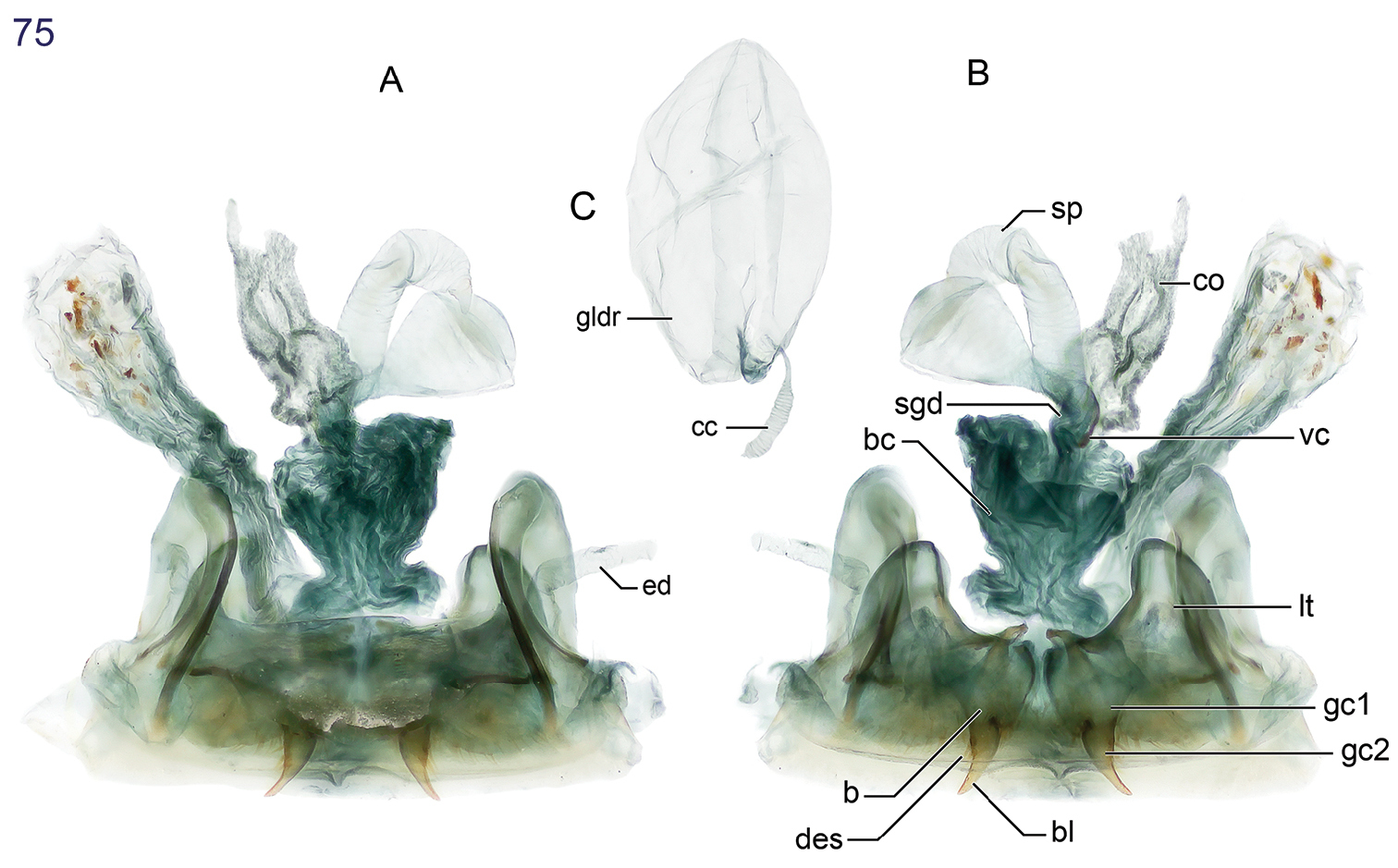
15 Lachnophorus sp. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132570 from Pakitza, Perú 16 Peruphorticus gulliveri sp. n. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect (specimen slightly teneral) based on specimen BIOLAT #10190 from Pakitza, Perú 17 Peruphorticus gulliveri sp. n. Illustrations, male aedeagus, dorsal, ventral, left lateral aspects, and details of armature of endophallus. BIOLAT/COLE13107, Pakitza, Perú. See Fig. 61 for labeled attributes 18 Peruphorticus gulliveri sp. n. Digital Photo-illustration, female genitalia, based on specimen BIOLAT/COLE16860 from Pakitza, Perú. A Ventral aspect. Legend, bc bursa copulatrix; co common oviduct; sg spermathecal gland; sgd spermathecal gland duct; sp spermatheca. dorsal aspect; vc villous canal; lt laterotergite; gc1 gonocoxite 1; gc2 gonocoxite 2. B Dorsal aspect. Legend, b base of gonocoxite 2; bl blade of gonocoxite 2; des dorsal ensiform seta.
http://zoobank.org/D1D6C243-89D4-433C-8EEE-F75CD80EAAA6
Figs 16, 74, 75, 79
Peruphorticus gulliveri Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
Peruvian beauty-bearing beetles.
(Figs 63, 74, 75). With the attributes of Lachnophorini (see above), body form robust, and occiput and pronotum deeply and coarsely punctate, the latter also partly rugose. Ultimate palpomeres elongate and slightly acuminate. Elytral interneurs striatopunctate, deeply engraved; intervals convex and multipunctate and with three shallow fossae in third interval; apex subtruncate, outer angle rounded.
The wings are fully developed, thus it is likely that these beetles are moderate to strong flyers.
As currently recorded, member species are known from Costa Rica, Ecuador, and Perú.
These small beetles are found in dry or wet leaf litter in Amazonian rainforests independent of water bodies, and particularly along dusty trails. In Costa Rica, they occur at higher elevations in cloud forest. At least two species with adults somewhat reddish in color are found only on the lateritic soils pushed up by members of the ant genus Atta during nest building and nest maintenance activities.
Nine species are represented in the NMNH, in addition to the one described herein. It is probable that the nine additional species are new to science; however, types of the genera Lachnophorus and Euphorticus need to be examined to make sure they are rightfully assigned to those genera and not Peruphorticus.
http://zoobank.org/1A142F39-A267-4708-8484-E25CC095AE84
Perú, Madre de Dios, BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Zone 5, Trocha Aguajal 92, 11.9427°S, 71.2926°W, 324m, 28 October 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT10190, male).
The epithet “gulliveri” is a Latinized eponym, genitive case, based on the name made famous by the Irish writer Jonathan Swift in 1726, namely Gulliver’s Travels. We so name this species because of its very large size in comparison to its congeners, reminding us of Gulliver’s travels on the island of Lilliput.
Gulliver’s beauty-bearing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Pseudophorticus, as described by
(Figs 16, 17, 18). Habitus: (Fig. 16). Size: [See also Appendix 2] Large for the genus; ABL = 5.52–6.86 mm, SBL = 5.21–6.05 mm, TW (total width) 2.30–3.6 mm, LP = 1.10–1.29 mm, WP = 1.52–1.81 mm, LE = 3.37–4.05 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 16): labrum rectangulate, sexsetose, clypeus convex with small tuberculate at middle and clearly demarcation from frons. Frons shallowly convex with moderately depressed lateral sulci, occiput shallowly domed; neck broad. Eyes large, moderately convex, longitudinal diameter coequal with length of antennomere 2 + 3; gena very short and flat. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 16) markedly broad and cordiform, about half as long as head (LP/LH: mean, males 1.51, females 1.49), moderately broader than long (W/L, mean: males, 1.39, females, 1.41); margin narrowly explanate with seta at anterior third and at hind angle; base convex and laterally depressed; hind angle flared laterally, slightly obtusely produced; multipunctate and rugose, setiferous, punctures large and deep. Pterothorax. Normal for tribe. Elytron about same width as pronotum (WP/TW: mean, both sexes, 0.628), moderately convex, intervals moderately convex and slightly more so laterally, interval 3 with very shallow fossae. Hind wings fully developed. Legs (Fig. 16). Overall, normal for subgenus. Male front tarsus with tarsomeres 1–3 slightly dilated and each ventrally with two biserial rows of white articulo-setae. Abdominal sterna. Setation as for genus. Male genitalia (Fig. 17, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with basal lobe about one-fifth length of shaft, basal opening small. Shaft moderately robust, sinuate ventrally, dorsally membranous except for two short sclerotized strips flanking distal part of long ostial opening; in ventral aspect constricted toward rather small hooked apex, preapically with prominent ridges lateral to a central trough, in lateral aspect, ridges converge in a small but prominently projected point. Parameres broad, apices rounded; left paramere longer than right paramere, about three quarters length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with two fields of densely packed spines. Female genitalia (Fig. 18). Ovipositor with broad laterotergite (lt) and two gonocoxites (gc 1, gc 2); gonocoxite 1 spinose (short thick setae); gonocoxite 2 moderately falcate, base (b) large, broad, blade (bl) rather short, with two dorsal ensiform setae (des), ensiform setae short; without ventral preapical nematiform setae. Reproductive tract proximally with short, broad bursa copulatrix (bc), continuous at its distal end with common oviduct (co) and short bulbous bifid spermatheca (sp), latter of three bulb sections; villous canal (vc) extended from near base of spermatheca well up in common oviduct; spermathecal gland (sg) bulbous; spermathecal gland duct (sgd) long, slender, attached to spermatheca at middle bulb.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
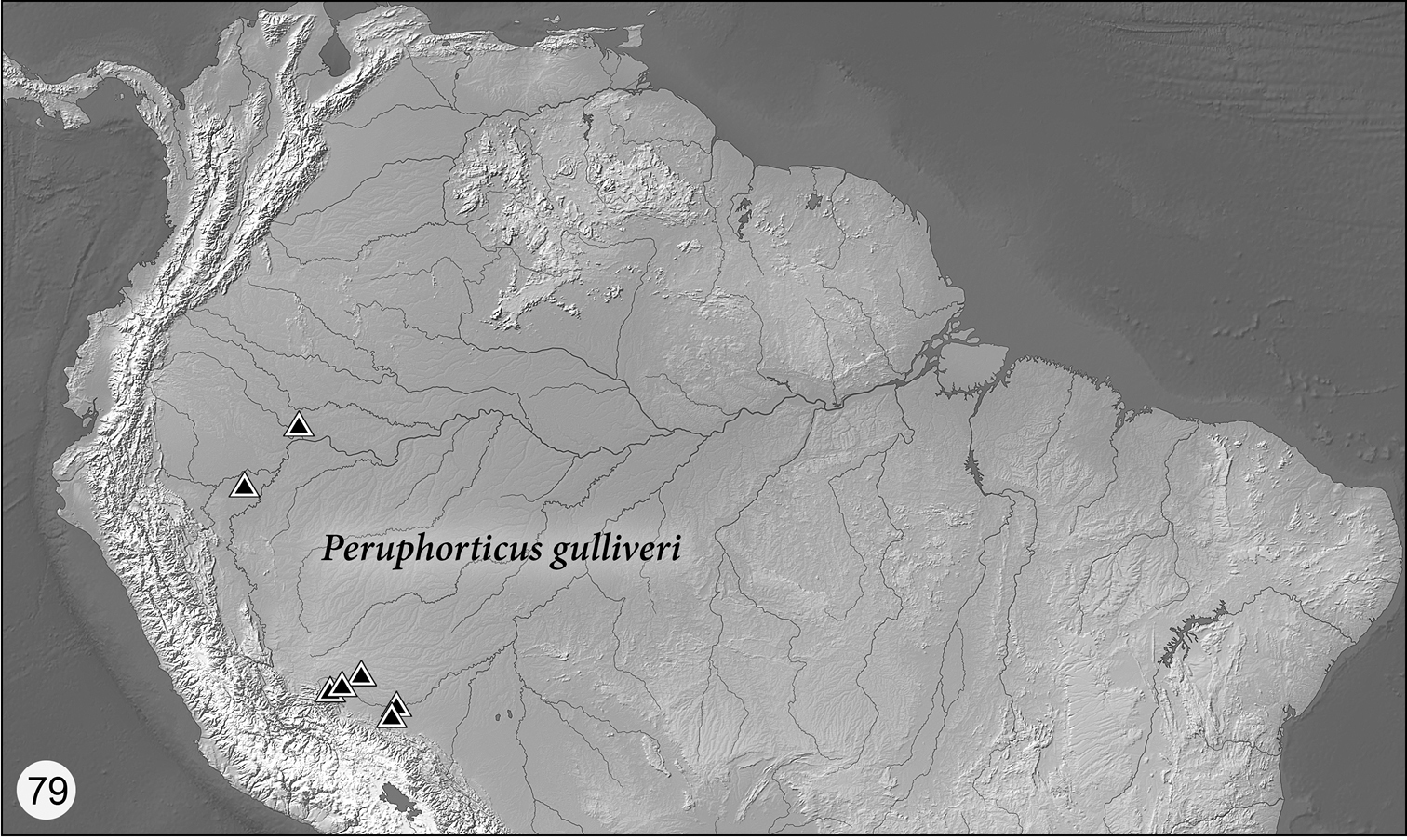
(Fig. 79) Currently known from Ecuador and Perú, but likely more widespread.
See
Ecuador, Napo, 75km E Coca, 16 September 1990 (D.L. Pearson)(NMNH: ADP133803, female paratype). Perú, Loreto, circa Explornapo Camp, Rio Napo, Cocha Shimagai, 3.3563°S, 73.0467°W, 88m, 5 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP023768, ADP023788, male paratypes); Explorama Lodge, Rio Sucusari, 3.257°S, 72.916°W, 101m, 6 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: ADP053355, ADP053596, female paratypes), 7 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: ADP053660, ADP053724, female paratypes); Explornapo Camp, Rio Sucusari, 3.225°S, 72.920°W, 95m, 7 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP053719, ADP053739, ADP008283, male paratypes, ADP008277, ADP008281, ADP008284, ADP008266, ADP008263, female paratypes), 18 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP009149, ADP009150, male paratypes, ADP009051, female paratype), 19 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP009261, ADP009262, ADP009263, ADP009264, ADP009265, ADP009266, ADP009267, male paratypes, ADP009060, female paratype), Rio Sucusari, Caño Yanamono, 3.257°S, 72.916°W, 101m, 30 May 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: ADP051053, ADP051053 male paratypes, ADP051011, female paratype), 31 May 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: ADP050771, female paratype), 22 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: ADP010281, ADP010285, ADP010286, ADP010293, ADP010294, ADP010295, ADP010301, ADP010303, ADP010304, ADP010408, male paratypes, ADP010296, ADP010287, female paratypes), 24 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: ADP010363, ADP010364, ADP010365, ADP010398, ADP010407, ADP010475, ADP010559, ADP010562, ADP010563, ADP010564, ADP010565, ADP010566, ADP010602, ADP010604, ADP010605, ADP010608, ADP010612, ADP010613, ADP010614, ADP010652, ADP010732, ADP010739, ADP010740, ADP010741, ADP010744, ADP010745, ADP010746, ADP010750, male paratypes, ADP010731, ADP010748, ADP010729, ADP010730, ADP010742, ADP010743, ADP010404, ADP010560, ADP010561, ADP010474, ADP010610, ADP010362, female paratypes); Pithecia, 5.1757°S, 74.655°W, 111m, 14 August 1989 (T.L. Erwin, G. Servat)(NMNH: ADP132743, male paratype, ADP132595, female paratype); Río Samiria, Boca Caño Inglés Camp, 5.1317°S, 75.0617°W, 117m, 20 August 1991 (G.E. Ball, D. Shpeley)(NMNH: ADP133807, male paratype); circa Pithecia, Cocha Shinguito, 5.1775°S, 74.6556°W, 111m, 26–29 August 1991 (G.E. Ball, D. Shpeley)(NMNH: ADP133809, male paratype); Río Samiria, Boca Caño Inglés Camp, 5.2265°S, 75.1058°W, 117m, 20 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M. Pogue, C. Reyes)(NMNH: ADP071551, female paratype); circa Pithecia, Cocha Shinguito, 5.1775°S, 76.6556°W, 112m, 25 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M. Pogue)(NMNH: ADP071181, female paratype), 26 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M. Pogue, C. Reyes)(NMNH: ADP071301, ADP071256, male paratypes); Madre de Dios, BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Zone 2, 11.9427°S, 71.2926°W, 324m, 5 September 1989 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT001189, BIOLAT008085, BIOLAT008086, BIOLAT008084, BIOLAT001191, BIOLAT007196, BIOLAT- 009090, BIOLAT002651, male paratypes), 5 February 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT006698, BIOLAT006698, BIOLAT006693, BIOLAT007042, male paratypes), 10 February 1990 (NMNH: BIOLAT002650), 11 February 1990)(NMNH: BIOLAT007041), 13 February 1990 (NMNH: BIOLAT007176, male paratype), 18 October 1990 (E. Vega)(NMNH: BIOLAT008767, BIOLAT008769, BIOLAT008771, BIOLAT008788, male paratypes), 29 September 1991 (E. Vega)(NMNH: BIOLAT12607, female paratype), 29 September 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M.G. Pogue)(NMNH: BIOLAT12597, male paratype), 5 October 1991 (NMNH: BIOLAT13107, male paratype, BIOLAT13140, BIOLAT13199, female paratypes), 9 October 1991 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT13435, BIOLAT13436, BIOLAT13443, BIOLAT13445, BIOLAT13447, BIOLAT13446, BIOLAT13428, BIOLAT13471, BIOLAT13440, BIOLAT13444, BIOLAT13442, BIOLAT13449, BIOLAT13448, BIOLAT13473, BIOLAT13474, BIOLAT13441, male paratypes, 8 July 1992 (NMNH: BIOLAT16858, BIOLAT16860, female paratypes), 10 July 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: BIOLAT17000, BIOLAT17001, BIOLAT17002, BIOLAT17004, BIOLAT17007, BIOLAT17008, BIOLAT17009, BIOLAT17005, BIOLAT17010, BIOLAT17011, BIOLAT17015, BIOLAT17018, BIOLAT17020, BIOLAT17021, BIOLAT17022, BIOLAT17023, BIOLAT17024, BIOLAT17028, BIOLAT17030, BIOLAT17019, BIOLAT17031, BIOLAT17033, BIOLAT17036, BIOLAT17037, BIOLAT17038, BIOLAT17043, BIOLAT17044, BIOLAT17045, BIOLAT17046, BIOLAT17049, BIOLAT17050, BIOLAT17051, BIOLAT17052, male paratypes, BIOLAT17003, BIOLAT17006, BIOLAT17012, BIOLAT17014, BIOLAT17016, BIOLAT17017, BIOLAT17026, BIOLAT17029, BIOLAT17032, BIOLAT17034, BIOLAT17035, BIOLAT17039, BIOLAT17041, BIOLAT17042, BIOLAT17053, BIOLAT16979, female paratypes), 12 July 1992 (NMNH: BIOLAT17107, BIOLAT17154, BIOLAT17142, BIOLAT17156, BIOLAT17155, male paratypes, BIOLAT17127, BIOLAT17151, female paratypes), 20 March 1992 (B. Brown, D. Feener)(NMNH: BIOLAT17440, male paratype), 28 October 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT10190, male paratype), 20–30 September 1991 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT12606, male paratype), 7–13 October 1991 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: BIOLAT13238, BIOLAT13248, male paratypes), 24 June 1993 (T.L. Erwin, F. Pfuno)(NMNH: BIOLAT19108, male paratype); Puerto Maldonado, Explorers Inn, 12.819°S, 69.260°W, 207, 23 October 1982 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP133815, male paratype), 31 August 1983 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP133811, female paratype), 3 October - 15 November 1983 (N.E. Stork)(NMNH: ADP134017, ADP134021, ADP134023, ADP134025, ADP134027, male paratypes, ADP133815, female paratype), Rio Tambopata, Culpa de Guacamayos, 300m, October 1995 (A. Forsyth)(NMNH: ADP132491, female paratype).
Figs 19, 28
Pseudophorticus puncticollis Erwin, 2004:8
Size range – 4.7 mm to 6.2 mm; these small beetles occur on the ground in rainforests; they are diurnal and run in clearings and on trails in open spots. Nothing is known about their way of life.
Costa Rica south to Perú and southeastern Brazil.
Currently, one described species is assigned to this genus. Many undescribed species are represented in collections, misidentified as either Euphorticus or Lachnophorus; the genus is in need of a taxonomic revision. In order to do such a revision, one would need to study all the primary types of both Euphorticus and Lachnophorus to discover their correct generic assignments.
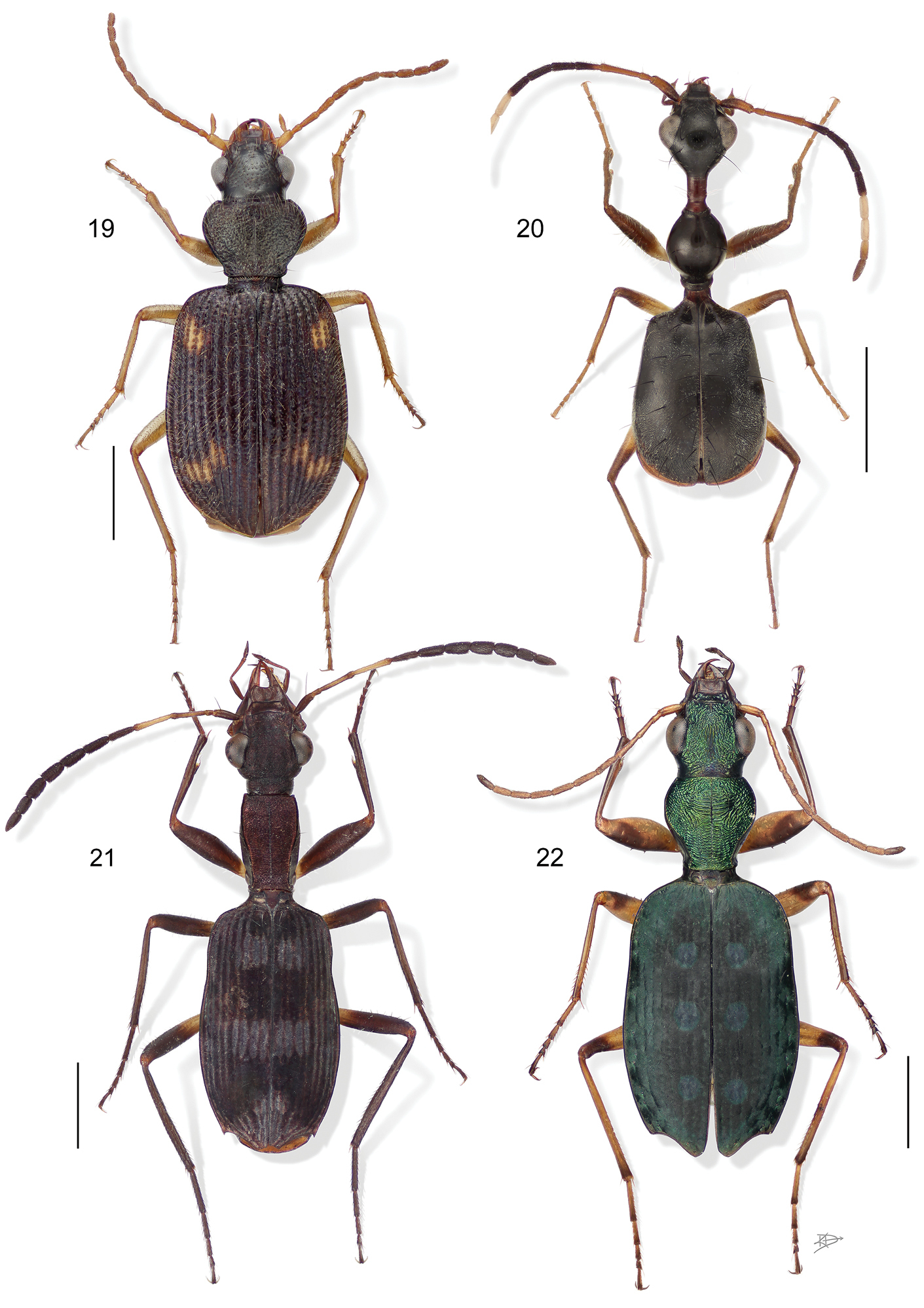
19 Pseudophorticus sp. (all species in South America are either undescribed or placed in Euphorticus G. Horn). Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132538 from Pakitza, Perú 20 Selina westermanni Motschulsky. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP132536 from China Bay, Sri Lanka 21 Stenocheila lacordairei Laporte de Castelnau. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP133801 from Chapada dos Guimãres, Brazil 22 Quammenis spectabilis Erwin. Digital Photo-illustration. Habitus, dorsal aspect, based on specimen ADP100513 from Estacíon Zurqui, Costa Rica.
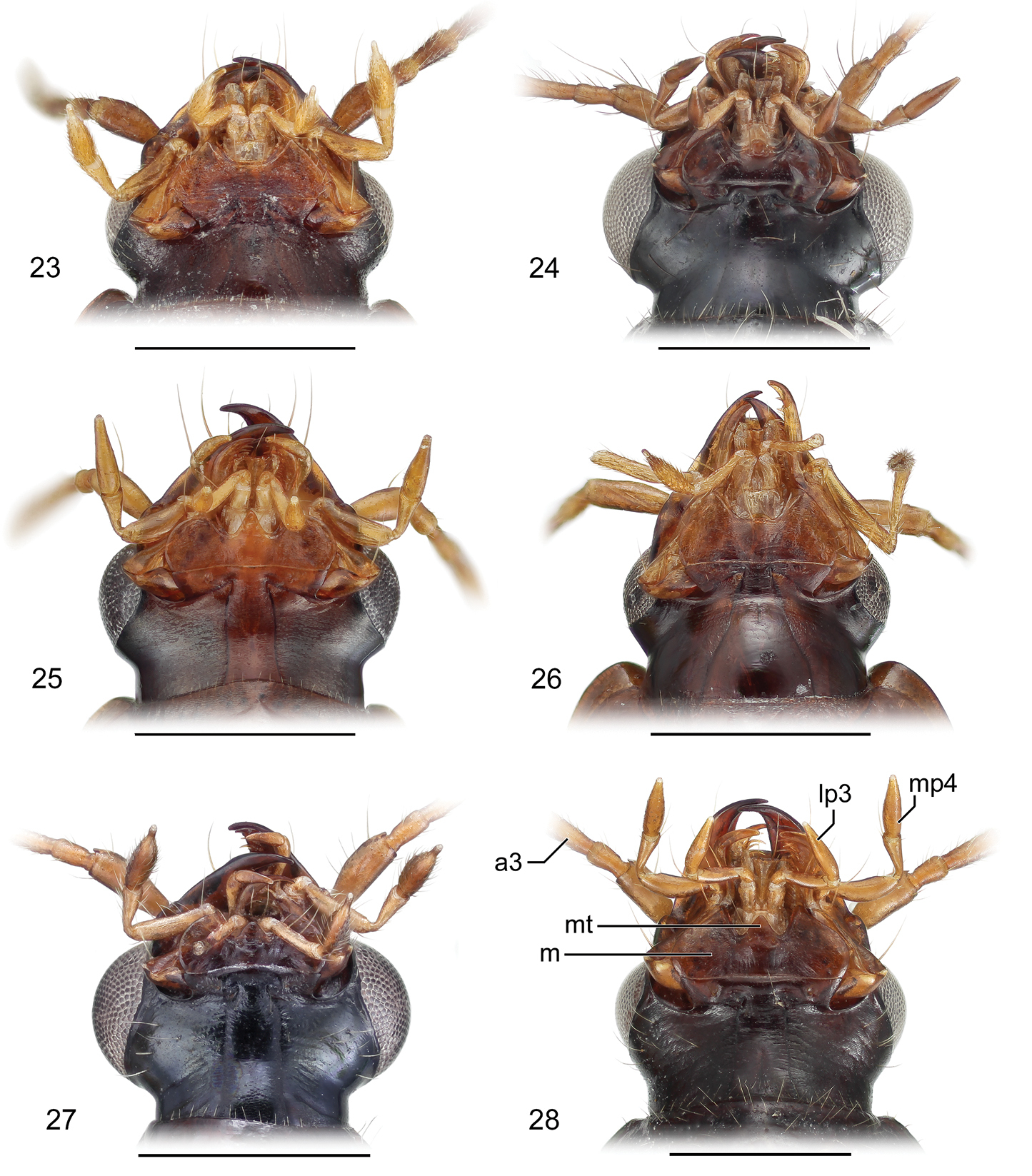
Mouthparts of adults. 23 Eucaerus sp. Mouthparts, ventral aspect, based on specimen ADP132552 from Pakitza, Perú 24 Euphorticus sp. Mouthparts, ventral aspect, based on specimen ADP132558 from Tapilula, México 25 Guatemalteca virgen Erwin. Mouthparts, ventral aspect, based on specimen ADP132546 from nr. La Virgen, Costa Rica 26 Lachnaces sp. Mouthparts, ventral aspect, based on specimen ADP132578 from Tambopata Reserved Zone, Explorer’s Inn, Perú 27 Lachnophorus sp. Mouthparts, ventral aspect, based on specimen ADP132570 from Pakitza, Perú 28 Pseudophorticus sp. Mouthparts, ventral aspect, based on specimen ADP132538 from Pakitza, Perú. Legend: a3 Antennomere 3; mt Mentum tooth; m Mentum; lp3 Labial palpomere 3; mp4 Maxillary palpomere 4.
Figs 1, 2, 22
Quammenis spectabilis Erwin, 2000:280
Size range – 6.5 mm to 7.0 mm; these beetles occur on steep or vertical wet rocky surfaces with mosses and ferns and other hygrophilous plants in cloud forests (e.g., hygropetric habitats such as vertical waterfalls, seeps, wet rocks, etc. (see Fig. 2)).
Costa Rica.
Currently, one described species is assigned to this genus.
Fig. 20
Selina westermanni Motschulsky, 1858:110
Size range – 3.9 mm to 5.0 mm; these small beetles occur on sandy banks of rivers (Lewis, 1882:480).
Africa, India, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, and Vietnam.
Currently, six described species are assigned to this genus; names of five of them are listed by
Fig. 21
Stenocheila lacordairei Laporte de Castelnau, 1832:12
Size range – 7.8 mm to 9.3 mm; these beetles have been found on the campus of INPA at Manaus, Brazil. The area was an open managed unnatural habitat among buildings.
Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Guyane, Perú.
This is a monobasic genus with a widespread species. See our notes under Diplacanthogaster Liebke, above.
Asklepia strandi Liebke, 1938:113.
Asklepius, a Greek God of healing. Why Liebke used this name is unknown. See: http://www.mythologydictionary.com/asclepius-mythology.html
Neat pattern-wing beetles.
Diagnosis (Figs 29–55, 57–75). Size range – ABL = 1.95 mm to 3.74 mm; with the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
Species are arrayed across three species groups based mainly on the armature of the male aedeagal endophallus: geminata species group (endophallus without spines, Fig. 57), hilaris species group (endophallus with multiple spines, Figs 58–63), and pulchripennis group (endophallus with two spines, Figs 64–74). In addition, the species of the geminata species group have elytral striae and moderately convex intervals; the hilaris group members have explanate lateral margins on the pronotum while those of the pulchripennis groups are feebly beaded only in the anterior half.
The wings are fully developed in most individuals we have studied, thus it is likely that these beetles are moderate to strong flyers; however, in at least two species there are also brachypterous adults. This is unusual in lowland Amazonian species; for example, see
Geographic
(Figs 76–78). As currently known, the range of this genus extends in cis-Andean South America from southeastern Colombia south to Bolivia and east to Guyana and Belém, Brazil, and from there south to Entre Ríos Province, Argentina.
These species live close to water in wet leaf litter and on aquatic vegetation (macrophytes) of backwashes along rivers, streams, and lakeshores of both Varzea and Igapó forests and among dead leaf accumulations on rocky or sandy stream banks. Immature stages are unknown; however, given the wide variation in adult size within a species as noted in the introduction, it is possible that larvae are ectoparasitoids (cf.
Not much has been previously published on this genus. We now know there are many undescribed species across the Amazon Basin and on the Guiana Shield and the southern part of the Brazilian Shield; hence it is not monobasic as reported by
The species list below, as well as arrangement of descriptions that follows, is ordered alphabetically.
Asklepia geminata (Bates), 1871:78, new combination, Brazil, Perú
Asklepia campbellorum Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia demiti Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia duofos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia grammechrysea Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Perú
Asklepia hilaris (Bates), 1871:79, comb. n., Brazil
Asklepia laetitia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Colombia
Asklepia lebioides (Bates), 1871:79, comb. n., Brazil
Asklepia matomena Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia adisi Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Brazil, Perú
Asklepia asuncionensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Paraguay
Asklepia biolat Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Perú
Asklepia bracheia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Perú
Asklepia cuiabaensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Ecuador
Asklepia kathleenae Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia macrops Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Argentina
Asklepia marchantaria Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia marituba Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Brazil
Asklepia pakitza Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Perú
Asklepia paraguayensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Paraguay
Asklepia pulchripennis (Bates), 1871:79, comb. n., Brazil
Asklepia samiriaensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Perú
Asklepia stalametlitos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Bolivia
Asklepia strandi Liebke, 1938:113 Guyana
Asklepia surinamensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n., Surinam
Asklepia vigilante Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n., Perú
Note. Because of the variability within species and the marked similarity across some species, only features of the male genitalia provide reliable means for identification of some species. Unfortunately, we did not have at our disposal males of all the species to image.
| 1 | Elytron markedly striate, intervals moderately convex (geminata species group) (Habitus, Fig. 29) | Asklepia geminata (Bates) |
| 1’ | Elytron devoid of striae, intervals and interneurs effaced from surface (although inconsistently spaced serial rows of interneur micropunctures can be seen through the transparent cuticle in some species and on the surface of others) | 2 |
| 2(1’) | Pronotum with lateral margin narrowly explanate (hilaris species group) | 3 |
| 2’ | Pronotum with lateral margin effaced posterior to medial lateral seta except just slightly anterior to hind angle — there shortly beaded; some species slightly beaded from anterior angle to medial lateral seta but not explanate (pulchripennis species group) | 9 |
| 3(2) | Antennal scape and pedicel testaceous, antennomeres 3–7 deeply infuscated, antennomeres 8–11 white | 4 |
| 3’ | Antennal scape and pedicel testaceous, antennomeres 3–6 deeply infuscated, antennomere 7 bicolored (Habitus, Fig. 32) | Asklepia duofos sp. n. |
| 4(3) | Pronotum completely infuscated or piceous (rarely median anterior margin slightly paler) | 5 |
| 4’ | Pronotum infuscated or piceous only laterally, disc concolorous with pale elytral maculae (Habitus, Fig. 33) | Asklepia grammechrysea sp. n. |
| 5(4) | Dorsal surface largely dark, elytral maculae if present very small | 6 |
| 5’ | Dorsal surface with dark fore body and large elytral maculae | 7 |
| 6(5) | Pronotum markedly constricted in basal third, markedly cordate. Mostly size larger (ABL = 3.2–3.83 mm; SBL = 2.18–3.20 mm; TW = 1.10–1.82 mm) (Habitus, Fig. 30) | Asklepia campbellorum sp. n. |
| 6’ | Pronotum much less constricted in basal third, tapered to base. Mostly size smaller (ABL = 2.47–2.96 mm; SBL = 2.2–2.5 mm; TW = 1.15–1.45 mm) (Habitus, Fig. 37) | Asklepia matomena sp. n. |
| 7(5’) | Pronotum longer and narrow (W/L ratio = 1.331–1.550) | 8 |
| 7’ | Pronotum short and wide (W/L ratio = 1.686–1.960), proportionally large, as wide as head across eyes (Habitus, Fig. 36) | Asklepia lebioides (Bates) |
| 7’’ | Pronotum short and wide (W/L ratio = 1.686–1.960), proportionally small, not as wide as head across eyes (Habitus, Fig. 34) | Asklepia hilaris (Bates) |
| 8(7) | Elytron with anterior macula very extensive; interneurs well impressed and striatopunctate (Habitus, Fig. 35) | Asklepia laetitia sp. n. |
| 8’ | Elytron with anterior macula small, divided in some individuals into two spots; interneurs of a very fine series of minute punctulae (Habitus, Fig. 31) | Asklepia demiti sp. n. |
| 9(2’) | Elytron with pale lateral margin restricted to apical half, mostly an extension inclusive of median macula in sector C | 10 |
| 9’ | Elytron with pale lateral margin extended nearly to humerus (Habitus, Fig. 53) | Asklepia strandi Liebke |
| 10(9) | Antenna mostly pale, only antennomeres 4, 5, and 6 darkly infuscated | 11 |
| 10’ | Antenna mostly infuscated, only antennomeres 1, 2, and 8–11 completely pale | 12 |
| 11(10) | Head infuscated | 13 |
| 11’ | Head pale, flavous | 14 |
| 12(10’) | Antennomere 7 bicolored, base infuscated, apex white | 15 |
| 12’ | Antennomere 7 entirely white | 21 |
| 13(11) | Pronotum wider than long (W/L ratio = 1.340–1.385 (Habitus, Fig. 54)) | Asklepia surinamensis sp. n. |
| 13’ | Pronotum nearly as wide as long (W/L ratio = 1.154 - 1.314) (Habitus, Fig. 38) | Asklepia adisi sp. n. |
| 14(11’) | Mostly size larger (ABL = 3.25 mm; SBL = 3.054 mm; MW = 1.648 mm). Eyes very large, anterior/posterior diameter markedly greater than length of antennomere 3. Elytra across humeri narrower than across apical third. Antennomere 3 testaceous (Habitus, Fig. 45) | Asklepia macrops sp. n. |
| 14’ | Mostly size smaller (ABL = 2.72 mm; SBL = 2.477 mm; MW = 1.27 mm). Eyes normal for genus, anterior/posterior diameter about equal in length to that of antennomere 3. Elytra across humeri about equal to that at apical third. Antennomere 3 slightly infuscated (Habitus, Fig. 39) | Asklepia asuncionensis sp. n. |
| 15(12) | Elytra markedly shiny, microsculpture effaced | 16 |
| 15’ | Elytra matte, microsculpture well developed, of isodiametric sculpticells (Habitus, Fig. 51) | Asklepia samiriaensis sp. n. |
| 16(15) | Head and pronotum markedly contrasting, head much darker in color than pronotum | 17 |
| 16’ | Head and pronotum concolorous | 18 |
| 17(16) | Head and pronotum flavous. Pronotum much wider than long (W/L ratio = 1.726) (Habitus, Fig. 42) | Asklepia cuiabaensis sp. n. |
| 17’ | Head and pronotum aurantiacus. Pronotum slightly wider than long (W/L ratio = 1.308–1.370) (Habitus, Fig. 48) | Asklepia pakitza sp. n. |
| 18(16’) | Head and pronotum pale, flavous, or aurantiacus | 19 |
| 18’ | Head and pronotum infuscated (Habitus, Fig. 43) | Asklepia ecuadoriana sp. n. |
| 19(18) | Pronotum with beaded lateral margin. Elytron with large macula of sectors A, B, and C markedly U-shaped (e.g., Fig. 55) | 20 |
| 19’ | Pronotum without beaded lateral margin. Elytron with large macula of sectors A, B, and C shallowly U-shaped in sector A (Habitus, Fig. 14) | Asklepia biolat sp. n. |
| 20(19) | Macula of sectors E and F extended to lateral margin (Habitus, Fig. 55) | Asklepia vigilante sp. n. |
| 20’ | Macula of sectors E and F not extended to lateral margin (Habitus, Fig. 52) | Asklepia stalametlitos sp. n. |
| 21(12’) | Head infuscated, pronotum pale | 22 |
| 21’ | Head and pronotum both pale, flavous or aurantiacus | 23 |
| 22(21) | Size larger (ABL = 2.81 mm; SBL = 2.478 - 2.769 mm; TW = 1.264–1.506 mm). Elytra across humeri square, lateral margins parallel; all available specimens alate (Habitus, Fig. 49) | Asklepia paraguayensis sp. n. |
| 22’ | Size smaller (ABL = 2.26 mm; SBL = 2.167 mm; TW = 1.241 mm). Elytra across humeri narrow, lateral margins rounded, sloped to humerus; both available specimens brachypterous (Habitus, Fig. 44) | Asklepia kathleenae sp. n. |
| 23(21’) | Elytra markedly short and convex (LE/LP ratio = 2.72–2.79) | 24 |
| 23’ | Elytra of normal length for genus (LE/LP ratio = 2.84–2.96) | 25 |
| 24(23) | Pronotum narrow, its width less than width across eyes (Habitus, Fig. 41) | Asklepia bracheia sp. n. |
| 24’ | Pronotum broad, its width equal to width across eyes (Habitus, Fig. 47) | Asklepia marituba sp. n. |
| 25(23’) | Pronotum globose, markedly convex and broad; frons markedly convex. Elytron with apex broadly infuscated (Habitus, Fig. 46) | Asklepia marchantaria sp. n. |
| 25’ | Pronotum moderately convex, narrow; frons barely convex. Elytron with apex completely pale (Habitus, Fig. 50) | Asklepia pulchripennis (Bates) |
This species group is monobasic and its single species is widespread from northern Perú to near the mouth of the Río Amazonas at Belém. Adults of the geminata species group are dark brown with markedly striate elytral interneurs, striae without punctures, intervals moderately convex; prothorax with narrowly explanate lateral margins and small, slightly produced obtuse hind angles. Endophallus of aedeagus without spines.
Figs 29, 57, 76
Brazil, Pará, Santarém, Río Tapajos, 2.4079°S, 54.7969°W, 30m, (H.W.Bates)(MNHP: ADP132513, male). Specimen labeled “Holotype” by George E. Ball in 1972.
The specific epithet, geminata, is a Latin adjective, meaning double (for example, the celestial Gemini, sign of the twins, Romulus and Remus, the mythological founders of Rome), or arranged in pairs as used here by Bates with reference to the two elytral spots.
Twin-spot pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 29, 57). Habitus: (Fig. 29). Size: [See also Table 1] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.768–2.997 mm, SBL = 2.512–2.794 mm, TW (total width) 1.411–1.440 mm, LP = 0.536–0.603 mm, WP = 0.733–0.820 mm, LE = 1.622–1.849 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 29): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 29) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 0.964), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.641), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.364); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; anterior angles feebly produced; base markedly constricted with medial lobe at base; hind angle moderately produced and setose; median line well defined, transverse impression punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as long as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.524) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.544), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs striate and continuous along length of entire elytron. Surface with finely impressed microsculpture, sculpticells isodiametric. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 57, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening moderately small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft narrow, moderately curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular, apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus without preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 76). The wide geographical range from near the mouth of the Río Amazon at Belém to the black-waters of Pacaya-Samiria Reserve in Perú on the upper Amazon drainage system is unusual for this genus. But as pointed out in the introduction, very small carabid beetles are not collected by any but carabid specialists, and there have been few of those, working the Amazon Basin.
See
Brazil, Pará, Belém, 5m, 1.46°S, 48.42°W, 8 October 1978, (G.E. Ball, K.E. Ball)(UASM: ADP132557, female), Santarém, Río Tapajos, 2.4079°S, 54.7969°W, 30m, no date, (CMNH: ADP133571. male). Perú, Loreto, Rio Samiria, Boca Caño Inglés Camp, 5.1317°S, 75.0617°W, 117m, 23 August 1991, (T.L. Erwin, G.E. Ball, D. Shpeley)(NMNH: ADP109186, male).
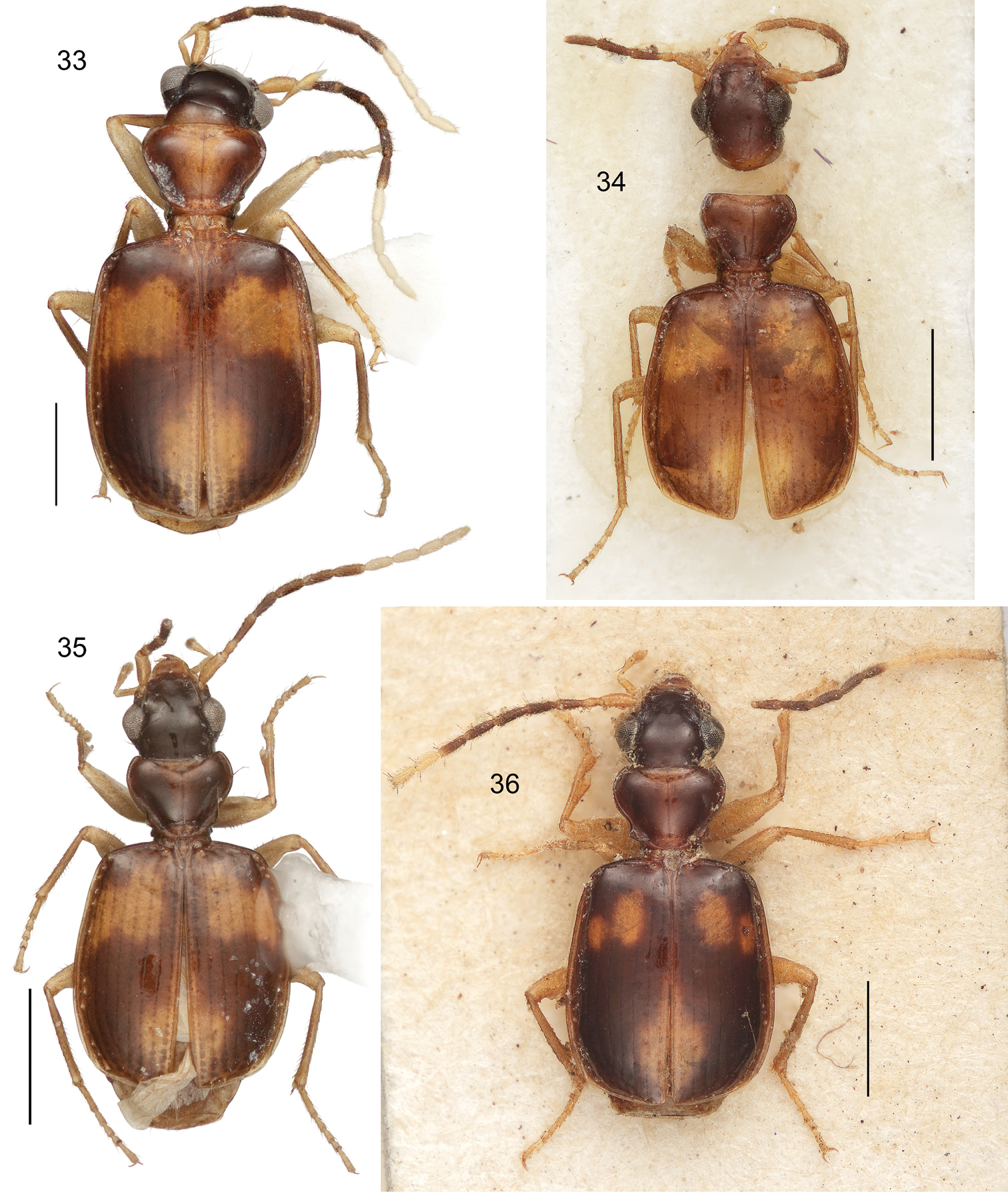
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 29 Asklepia geminata (Bates, 1871) ADP132513, Santarém, Río Tapajos, Brazil 30 Asklepia campbellorum Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP133032, 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil 31 Asklepia demiti Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132539, Río Demiti, Brazil. Note that the holotype has feebly infuscated antennomeres 3-7, others in the series have more normal infuscation, as in other species with this attribute 32 Asklepia duofos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP133147, 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil. Scale line = 1 mm.
This species group contains eight species and is widespread from northern Perú to at least Santarém on the lower Río Amazonas, north into Venezuela and only known south of the Río Amazonas at Manaus and Santarém by a few kilometers. Dorsal surface mostly dark, particularly the head and pronotum and base color of the elytra; abdominal sterna infuscated except VII which is aurantiacus. Pronotum with lateral margin narrowly explanate; hind angles produced and about right or acute. Endophallus of aedeagus with 6–12 spines, depending on the species.
http://zoobank.org/EDA34F46-B81B-4D4E-8CF4-ECD7EFEE39F9
Figs 30, 58, 77
Brazil, Amazonas, 20 km SW Manaus, 3.166°S, 60.234°W, 47m, 6 November 1969 (J.M. Campbell, B.A. Campbell)(NMNH: ADP133032, male).
The specific epithet, campbellorum, is an eponym based on the family name of Milt and Beverly Campbell†, collectors of the type series.
Campbells’ pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 30, 58). Habitus: (Fig. 30). Size: [See also Table 2] Small-size to large-size for the genus; ABL = 3.17–3.61 mm, SBL = 2.182–3.198 mm, TW (total width) 1.106–1.824 mm, LP = 0.467–0.691 mm, WP = 0.611–0.956 mm, LE = 1.386–2.069 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 30): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 30) moderately broad, slightly wider than head across eyes (WH/WP, both sexes: 0.966), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.414), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.395); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted and lobed medially; anterior angles markedly produced, hind angle markedly prominent, produced and setose; median line moderately defined, apical transverse impression punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.492) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.510). Elytral interneurs evident as rows of continuous closely spaced fine punctures; punctures homogeneous. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 58, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly acute apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 7 preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at only one location on the shore of a small lake near the middle of the Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its actual distribution: As has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Amazonas, 20 km SW Manaus, 3.166°S, 60.234°W, 47m, 6 November 1969 (J.M. Campbell, B.A. Campbell)(NMNH: ADP132693, ADP133141, ADP133167, ADP132734, ADP133165, ADP133155, ADP132705, ADP133064, ADP109196, female paratypes, ADP133177, ADP132685, ADP133113, ADP133127, ADP133157, ADP132727, ADP133119, ADP133010, ADP133004, ADP133135, ADP132723, ADP133137, ADP133191, ADP133147, male paratypes), (ADP133137, male, forebody missing).
http://zoobank.org/A36C1689-CB6E-450D-81E0-18B6027A7B1E
Figs 31, 59, 75, 77
Brazil, Amazonas, circa Rio Demiti, 0.5748°N, 66.6869°W, 116m, 13 September 1978 (G.E Ball, K.E. Ball) (NMNH: ADP132539, male).
The specific epithet, demiti, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the river along which these beetles are found.
Río Demiti pattern-wing beetles.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 31, 59, 75). Habitus: (Fig. 31). Size: [See also Table 3] Medium to large-size for the genus; ABL = 2.089–3.071 mm, SBL = 2.590–3.131 mm, TW (total width) 1.491–1.815 mm, LP = 0.545–0.642 mm, WP = 0.762–0.888 mm, LE = 1.721–2.036 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 31): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 31) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WP/WH, both sexes: 1.025), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.471), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.380); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; apical margin straight, base markedly constricted with medial lobe at base; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle markedly prominent and setose; median line moderately defined, apical transverse impression punctate, punctures coarse and infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.492) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.504). Elytral interneurs evident as short discontinuous rows of fine punctures; punctures with a fuscous halo at basal and apical proximal quadrant of elytron. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 59, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fifth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a broadly rounded apex. Left paramere very large and broad, right small and triangular, apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 10 small medial spines and one large distal spine. Female genitalia. (Fig. 75A and B) Ovipositor with broad laterotergite (lt) and two narrow gonocoxites (gc 1, gc 2); gonocoxite 1 apico-laterally not setose; gonocoxite 2 shallowly falcate, base (b) medium-size much broader than narrow blade (bl) which is elongate, with two dorsal ensiform setae (des), ventral ensiform seta absent, ensiform setae moderately short and robust; without ventral preapical nematiform setae. Reproductive tract proximally with moderately short, broad bursa copulatrix (bc), continuous at its distal end with common oviduct (co) and long robust bipartite spermatheca (sp) distal to broad short villous canal (vc), one lobe slightly narrowed distally; spermathecal gland not found in dissection; spermathecal gland duct (sgd) robust, heavily sclerotized, attached to oviduct at base of its broadened portion. Defense gland (Fig. 75C) with an annulated sausage-shaped accessory gland (cc) and large reservoir (gldr) distal to a long efferent duct (ed).
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at only two locations on second-order white-water streams of the Río Negro drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Amazonas, circa Rio Demiti, 0.5748°N, 66.6869°W, 116m, 13 September 1978 (G.E Ball, K.E. Ball)(NMNH: ADP132585, female paratype, ADP132483, ADP132501, male paratypes). Venezuela, Amazonas, 29 km S Puerto Ayacucho, Río Paria Chico, 5.4694N, 67.6029W, 71m, (J.T. Polhemus)(NMNH: ADP132605, male paratype).
http://zoobank.org/45600768-3727-45A2-BDD8-F1C07ACA6CD8
Figs 32, 77
Brazil, Amazonas, 20 km SW Manaus, 3.166°S, 60.234°W, 47m, 6 November 1969 (J.M. Campbell, B.A. Campbell)(NMNH: ADP132555, male).
The specific epithet, derived from the Greek duofos, δυο (duo) = two, fɸσ (fos) = lights) is a noun used in apposition referring to the two bright spots on the elytra.
Two-lights pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
Habitus (Fig. 32). Size: [See also Table 4] Small-sized for the genus; ABL = 2.433 mm, SBL = 2.248 mm, TW (total width) 1.124 mm, LP = 0.495 mm, WP = 0.666 mm, LE = 1.407 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 32): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 32) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP: 0.939), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.423), wider than long (PW/PL: 1.397); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle markedly prominent, produced and setose; median line markedly defined, apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/MW: 0.489) and pronotum (WP/MW: 0.521), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as short rows of discontinuous widely spaced coarse punctures. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. The male paratype was dissected for illustrating the male aedeagus; however, it was damaged in the process and we were hesitant to dissect the holotype at this time. We do note the presence of multiple spines on the endophallus. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at only one location on the shore of a small lake near the middle Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
http://zoobank.org/26ADBF2A-0A81-4009-A1F2-54FB25AC978F
Figs 33, 60, 77
Perú, LORETO, circa Pithecia, Cocha Shinguito, 5.1757°S, 74.655°W, 111m, 16 August 1989 (T.L. Erwin, G.P. Servat)(MUSM: ADP133151).
The specific epithet, grammechrysea derived from the Greek γραμμή (grammae) = line, κριχισηα (chrysea) = golden), is a noun in apposition referring to the yellow (flavous) line on the pronotum.
Golden-line pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 33, 60). Habitus: (Fig. 33). Size: [See also Table 5] Small to large-sized for the genus; ABL = 2.336–3.78 mm, SBL = 2.265–3.736 mm, TW (total width) 1.382–2.216 mm, LP = 0.481–1.016 mm, WP = 0.659–1.065 mm, LE = 1.440–2.381 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 33): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 33) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.002), larger than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.512), about as wider than long (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.381); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded and fuscous with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted and lobed medially; anterior angles moderately produced, hind angle markedly produced and setose; median line markedly defined, basal and apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures fuscous; surface smooth throughout.
Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as width as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.481) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.493), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as continuous rows of fine closely spaced punctures; punctures each with a fuscous halo in the basal and apical proximal quadrant of elytron. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 60, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 7 preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at locations on black-water systems across the northern and western areas of the Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Adults of this species are active in lowland Igapó rainforest during the rainy season. They have been found in wet leaf litter at the edge of small streams and lake shores as well as in old levee forests of Attalea palms near a black water river; they also occur on mud with grasses and among crumbly clods of yellowish clay at salt licks, as well as near rotting tree trunks at the water’s edge in low lying inundation forest at the edge of a black water lake and on sandy shorelines with matted rhizomes and dry leaf litter.
Perú, Loreto, circa Pithecia, Cocha Shinguito, 5.1757°S, 74.655°W, 111m, 16 August 1989 (T.L. Erwin, G.P. Servat)(NMNH: ADP132980, ADP132709, ADP132741, ADP133197, ADP132717, ADP133161, ADP133163, ADP- 132739, ADP133187, ADP133053, ADP133185, ADP132697, ADP133123, ADP133101, ADP133099, ADP133111, ADP132978, ADP133143, ADP133153, ADP132465, ADP132537, ADP132591, ADP132471, ADP132533, ADP132579, ADP132517, ADP132522, ADP132559, ADP132497, ADP132526, ADP132511, ADP132573, ADP132459, female paratypes, ADP013271, ADP132753, ADP133183, ADP- 133173, ADP132721, ADP133107, ADP133095, ADP133060, ADP132703, ADP109204, ADP133129, ADP132715, ADP133139, ADP133117, ADP133175, ADP133179, ADP132683, ADP132725, ADP133079, ADP132735, ADP133072, ADP132747, ADP133105, ADP132730, ADP133125, ADP132488, ADP132462, ADP132479, ADP132516, ADP132461, ADP132498, ADP132504, ADP132514, ADP132486, ADP132502, ADP132577, ADP132472, ADP132473, ADP132567, ADP132599, male paratypes; Cocha Shinguito, south side, 5.19543°S, 74.640°W, 121m, 17 May 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP093477, ADP094131, ADP071242, ADP066673, ADP093475, ADP093474, ADP093453 ADP093457, ADP093431, ADP071517, female paratypes, ADP071518, ADP071516, ADP094133, ADP093458, ADP093430, ADP093456, ADP093436, male paratypes); 25 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M.G. Pogue)(NMNH: ADP071240, ADP071201, female paratypes, ADP071249, ADP071247, ADP- 071239, ADP071240, ADP071241, ADP071225, ADP071226, ADP071243, ADP071244, ADP071217, ADP071224, ADP071198, ADP071218, ADP071202, ADP071588, male paratypes); Cocha Shinguito, 5.1757°S, 74.655°W, 111m, 14 June 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP094139, female paratypes, ADP094109, ADP094109, ADP094117, ADP094111, ADP094135, ADP094136, ADP094140, male paratypes); 25 August 1991 (G.E. Ball, D. Shpeley)(NMNH: ADP132551, female paratype, ADP132593, ADP132563, male paratypes); Cocha Shinguito, 5.1746°S, 74.6581°W, 119m, 26 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M.G. Pogue)(NMNH: ADP071520, ADP071521, female paratypes, ADP071519, male paratype); Cocha Shinguito, margin of Río Samiria, 5.1867°S, 74.6187°W, 124m, 17 May 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP066600, ADP066669, female paratypes, ADP066581, ADP066597, ADP066625, ADP066647, male paratypes); Río Samiria, Camp Terry, 5.4883°S, 75.1927°W, 132m, 14 May 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP094434, ADP094362, ADP094318, ADP094374, ADP094323, ADP094322, ADP132528, ADP132464, ADP094321, female paratypes ADP094348, ADP094342, ADP094345, ADP094349, ADP094344, ADP094324, ADP132510, ADP094341, ADP094346, ADP132541, ADP132549, ADP094365, ADP132523, male paratypes); Hamburgo, Boca Caño Inglés Camp, 5.1317°S, 75.0617°W, 117m, 20 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP071046, female paratypes, ADP071633, male paratype); Explornapo Camp, Río Napo, Río Sucusari, 3.2494°S, 72.9205°W, 101m, 4 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP023587, ADP023593, female paratypes, ADP023587, ADP091311, male paratypes); 14 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP052649, ADP052564, ADP052650, female paratypes, ADP052548, ADP052548, male paratypes); 19 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP009175, ADP009123, ADP052565, female paratypes, ADP009173, ADP052563, ADP009176, ADP009174, male paratypes); circa Explornapo Camp, Río Napo, Cocha Shimagai, 3.3563°S, 73.0467°W, 88m, 13 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP008129, ADP008114, ADP008128, ADP094109, female paratypes, ADP008122, ADP008124, ADP008127, ADP008118, ADP008115, ADP008116, ADP008119, male paratypes).
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 33 Asklepia grammechrysea Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP133151, Pithecia, Perú 34 Asklepia hilaris (Bates, 1871), comb. n., Brazil ADP132543, São Paulo de Olivença, Brazil 35 Asklepia laetitia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP109190, Leticia, Colombia 36 Asklepia lebioides (Bates, 1871), comb. n., ADP109194, Santarém, Río Tapajos, Brazil. Scale line = 1 mm.
Figs 34, 77
Brazil, Amazonas, São Paulo de Olivença, 3.4622°S, 68.9499°W, 77m, (H.W. Bates)(BMNH: ADP132543, male). This specimen labeled “Holotype” by George E. Ball in 1972.
The specific epithet, hilaris, is a Latin adjective that adequately describes this species with gaily colorful elytra.
Cheerful pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
Habitus (Fig. 34). Size: [See also Table 6] Small in size for the genus; ABL = 2.464 mm, SBL = 2.336 mm, TW (total width) 1.233 mm, LP = 0.483 mm, WP = 0.617 mm, LE = 1.495 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 34): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 34) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.085), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.346), wider than long (W/L: 1.294); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; apical margin straight; base markedly constricted; hind angle moderately produced and setose; median line moderately well defined, apical transverse impression punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third about same width as head across eyes (WH/TW: 1.099) and pronotum (WP/TW: 1.013). Elytral interneurs evident as rows of discontinuous, widely spaced, coarse punctures. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Dissected by G.E. Ball in 1972 at the BMNH, but the genitalia are missing from the microvial pinned under the holotype. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at only one location on the white-water system of the Río Amazonas drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
The holotype and only specimen seen by us is glued to a card and is somewhat damaged.
http://zoobank.org/628C9676-9823-4241-AA36-3226C8561E7E
Figs 35, 61, 77
Colombia, Amazonas, Leticia, 4.1896°S, 69.9711°W, 72m, no date, (F.M. Oliveira, P. Wygodzinsky)(AMNH: ADP109190, male).
The specific epithet, laetitia, from the Latin greeting laetitia used in the nominative case, is a singular feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the town near which these beetles were found, and meaning happiness, joy, gladness, and delight.
Colombian pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 35, 61). Habitus: (Fig. 35). Size: [See also Table 7] Small-size for the genus; ABL = 2.99 mm, SBL = 2.494 mm, TW (total width) 1.463 mm, LP = 0.489 mm, WP = 0.706 mm, LE = 1.633 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 35): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 35) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.032), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.316), wider than long (W/L: 1.444); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; apical margin straight; base markedly constricted; hind angle moderately produced and setose; median line well defined, basal and apical transverse impression punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third markedly wider than head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.468) and twice as wide as pronotum (WP/TW: 0.504). Elytral interneurs evident as rows of continuous, coarse punctures widely spaced, coarse punctures with infuscated halo in the proximal basal and apical quadrants. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 61). Median lobe (ml) with phallobase (pb) of moderate length about a fourth the length of shaft (ps), basal opening (bo) large, oriented parallel to shaft’s apical third. Shaft broad, moderately curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium (oo, om); in ventral aspect tapered toward rather rounded apex (a), in lateral aspect, a narrowly rounded apex. Left paramere (lp) very large and broad, right (rp) small and triangular, apex of left paramere lobate and much longer than right paramere, about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 5 medial spines (ms), and one very large distal spine (ds). Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at only one location on the white-water system of the Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its actual distribution, as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
Figs 36, 62, 77
Brazil, Pará, Santarém, Río Tapajos, 2.4079°S, 54.7969°W, 30m, (H.W. Bates)(MNHP: ADP132553, female). This specimen was labeled “Lectotype” by George E. Ball in 1972.
The specific epithet, lebioides, is a Latin adjective that adequately describes this species with adults resembling (-oides) some adults in the lebiine genus, Lebia.
Lebia-like pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 36, 62). Habitus: (Fig. 36). Size: [See also Table 8] Medium to large-size for the genus; ABL = 2.605–3.064 mm, SBL = 2.692–3.142 mm, TW (total width) 1.504–1.790 mm, LP = 0.551–0.647 mm, WP = 0.747–0.869 mm, LE = 1.698–2.023 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 36): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 36) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 0.973) longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.349), wider than long (W/L: mean both sexes: 1.824); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted and lobed; anterior angles moderately produced, hind angle markedly acutely produced and setose; median line moderately defined, basal and apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as the head across eyes (WH/TW: mean, 0.487) and pronotum (WP/TW: mean, 0.5). Elytral interneurs evident as rows of continuous fine closely spaced coarse punctures; punctures of the apical margin each with a halo. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 62, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fifth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft’s apical third. Shaft broad, moderately curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather broadly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a narrowly rounded apex. Left paramere very large and broad, right small and triangular, apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere, about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 11 medial spines, and one large distal spine. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at locations on both the clear-water and white-water systems of the Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Brazil, Pará, Santarém, Río Tapajos, 2.4079°S, 54.7969°W, 30m, (H.W. Bates)(BMNH: ADP109194, male paralectotype); Amazonas, circa Rio Demiti, 0.5748°N, 66.6869°W, 116m, 22 August 1978 (G.E. Ball, K.E. Ball)(UASM: ADP109208, ADP130048, ADP130052, ADP130050, males), 13 September 1978 (G.E. Ball, K.E. Ball)(NMNH: ADP109202, ADP132689, ADP133133, ADP132506, ADP132731, females, ADP132687, ADP133181, ADP133145, ADP132751, ADP133159, ADP132691, ADP132719, ADP132729, ADP132733, ADP133131, ADP133026, ADP132499, ADP133103, circa Cucui, Rio Negro, 1.1972°N, 66.8382°W, 79m, 17 September 1978 (G.E Ball, K.E. Ball)(NMNH: ADP132701, male).
http://zoobank.org/A75BFD33-D209-4B7A-BE42-DC480915524B
Figs 37, 63, 77
Brazil, Amazonas, 20 km SW Manaus, 3.166°S, 60.234°W, 47m, 6 November 1969 (J.M. Campbell, B.A. Campbell)(NMNH: ADP132519, male).
The specific epithet, matomena, is derived from the Greek ματωμενα (bleeding) and used as an adjective in reference to the blood-red color of the head and elytra of these beetles.
Reddish pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 37, 63). Habitus: (Fig. 37). Size: [See also Table 9] Small to medium-sized for the genus; ABL = 2.476–2.961 mm, SBL = 2.189–2.551 mm, TW (total width) 0.575–0.726 mm, LP = 0.447–0.546 mm, WP = 0.603–0.730 mm, LE = 1.411–1.622 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 37): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 37) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean males: 1.011), longer than head (LP/LH, mean males: 1.387), wider than long (W/L, mean males 1.345); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted and lobed medially; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle markedly prominent, produced and setose; median line moderately defined, apical transverse impression punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: mean males, 0.520) and pronotum (WP/TW: mean males, 0.514), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as rows of continuous fine punctures closely spaced; punctures homogeneous. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 63, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly acute apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 7 preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 77). This species has been found at only one location on the shore of a small lake near the middle Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Amazonas, 20 km SW Manaus, 3.166°S, 60.234°W, 47m, 6 November 1969 (J.M. Campbell, B.A. Campbell)(NMNH: ADP133527, ADP133097, male paratypes).
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 37 Asklepia matomena Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP132519, 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil 38 Asklepia adisi Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. Adis #000691, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil 39 Asklepia asuncionensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP130036, Asunción, Rio Paraguay, Paraguay 40 Asklepia biolat Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132509, Pakitza, Perú. Scale line = 1 mm.
Dorsal color variable, some species with lighter adults and some with darker ones; abdominal sterna III-VI aurantiacus, sternum VII infuscated. Without explanate pronotal lateral margins, although some with a partial bead from the hind angle to apical third and some with a bead extended slightly beyond the lateral seta; pronotum sub-spherical in anterior two-thirds; elytra patterned. Brachyptery present in two species. Endophallus of aedeagus with two rather large spines, one larger than the other.
http://zoobank.org/01A360AD-0E9E-4626-B2FC-D90DB089F19F
Figs 38, 64, 78
Brazil, Amazonas, Rio Solimões, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, 3.2488°S, 59.9556°W, 7m, 11 April 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 000691, female).
The specific epithet, adisi, is an eponym, masculine, genitive case, based on the family name of Joachim Adis† who collected the type series.
Adis’ pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 38, 64). Habitus: (Fig. 38) Size: [See also Table 10] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.582–3.199 mm, SBL = 2.542–2.688 mm, TW (total width) 1.341–1.473 mm, LP = 0.513–0.591 mm, WP = 0.660–0.717 mm, LE = 1.578–1.712 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 38): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 38) moderately broad, slightly narrower than head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.103), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.327), wider than longer (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.226); markedly cordiform and convex, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly define as an infuscate line, transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscate; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra markedly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.535) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.520), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as short discontinuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 64, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase moderate in length, about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening large, oriented parallel to the central part of the shaft. Shaft broad, slightly twisted ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather broad apex, in lateral aspect, a thick rounded apex. Left paramere very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere, about two-thirds the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with one median spine, and one large distal spine. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and capable of flight as they have been captured at lights. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at locations on both the clear-water and black-water systems of the upper and middle Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Amazonas, Rio Solimões, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, 3.2488°S, 59.9556°W, 7m, 11 April 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 001149, female paratype), 28 July 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 001650, female); 14 September 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 000356, female paratype); 1 October 1981 (J. Adis)(NMNH: ADIS # 000662, ADIS # 000621, ADIS # 000667, ADIS # 000664, ADIS # 000666, ADIS # 000233, ADIS # 000239, ADIS # 000236, ADIS # 000241, ADIS # 000231, female paratypes, ADIS # 000670, ADIS # 000622, ADIS # 000659, ADIS # 000226, ADIS # 000232, ADIS # 000238, ADIS # 000240, ADIS # 000228, ADIS # 000265, ADIS # 000653, male paratypes), 1 October 1981 (NMNH: Adis # 000656, male, not paratype, damaged, Adis # 000185, female, not paratype, damaged), 20 October 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 000750, ADIS # 000727, female paratypes, ADIS # 001335, ADIS # 001106, ADIS # 001623, ADIS # 001344, ADIS # 001418, male paratypes) 4 November 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 001106, females); 13–17 September 1991 (C. Martius, A. Rebello)(NMNH: ADIS # 000849, male paratype); Pará, Santarém, Río Tapajos, 2.4079°S, 54.7969°W, 30m, 27-28 December 1967 (H. Reichardt)(MZUSP: ADP132811, ADP132817, ADP132809, male paratypes, ADP132807, ADP132805, ADP133655, ADP132819, ADP132813, female paratypes, Pacoval, Rio Curuá, 1.7733°S, 54.9971°W, 12m, 16 February 1968 (H. Reichardt)(MZUSP: ADP132815, female paratype). Perú, Loreto, Boca del Río Samiria, 1 km SW Vigilante post No. 1, 4.5005°S, 74.0659°W, 99m, 6 May 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(MUSM: ADP093365, female).
http://zoobank.org/2410C225-543E-46ED-B94A-FAD157AF8157
Figs 39, 78
Paraguay, Central, Asunción, Rio Paraguay, 25.320°S, 57.668°W, 54m, June (unknown)(CMNH: ADP130036, female).
The specific epithet, asuncionensis, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the place near where these beetles are found.
Asunción pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
Habitus (Fig. 39). Size: [See also Table 11] Small-size for the genus; ABL = 2.70 mm, SBL = 2, 477 mm, TW (total width) 1.270 mm, LP = 0.533 mm, WP = 0.648 mm, LE = 1.566 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 39): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 39) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, 1.035 mm), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.410), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.714); markedly cordiform and rounded, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line moderately defined, apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderate convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 1.071) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 1.018). Elytral interneurs evident as short discontinuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures, interneurs effaced in the medial quadrants. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male unknown. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on white-water of the middle Río Paraguay drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
http://zoobank.org/F1BBAF55-DA55-407E-A3FD-12C00891707A
Figs 40, 65, 78
Perú, Madre de Dios, BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Zone 9, 11.8931°S, 71.2564°W, 382m, 1 October 1989 (T.L. Erwin)(MUSM: ADP132509, male).
The specific epithet, biolat, is used as a noun in apposition based on the acronym of the Smithsonian Institution’s past program “Biodiversity in Latin America” (BIOLAT) which sought to field-train young Latin American biology students in biodiversity techniques and did so for more than 200 of them between 1987 and 1991 in Perú and Bolivia. These beetles were collected under the auspices of the BIOLAT Program.
Biolat pattern-wing beetles.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 40, 65). Habitus: (Fig. 40). Size: [See also Table 12] Large-size for the genus; ABL = 3.127–3.421 mm, SBL = 2.787–3.247 mm, TW (total width) 0.694–0.908 mm, LP = 0.637–0.746 mm, WP = 0.747–0.935 mm, LE = 1.750–2.035 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 40): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 40) moderately broad, not quite as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.007), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.603), slightly wider than long (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.244); markedly cordiform, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; base markedly constricted; hind angle slightly acutely produced and setose; surface markedly smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytron twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: mean, both sexes, 0.522), and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.518), longer than wide, moderately convex, intervals and interneurs effaced (see diagnosis above), interneur 2 with 7 setae, interneur 5 with two setae. Hind wings dimorphic; most specimens studied are brachypterous. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 65, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase moderate in length, about a fifth the length of shaft, basal opening large, oblique to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally at distal sixth, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather moderately rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded blunt apex. Left paramere very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with one very large preapical spine. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at locations on the white-water system of the upper Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Perú, Madre de Dios, BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Zone 9, 11.8931°S, 71.2564°W, 382m, 1 October 1989 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP132525, ADP132524, ADP132490, ADP132505, ADP132492, ADP132508, female paratypes, ADP132509, ADP132467, ADP132474, ADP132481, ADP132487, ADP132489, ADP132484, ADP132469, ADP132475, ADP132463, ADP132478, male paratypes), Río Manu, 11.9350°S, 71.3032°W, 329m, 18 & 21 February 1990 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP132575, ADP132480, male paratypes); Río Manu, Pakitza, 11.5647°S, 71.1700°W, 356m, 11 July 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP109198, ADP132996, female paratypes); 11.9350°S, 71.3032°W, 329m, 13 July 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP132988, female paratype, ADP133195, male paratype); 11.9099°S, 71.2717°W, 395m, 24 June 1993 (T.L. Erwin, F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP133189, female paratype, ADP133193, ADP133149, ADP132707, ADP133171, male paratypes).
See Erwin (1990) and Venable & Erwin (1996) for detailed trail maps of the BIOLAT Biodiversity Station.
http://zoobank.org/05701FC7-7994-4D81-A068-849C5F60FD85
Fig. 41, 66, 78
Perú, Loreto, circa Explornapo Camp, Río Napo, Cocha Shimagai, 3.3563°S, 73.0467°W, 88m, 13 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP08121, female).
The specific epithet, bracheia, is derived from the Greek βραχεια (small) and used as an adjective in reference to the small size of the elytra of these beetles.
Short pattern-wing beetles.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 41, 66). Habitus: (Fig. 41). Size: [See also Table 13] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.343–2.537 mm, SBL = 1.952–2.344 mm, TW (total width) 1.074–1.274 mm, LP = 0.457–0.558 mm, WP = 0.557–0.701 mm, LE = 1.275–1.424 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 41): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 41) slightly broad, about as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.042), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.590), wider than long (WP/LP: mean both sexes: 1.205); markedly cordiform, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; base markedly constricted; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly defined, basal and apical transverse impressions evident as infuscated dots in the surface, surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderately convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.529) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.507), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as discontinuous rows of widely spaced punctures, rows effaced at lateral area of medial third and apical third, punctures present fuscous; elytron substantially transparent. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 66, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase long about a third the length of shaft, basal opening large, oriented parallel to shaft at apical third. Shaft narrow, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather moderately narrow rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 2 preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at locations on the black-water systems of the upper Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Perú, Loreto, 1 km SW Boca del Río Samiria, Vigilante post No. 1, 4.5005°S, 74.0659°W, 99m, 14 & 15 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, G.E. Ball, D. Shpeley)(NMNH: ADP133028, female paratype, ADP133169, male paratype), 5 May 1990 (T.L. Erwin, G.E. Ball, D. Shpeley)(NMNH: ADP086696, female paratype, ADP086682, ADP086742, ADP067305, ADP067304, male paratypes); circa Explornapo Camp, Río Napo, Cocha Shimagai, 3.3563°S, 73.0467°W, 88m, 13 June 1992 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(NMNH: ADP008125, female paratype, ADP008072, ADP008120, male paratypes).
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 41 Asklepia bracheia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP008121, Cocha Shimagai, Perú 42 Asklepia cuiabaensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP130044, Cuiabá, Brazil 43 Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132485, Limoncocha, Ecuador 44 Asklepia kathleenae Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132460, Belém, Brazil. Scale line = 1 mm.
http://zoobank.org/CD3F2AE4-0CF7-4F6F-846F-224A25DE01A1
Figs 42, 78
Brazil, Mato Grosso, Cuiabá, 15.6416°S, 56.0732°W, 149m, August (unknown)(CMNH: ADP130044, female).
The specific epithet, cuiabaensis, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the place near where these beetles are found.
Cuiabá pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
Habitus (Fig. 42). Size: [See also Table 14] Medium-size to large for the genus; ABL = 2.610 mm, SBL = 2.191 mm, TW (total width) 1.270 mm, LP = 0.46 mm, WP = 0.592 mm, LE = 1.372 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 42): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 42) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, 1, 062) longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.388), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.726); slightly cordiform and rounded, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly defined, apical transverse impressions punctate, surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderate convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0, 495) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0, 495). Elytral interneurs evident as continuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures, interneurs continuous along length of entire elytron. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Male unknown. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on the middle Rio Cuiabá. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
http://zoobank.org/40AFE3C2-454B-42E4-998A-BBC8014E7406
Figs 43, 67, 68, 78
Ecuador, Sucumbíos, Limoncocha, 0.4088°S, 76.6176°W, 233m, 11 June 1977 (W.E Steiner)(NMNH: ADP132485, male).
The specific epithet, ecuadoriana, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the country in which these beetles are found.
Ecuadorian pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 43, 67, 68). Habitus: (Fig. 43). Size: [See also Table 15] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.894–2.995 mm, SBL = 2.501–2.598 mm, TW (total width) 1.325–1.490 mm, LP = 0.555–0.595 mm, WP = 0.638–0.691 mm, LE = 1.607–1.632 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 43): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 43) moderately broad, slightly narrower than head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.140), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.586), about as longer than wide (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.157); markedly cordiform and convex lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle slightly acutely produced and setose; median line feebly defined, basal transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderately convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.535) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.469), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs effaced from most of the elytron surface, only evident as short discontinuous rows of coarse punctures, punctures with fuscous halo. Scattered fuscous punctures in the medial and apical quadrants present in some individuals. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Figs 67, 68, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally then curved dorsally near apex, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather broadly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a narrowly rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere narrowly rounded much longer than right paramere about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 2 preapical spines; we have illustrated an everted endophallus to demonstrate the location of the spines in a median field and an apical field. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on a lake shore near the white-water system of the Río Napo drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Ecuador, Orellana, Limoncocha, 0.4088°S, 76.6176°W, 233m, 11 June 1977 (W.E Steiner)(NMNH: ADP132500, female paratype, ADP109192, ADP132468, male paratypes).
http://zoobank.org/5E51D7E3-F8BB-4005-98F4-3688921D1674
Figs 44, 69, 78
Brazil, Pará, Belém, 5m, 1.46°S, 48.42°W, 5-8 October 1978 (G.E Ball, K.E. Ball)(NMNH: ADP132460, male).
The specific epithet, kathleenae, is an eponym, feminine singular, genitive case, based on the given name of Kathleen E. Ball, who along with her husband, George E. Ball, collected the holotype.
Kathleen’s pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Figs 44, 69). Habitus: (Fig. 44). Size: [See also Table 16] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.428 mm, SBL = 2.167 mm, TW (total width) 1.241 mm, LP = 0.484 mm, WP = 0.569 mm, LE = 1.341 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 44): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 44) slightly broad, narrower than head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.135), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.414), longer than wide (WP/LP: 1.176); surface markedly cordiform, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; base markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose, median line feebly defined, apical transverse impression punctate, punctures infuscated; smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.520) and pronotum (WP/TW: 0.459), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as continuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures; punctures infuscated; elytron substantially transparent. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 69, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase moderately long about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening moderately large, oriented parallel to shaft at apical third. Shaft moderately broad, abruptly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly acute apex, in lateral aspect, a moderately broad rounded apex. Parameres: left very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere about two-thirds the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 2 preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at two nearby locations in open grassy swamps along the shore of the lower Río Amazonas. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Pará, Belém, 5m, 1.46°S, 48.42°W, 5–8 October 1978 (G.E Ball, K.E. Ball)(NMNH: ADP132529, male paratype).
http://zoobank.org/9F65FBFB-63E9-484A-A195-3F4A441D8F9C
Figs 45, 78
Argentina, Entre Ríos, Concordia, Río Uruguay, 31.368°S, 57.993°W, 9m, (M.A. Cazier)(AMNH: ADP132496, female).
The specific epithet, macrops, is a Latin adjective descriptive of the eyes of adults of this species, which are bigger than those of congeners.
Argentina pattern-wing beetles.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
Habitus (Fig. 45). Size: [See also Table 17] Medium-size to large-size for the genus; ABL = 3.141 mm, SBL = 3.054 mm, TW (total width) 1.648 mm, LP = 0.621 mm, WP = 0.779 mm, LE = 1.942 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 45): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 45) moderately broad, slightly narrower than head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.119), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.267), wider than longer (W/L: 1.254); markedly cordiform and convex, apical margin straight, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly define as an infuscated line, transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra markedly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.529) and pronotum (WP/TW: 0.472), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as short rows of discontinuous, coarse and spaced punctures. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Male unknown. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on the Río Uruguay drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
The single known specimen is damaged, i.e., missing some appendages; however, there is the entire body with enough physical attributes and enough antennomeres to determine it represents a distinct species.
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 45 Asklepia macrops Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132496, Concordia, Río Uruguay, Argentina 46 Asklepia marchantaria Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. Adis #000727, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil 47 Asklepia marituba Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP132494, Ananindeua, Marituba, Brazil 48 Asklepia pakitza Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132466, Patkitza, Perú. Scale line = 1 mm.
http://zoobank.org/012D955A-C67A-4280-B602-38678E1EFA35
Figs 46, 70, 78
Brazil, Amazonas, Rio Solimões, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, 3.2488°S, 59.9556°W, 7m, 20 October 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 000727, female).
The specific epithet, marchantaria, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the island on which these beetles are found.
Marchantaria pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 46, 70). Habitus: (Fig. 46). Size: [See also Table 18] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.80–3.41 mm, SBL = 2.599–2.828 mm, TW (total width) 1.324–1.582 mm, LP = 0.542–0.619 mm, WP = 0.670–0717 mm, LE = 1.613–1.809 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 46): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 46) slightly broad, narrower than head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.109), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.382), wider than long (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.185); markedly cordiform and convex, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly prominent and setose; median line feebly defined, transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderately convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.529) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.476), longer than wide. Elytral interneur effaced from greater part of the elytron surface, only evident as short discontinuous rows of scattered, coarse punctures unevenly spaced in the medial quadrants and along interneur 1. Hind wings fully developed.
Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 70, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening moderately large, oriented slightly oblique to shaft. Shaft broad, moderately curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except moderate-length ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward narrowly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a broadly rounded apex. Parameres missing. Endophallus with 2 preapical spines. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on a white-water lake shore within the Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Brazil, Amazonas, Rio Solimões, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, 3.2488°S, 59.9556°W, 7m, 1 October 1981 (J. Adis)(NMNH: ADIS # 000235, female paratype, ADIS # 000654, male paratype), 20 October 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 001459, ADIS # 001429, ADIS # 001897, female paratypes; 4 November 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 000864, ADIS # 001041, female paratypes). Non-paratypes and damaged: Brazil, Amazonas, Rio Solimões, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, 3.2488°S, 59.9556°W, 7m, ADIS # 000780, ADIS # 001103, males, ADIS # 001282, ADIS # 001034, females, 14 August 1981 (NMNH: ADIS # 001663, female).
http://zoobank.org/7DFCFA8B-D046-473E-BB61-E68FF399A356
Figs 47, 78
Brazil, Pará, Marituba, Ananindeua, 1.3712 °S, 48.3689°W, 10m, (F.M. Oliveira, P. Wygodzinsky)(AMNH: ADP132494, female).
The specific epithet, marituba, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the place where these beetles are found.
Marituba pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Habitus, Fig. 47). Size: [See also Table 19] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.924 mm, SBL = 2.732 mm, TW (total width) = 0.820 mm, LP = 0.605 mm, WP = 0.768 mm, LE = 1.694 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 47): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 47) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes, (WH/WP: 1.069), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.398), slightly wider than long (WP/LP: 1.268); markedly cordiform and explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted with medial lobe at base; anterior angles moderately produced, hind angle slightly produced, a right angle, and setose; median line markedly defined, basal and apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.521) and pronotum (WP/TW: 0.488), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as rows of continuous punctures; punctures homogeneous. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Male unknown. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight; they are attracted to lights. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on a white-water system on the lower Río Amazonas. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
http://zoobank.org/3537EF7A-F9CD-4395-A43B-57C286DE2EB8
Figs 48, 71, 78
Perú, Madre de Dios, BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Rio Manu, 11.9350°S, 71.3032°W, 329m, 18 & 21 February 1990 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.)(MUSM, ADP132466, male).
The specific epithet, pakitza, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the area in which these beetles are found. These beetles were collected under the auspices of the BIOLAT Program (see above under Asklepia biolat sp. n.).
Pakitza pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 48, 71). Habitus: (Fig. 48). Size: [See also Table 20] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 3.080–2.873 mm, SBL = 2.635–2.683 mm, TW (total width) 1.399–1.430 mm, LP = 0.564–0.572 mm, WP = 0.748–0.772 mm, LE = 1.701–1.743 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 48): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 48) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.009), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.539), wider than long (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.338); markedly cordiform and feebly explanate, lateral margin beaded with seta at anterior third; base markedly constricted with medial lobe at base; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle markedly produced and setose; median line markedly define, apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.542) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.538), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs effaced from greater part of the elytron surface, only evident as scattered punctures in the medial quadrants, as well as along interneur 1; elytron substantially transparent. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 71, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase very short about a fifth the length of shaft, basal opening small, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft swollen at middle, slightly sinuate ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for moderate-length ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Parameres: left large and broad, right small and lobed; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere, about two-thirds the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with one preapical spine. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on the shore of an isolated black-water of the Río Manu a part of the upper Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Perú, Madre de Dios, BIOLAT Biological Station, Pakitza, Rio Manu, 11.9350°S, 71.3032°W, 329m, 18 & 21 February 1990 (T.L. Erwin, E. Pfuno S., F. Pfuno S.) (NMNH, ADP132575, female paratype).
See Erwin (1990) and Venable & Erwin (1997) for detailed trail maps of the BIOLAT Biodiversity Station. Adults of this species have a slightly explanate pronotal margin; however, they have the male endophallus of the pulchripennis group, thus the placement we suggest here. We have a specimen, in poor condition, that represents an undescribed species from Posto Jacaré, Brazil that also has a slightly explanate pronotal margin; however, it has the male endophallus of the hilaris group. With additional collecting and more specimens in the future, there may be an additional species group that we cannot, at present, define.
http://zoobank.org/717F296B-E122-4CF2-8DBB-F43574AB5E3D
Figs 49, 72, 78
Paraguay, Central, San Lorenzo, Rio Paraguay, 25.385°S, 57.621°W, 52m, 23–24 November 1986 (J. Kochalka)(CMNH: ADP130038, male).
The specific epithet, paraguayensis, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the country in which these beetles are found.
Paraguayan pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 49, 72). Habitus: (Fig. 49). Size: [See also Table 21] Medium-size to large for the genus; ABL = 3.002–3.372 mm, SBL = 2.478–2.769 mm, TW (total width) 1.397–1.598 mm, LP = 0.556–0.751 mm, WP = 0.703–0.861 mm, LE = 1.623–2.024 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 49): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 49) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.072), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.397), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.693); markedly cordiform and rounded, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line moderately defined, apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderate convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.526) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.491). Elytral interneurs effaced from most of the elytron surface, only evident as short discontinuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 72, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase moderate, about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening large, oriented oblique to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather narrowly acute apex, in lateral aspect, a slightly rounded apex. Left paramere (missing) (lp), probably very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere probably lobate and much longer than right paramere (rp). Internal sac with one median spine, one long distal spine. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and capable of flight; they are attracted to lights. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location along the white-water river of the middle Río Paraguay drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Paraguay, Central, San Lorenzo, Rio Paraguay, 25.385°S, 57.621°W, 52m, 23–24 November 1986 (J. Kochalka) (CMNH: ADP132769, ADP132767, male paratypes; ADP132765, female paratype).
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 49 Asklepia paraguayensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP130038, San Lorenzo, Río Paraguay, Paraguay 50 Asklepia pulchripennis (Bates, 1871), comb. n., ADP132531, Santarém, Río Tapajos, Brazil 51 Asklepia samiriaensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP051663, Boca del Río Samiria, Perú 52 Asklepia stalametlitos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP132535, Guayamerín, Río Mamoré, Bolivia. Scale line = 1 mm.
Fig. 50, 78
Brazil, Pará, Santarém, Rio Tapajos, 2.4079°S, 54.7969°W, 30m, (H.W.Bates) (MNHP: ADP132531, female). Specimen labeled “Holotype” by George E. Ball in 1972.
The specific epithet, pulchripennis, is a noun in apposition that adequately describes this species with pretty (pulchri-) patterned elytra (-pennis) contrasted with shiny aurantiacus head and pronotum.
Beautiful pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Habitus, Fig. 50). Size: [See also Table 22] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 3.019 mm, SBL = 2.718 mm, TW (total width) 1.366 mm, LP = 0.584 mm, WP = 0.700 mm, LE = 1.732 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 50): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 50) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.0987), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.454), about as longer than wide (WP/LP: 1.198); markedly cordiform and convex, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly defined, basal and apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra slightly convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.563) and pronotum (WP/TW: 0.512), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs effaced from the greater part of the elytron surface, only evident as pale coarse punctures of the apical proximal quadrant and scattered punctures on medial quadrants, as well as along entire interneurs 1 and 2. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Unknown. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on a clear-water system of the middle Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
http://zoobank.org/3B4E42CE-FDE3-43D2-9706-00DF613D2FF2
Figs 51, 78
Perú, Loreto, Boca del Río Samiria, 1 km SW Vigilante post No. 1, 4.5005°S, 74.0659°W, 99m, 16 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M.G. Pogue)(MUSM: ADP051663, male).
The specific epithet, samiriaensis, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the river near which these beetles were found.
Samiria pattern-wing beetles.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Habitus, Fig. 51). Size: [See also Table 23] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 2.853 mm, SBL = 2.436 mm, TW (total width) 1.274 mm, LP = 0.537 mm, WP = 0.613 mm, LE =1.503 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 51): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 51) slightly broad, slightly narrower than head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.188), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.357), about as wide as long (W/L: 1.141); markedly cordiform and rounded, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angles feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose, median line feebly defined, basal margin fuscous; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderately convex; twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.571) and pronotum (WP/TW: 0.481), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs effaced from greater part of the elytron surface, only evident as short discontinuous rows of spaced punctures at apical and basal sutural area, punctures fuscous; elytron substantially transparent. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Not investigated due to the fragile nature of the holotype. Female genitalia. Unknown.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on a black-water system of the upper Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
http://zoobank.org/2A7E97C1-458D-42D3-9D17-C5B41DD22579
Fig. 52, 78
Bolivia, Beni, Guayamer, Rio Mamoré, 10.8033°S, 65.3476°W, 118m, 24 August 1964 (J.K. Bouseman, L. Lussenhop)(AMNH: ADP132535, female).
The specific epithet, stalametlitos, is derived from the Greek, σταλα (stalas) = drop, μηλλιτοσ (melitos) = of honey, drop of honey, and used as a noun in apposition in reference to the golden color of the elytra of these beetles.
Honey-drop pattern-wing beetles.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Habitus, Fig. 52). Size: [See also Table 24] Medium-size for the genus; ABL = 3.043 mm, SBL = 2.815 mm, TW (total width) 1.467 mm, LP = 0.597 mm, WP = 0.751 mm, LE = 1.788 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 52): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 52) moderately broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP: 1.089), longer than head (LP/LH: 1.388), wider than longer (W/L: 1.024); markedly cordiform and convex, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; devoid of median line and transverse impression; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderately convex; twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW: 0.557) and pronotum (WP/TW: 0.512), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs effaced from the greater part of the elytron surface, only evident as pale spots on apical proximal quadrant and scattered punctures on medial quadrants. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia. Male unknown. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on a white-water system of the upper Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
None.
Figs 53, 78
Guyana (not seen by us, not listed by
The specific epithet, strandi, is an eponym, noun in apposition, genitive case, based on the family name of Professor Dr. Embrik Strand, Norwegian Arachnologist, who spent his later years as a Professor in Germany.
Strand’s pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
“Asklepia Strandi n. sp. (Fig. 113).
Hellgelbbraun, Kopf dunkelbraun. Spitze des vierten Fühlerglie-
Des, fünftes und sechstes Glied vollständig dunkelbraun, siebentes
bis elftes Glied gelblichweiss. Flügeldecken zum grössten Teil dun-
kelgelbbraun, ein grosser Skutellarfleck. 2 Scheibenflecke, der Spit-
zenrand in breitem Umfange und der Seitenrand bis fast zur Schulter
hinauf schmal blassgelb. Der vordere Teil der Epipleuren, die Hin-
terbrust und die Rückenringe des Hinterleibes sind dunkelbraun.
Kopf rundlich, kurz, stark gewölbt, mit sehr grossen, stark ge-
wölbten, stark vorstehenden Augen, dieselben sind ungewöhnlich
grob fazettiert. Schläfen sehr kurz, leicht verengt. Kopfschild voll-
kommen glatt und unpunktiert. Hals sehr kurz und sehr dick. Hals-
schild stark herzförmig, etwa 1/6 breiter als lang, kaum merklich
schmäler als der Kopf, stark gewölbt: Vorderrand gerade, Vorder-
winkel breit abgerundet. Seiten vor der Mitte stark gerundet erwei-
tert, sodann stark verengt, kurz vor der Basis am stärksten einge-
schnürt; Basalwinkel spitz, etwas vorspringend; Basalrand gerade.
Seiten undeutlich gerandet, Rand im Vorderdrittel vollkommen ver-
loschen. Mittellängslinie schwach eingedrückt. Ganze Oberseite
vollkommen glatt, unpunktiert. Am Seitenrand kurz vor der Mitte
eine lange Borste. Flügeldecken kurzviereckig, stark gewölbt, nach
hinten stark verbreitert, etwa ein Viertel länger als der Vorderkör-
per, an der breitesten Stelle (im zweiten Drittel) kaum schmäler
als lang; Schultern schräg abfallend. Schulterwinkel abgerundet, an
der Spitze gerade abgestutzt, Spitzenrand gerade, Spitzenaussen-
winkel breit abgerundet. Epipleuren der Flügeldecken an der Schul-
ter sehr breit, dann aber, in etwa 1/3 der Länge, verschmälern sie
sich plötzlich sehr stark, behalten höchstens noch 1/5 der vorderen
Breite, um dann allmählich spitz auszulaufen. Punktstreifen nicht
erkennbar, wohl aber sind schwach gewölbte Zwischenräume er-
kennbar, diese sind g1att und unpunktiert, jedoch im Grunde äusserst
fein netzmaschig gerunzelt; auf dem 3., 5. und 7. stehen je 3-4 lange
aufrechte Borstecn. Länge 3 mm.
Ein Stück. bezettelt «Guyana », in meiner Sammlung.
Dem Jubilar, Professor Dr. Embrik Strand gewidmet.”
From Liebke’s drawing, enhanced here (Fig. 53), we can classify this species in the pulchripennis species group because the pronotum is not laterally explanate, an attribute that is always associated with an aedeagal endophallus having only two spines. We have seen no specimens from Guyana, nor any specimens matching this illustration from anywhere. The distinguishing attribute is the pale elytral margin extended from the apex into quadrant A (Fig. 53). A neotype will be needed upon discovery of more specimens from Guyana that match Liebke’s description and illustration.
Digital Photo-illustrations, habitus, dorsal aspect of holotypes. 53 Asklepia strandi Liebke, 1938, Guyana, ABL = 3.00 mm (from Liebke, 1938:114). Liebke’s illustration of Asklepia strandi Liebke. The single specimen Liebke described was likely lost during World War II. We have seen no specimens from Guyana, nor any specimens matching this illustration from anywhere 54 Asklepia surinamensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP130040, l’Hermitage, Surinam River, Surinam 55 Asklepia vigilante Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP051642, Boca del Río Samiria, Perú. Scale line = 1 mm.
Image of elytron with diagram of quadrants used in the descriptions.
http://zoobank.org/EEC60AF5-9DBC-4304-AE84-901AFEF674FD
Figs 54, 73, 78
Surinam, Paramaribo, l’Hermitage, Surinam River, 5.8182°N, 55.1639°W, 2m, 14 July 1969 (N. Nieser)(CMNH: ADP130040, male).
The specific epithet, surinamensis, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the country in which these beetles are found.
Surinam pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 54, 73). Habitus: Fig. 54). Size: [See also Table 25] Medium-size to large for the genus; ABL = 3.002–3.372 mm, SBL = 2.841–2.992 mm, TW (total width) 1.420–1.584 mm, LP = 0.575–0.626 mm, WP = 0.795–0.836 mm, LE = 1.709–1.803 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 54): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 54) slightly broad, as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.101), length about the same (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.093), wider than long (W/L, mean both sexes: 1.367); markedly cordiform and rounded, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly defined, apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderate convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.542) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.4923). Elytral interneurs evident as continuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures, punctures infuscated, interneurs continuous along length of entire elytron. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 73, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase moderate in length, about a fifth the length of shaft, basal opening moderate, oriented oblique to shaft. Shaft broad, slightly curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward broadly rounded apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded blunt apex. Left paramere very large and broad, right paramere moderately large and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much, longer than right paramere about two-thirds the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with one small median spine, and one very large distal spine. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and capable of flight; they are attracted to lights. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on the white-water system of the middle Surinam River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Surinam, Paramaribo, l’Hermitage, Surinam River, 5.8182°N, 55.1639°W, 2m, 10 July 1969 (N. Nieser)(CMNH: ADP130042, ADP132761, female paratypes; ADP132763, ADP132759, ADP132757, ADP133569 male paratypes).
http://zoobank.org/47519645-5E47-4EA7-A8E2-A3B30C7E251B
Figs 55, 74, 78
Perú, Loreto, Boca del Río Samiria, 1 km SW Vigilante post No. 1, 4.5005°S, 74.0659°W, 99m, 16 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M.G. Pogue)(MUSM: ADP051642, female).
The specific epithet, vigilante, is a singular Latinized feminine noun in apposition, based on the name of the place near which these beetles are found.
Vigilante pattern-wing beetle.
With the attributes of the genus Asklepia as described by
(Fig. 55, 74). Habitus: (Fig. 55). Size: [See also Table 26] Medium-size to large for the genus; ABL = 3.002–3.372 mm, SBL = 2.589–3.259 mm, TW (total width) 1.397–1.598 mm, LP = 0.556–0.751 mm, WP = 0.703–0.861 mm, LE = 1.623–2.024 mm. Color: See diagnosis above. Luster: See diagnosis above. Head (Fig. 55): as in description for genus above. Prothorax. Pronotum (Fig. 55) slightly broad, about as wide as head across eyes (WH/WP, mean both sexes: 1.051), longer than head (LP/LH, mean both sexes: 1.436), about as wide as long (WP/LP, mean both sexes: 1.209); markedly cordiform and rounded, lateral margin effaced with seta at anterior third on slightly raised area; apex markedly constricted; anterior angle feebly produced, hind angle slightly produced and setose; median line feebly defined, apical transverse impressions punctate, punctures infuscated; surface smooth throughout. Pterothorax. Normal for genus, see description for genus above. Elytra moderate convex; at apical third twice as wide as head across eyes (WH/TW, mean both sexes: 0.534) and pronotum (WP/TW, mean both sexes: 0.508), longer than wide. Elytral interneurs evident as short discontinuous rows of widely spaced coarse punctures, interneurs effaced in the medial quadrants. Hind wings fully developed. Legs. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Abdominal sterna. Overall, normal for genus, see description for genus above. Male genitalia (Fig. 74, see Fig. 61 for attribute labels). Median lobe with phallobase short about a fourth the length of shaft, basal opening large, oriented parallel to shaft. Shaft broad, moderately curved ventrally, dorsally sclerotized except for short ostium; in ventral aspect tapered toward rather broadly acute apex, in lateral aspect, a rounded apex. Left paramere very large and broad, right small and triangular; apex of left paramere lobate much longer than right paramere, about half the length of shaft (measured in left lateral aspect). Endophallus with 2 preapical spines, distal one very large. Female genitalia. Not investigated, presumably similar to that of Asklepia demiti sp. n.
These beetles are macropterous and probably capable of flight. They are moderately swift and agile runners.
(Fig. 78). This species has been found at only one location on the black-water system of the upper Amazon River drainage system. But that does not at all indicate its real distribution: as has been pointed out above, very small beetles are inadequately sampled, especially in the Neotropics.
See
Perú, Loreto, 1 km SW Boca del Rio Samiria, Vigilante post No. 1, 4.5005°S, 74.0659°W, 99m, 5 May 1990 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP132520, female paratype), 14 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin)(NMNH: ADP067302, female paratype, ADP067301, male paratype), 16 August 1991 (T.L. Erwin, M.G. Pogue) (NMNH: ADP051665, male paratype).
Illustrations, male aedeagus, dorsal, ventral, left lateral aspects. 57 Asklepia geminata (Bates, 1871) ADP109186, Río Samiria, Boca Caño Inglés Camp, Perú 58 Asklepia campbellorum Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP109196, 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil 59 Asklepia demiti Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132585, Rio Demiti, Brazil 60 Asklepia grammechrysea Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP052565, Río Sucusari, Perú 61 Asklepia laetitia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP109190, Leticia, Colombia. Legend: a apical area; bl basal lobe; bo basal orifice; lp left paramere; ml median lobe; om ostial membrane; oo ostial opening; rp right paramere; sh shaft; pb phallobase; ps phallobase shaft; ms medial spine; ds distal spine 62 Asklepia lebioides (Bates, 1871), comb. n., ADP109208, Rio Demiti, Brazil. Scale line = 0.25 mm.
Illustrations, male aedeagus, dorsal, ventral, left lateral aspects. 63 Asklepia matomena Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP132527, 20 km SW Manaus, Brazil 64 Asklepia adisi Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. Adis # 001335, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil 65 Asklepia biolat Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132480, Pakitza, Perú 66 Asklepia bracheia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP067304, Boca del Río Samiria Perú 67 Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132468, Limoncocha, Ecuador. Endophallus not everted 68 Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132468, Limoncocha, Ecuador. Endophallus everted. Scale line = 0.25 mm.
69 Asklepia kathleenae Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132529, Belém, Brazil 70 Asklepia marchantaria Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. Adis # 001103, Ilha de Marchantaria, Lago Camaleão, Brazil 71 Asklepia pakitza Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP132466, Pakitza, Perú 72 Asklepia paraguayensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP132769, San Lorenzo Paraguay 73 Asklepia surinamensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n. ADP132763, l’Hermitage, Surinam 74 Asklepia vigilante Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n. ADP067301, Boca del Río Samiria, Perú.
Asklepia demiti sp. n. Digital Photo-illustration, female genitalia based on specimen ADP132483 from Rio Demiti, Brazil. A Dorsal aspect. Legend, bc, bursa copulatrix; co common oviduct; sg spermathecal gland; sgd spermathecal gland duct; sp spermatheca. dorsal aspect; vc villous canal; lt laterotergite; gc1 gonocoxite 1; gc2 gonocoxite 2. B Gonocoxite 2, dorsal aspect: Legend, b base of gonocoxite 2; bl blade of gonocoxite 2; des dorsal ensiform seta. C. Defense gland (gldr); cc accessory gland; ed efferent duct.
76 Distribution map for known localities of Asklepia geminata (Bates) 77 Distribution map for known localities of Asklepia species of the hilaris group.
Distribution map for known localities of Asklepia species of the pulchripennis group.
Distribution map for known localities of Peruphorticus gulliveri sp. n.
The lachnophorine assemblage is species rich as evidenced by vast collections in museums. Adults are diverse and divergent in physical attributes ranging from the agonine-like Anchonoderus and Homethes to the rather elegant and bizarre ant-like Ega, Selina, and Stenocheila. In color attributes, the adults range from some charcoal black Anchonoderus to those of the incredibly beautiful, multi-hued Quammenis spectabilis (Fig. 1). In spite of this strikingly broad, readily perceived range of attributes that are pleasing to the eye, and challenging to the mind of evolutionary biologists, revisions, or monographs for the Tribe, or its component genera, surprisingly are lacking. The literature contains many single species descriptions in several of the genera, mostly from the 19th century – the golden age of exploration and descriptive entomology.
That information, noted above, was the platform available to us for beginning construction of a robust understanding of the Lachnophorini to at least a level represented by many Northern Hemisphere tribes of Carabidae. So that others may join in this potentially exciting pursuit, we have offered an illustrated preliminary taxonomic synopsis of the known lachnophorine genera, with keys, and a species-level treatment of the taxonomically complex Asklepia Liebke.
During this study, it became readily apparent that the tropics, in both New and Old world, are the center of origin and radiation of taxa. A very few species occur in the southern parts of the United States, likewise south only to mid Argentina. Relationships between New and Old world taxa need to be understood and that will only come with a well-founded understanding of the phylogeny. With regard to the species of Asklepia, it is quite obvious that the three species groups (defined so well by attributes of the endophallus and pronotal margins) have co-evolved in an Amazon center, probably tied in some way to Varzea and Igapó waters as habitats for differentiation of species groups; however, we do not have sufficient samples of most species to test this idea. Some species occur south as far as Argentina, but none have made it to Middle America; all are cis-Andean. Additionally, thanks to an observation made by George E. Ball (pers. comm.), it seems that the least derived species groups, geminatus (typical carabid pronotum with lateral explanations, convex elytral intervals, and no spines on the endophallus) and hilaris (typical carabid pronotum with lateral explanations and multiple small spines on the endophallus) are confined to the central Amazon River drainage, while the most derived group pulchripennis (lacking pronotal explanations and having two large spines on the endophallus) is not confined and has member species occurring as far south as Argentina and Uruguay, as well as on extreme tributaries of the Amazon drainage (see Figs 76–78). We ponder whether this is indicative of a flatland continental taxon cycle and suggest that with better collections, this should be tested.
The path forward is branched. For the near future, the branch to be followed by one of us, (LSZ), will lead to an attempt, using morphological and molecular attributes, to reconstruct the phylogeny of the known lachnophorine genera, with the expectation that the inferred system of relationships will provide a firm basis for a stable classification. In turn, this classification will provide a rational basis for exploration of diversity and divergence within each of the lachnophorine genera, the second branch.
In addition to the collections people mentioned under Materials and Methods above, we extend hearty thanks to Charyn Micheli, Karolyn Darrow, and Vichai Malikul (all at the Department of Entomology at the Smithsonian Institution) friendly review of the manuscript, and images and review of the figure captions, and illustrations of the male genitalia, respectively. In addition, we extend a sincere thanks to Diego Mosquera, Station Manager at Tiputini Biodiversity Station in Amazonian Ecuador, for various types of field support during our stay there and where LSZ was able to collect in 97% ethanol adults of nine of the eighteen genera covered in this paper, and larvae of two of them. The NMNH of the Smithsonian Institution and Pensoft Publishers provided funding for publication.
Morphological measurements and ratios for adults of species of Asklepia Liebke, 1938. All values are in millimeters. Apparent body length (ABL) is provided in the descriptions. Means provided for ratios are “harmonic means.”
Asklepia geminata (Bates, 1871)
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.199 | 0.021 | 0.009 | 0.048 | 0.161 | 0.033 | 0.061 | 0.010 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 2.512–2.794 | 2.653 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 1.411–1.440 | 1.426 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 0.513–0.536 | 0.524 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 1.359–1.368 | 1.364 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.514–1.768 | 1.631 | |||||
Asklepia campbellorum Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.282 | 0.174 | 0.041 | 0.060 | 0.190 | 0.073 | 0.079 | 0.087 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 25 | 2.182–3.199 | 2.254 | |||||
| Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 25 | 1.107–1.824 | 1.615 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 25 | 0.458–0.547 | 0.491 | |||||
| Pronotum: width (at widest part)/length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 25 | 1.294–1.498 | 1.372 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 25 | 1.265–1.590 | 1.411 | |||||
Asklepia demiti Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.135 | 0.092 | 0.053 | 0.028 | 0.086 | 0.027 | 0.029 | 0.046 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 2.590–3.131 | 2.953 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.491–1.815 | 1.678 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 0.459–0.525 | 0.491 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.331–1.550 | 1.380 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.185–1.928 | 1.446 | |||||
Asklepia duofos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| N | SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 1 | 2.941 | 1.592 | 0.417 | 0.593 | 1.931 | 0.779 | 0.829 | 0.796 |
| WH/TW | PW/PL | LP/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||||
| 0.489 | 1.397 | 1.423 | 0.521 | 0.939 |
Asklepia grammechrysea Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.128 | 0.260 | 0.071 | 0.103 | 0.126 | 0.115 | 0.012 | 0.163 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 33 | 2.265–3.736 | 3.095 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 33 | 1.382–2.216 | 1.811 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 33 | 0.430–0.491 | 0.481 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 33 | 1.273–2.228 | 1.381 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 33 | 1.273–2.228 | 1.512 | |||||
Asklepia hilaris (Bates, 1871), comb. n.
| N | SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 1 | 2.336 | 1.233 | 0.359 | 0.483 | 1.495 | 0.678 | 0.625 | 0.617 |
| WH/TW | PW/PL | LP/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||||
| 1.099 | 1.294 | 1.346 | 1.013 | 1.085 |
Asklepia laetitia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| N | SBL | MW | ABL | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 1 | 2.494 | 1.463 | 2.990 | 0.372 | 0.489 | 1.633 | 0.684 | 0.706 | 0.731 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/TW | WP/WH | |||||
| 0.468 | 1.444 | 1.316 | 0.483 | 1.032 |
Asklepia lebioides (Bates, 1871), comb. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.108 | 0.088 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.082 | 0.029 | 0.030 | 0.044 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 2.692–3.142 | 2.991 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.504–1.790 | 1.666 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 0.460–0.547 | 0.487 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.686–1.960 | 1.824 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.244–1.430 | 1.349 | |||||
Asklepia matomena Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.343 | 0.256 | 0.213 | 0.036 | 0.070 | 0.149 | 0.062 | 0.090 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 2.189–2.551 | 2.370 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 1.150–1.452 | 1.301 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 0.493–0.546 | 0.518 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 1.338–1.351 | 1.345 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 1.348–1.425 | 1.385 | |||||
(Note: There are no measures for Asklepia strandi Liebke except ABL).
Asklepia adisi Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.055 | 0.045 | 0.016 | 0.028 | 0.042 | 0.017 | 0.021 | 0.022 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 2.542–2.688 | 2.632 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 1.341–1.473 | 1.412 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 0.517–0.573 | 0.535 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 1.154–1.314 | 1.226 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 1.221–1.464 | 1.327 | |||||
Asklepia asuncionensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| N | SBL | TW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 1 | 2.477 | 1.27 | 0.378 | 0.533 | 1.566 | 0.671 | 0.648 | 0.635 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||||
| 0.528 | 1.714 | 1.191 | 0.337 | 2.555 |
Asklepia biolat Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard Deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.123 | 0.103 | 0.060 | 0.028 | 0.074 | 0.034 | 0.041 | 0.051 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 24 | 2.787–3.247 | 3.014 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 24 | 1.388–1.816 | 1.633 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 24 | 0.490–0.594 | 0.522 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 24 | 1.141–1.322 | 1.244 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 24 | 1.398–2.162 | 1.603 | |||||
Asklepia bracheia Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.113 | 0.059 | 0.037 | 0.035 | 0.051 | 0.034 | 0.048 | 0.030 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 8 | 1.952–2.345 | 2.150 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 8 | 1.074–1.274 | 1.197 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 8 | 0.502–0.584 | 0.529 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 8 | 1.000–1.304 | 1.205 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 8 | 1.359–2.050 | 1.590 | |||||
Asklepia cuiabaensis Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| SBL | TW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 2.191 | 1.27 | 0.343 | 0.476 | 1.372 | 0.629 | 0.592 | 0.635 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | |||
| 0.495 | 1.726 | 1.334 | 0.361 | 2.744 |
Asklepia ecuadoriana Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.135 | 0.092 | 0.053 | 0.028 | 0.086 | 0.027 | 0.029 | 0.046 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 2.590- 3.131 | 2.953 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.491–1.815 | 1.678 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 0.459–0.525 | 0.491 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.331–1.550 | 1.380 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 17 | 1.185–1.928 | 1.446 | |||||
Asklepia kathleenae Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 2.167 | 1.241 | 0.342 | 0.484 | 1.341 | 0.646 | 0.569 | 0.620 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | LE/WE | ||
| 0.520 | 1.176 | 1.414 | 0.459 | 1.135 | 2.162 |
Asklepia macrops Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| N | SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 1 | 3.054 | 1.648 | 0.490 | 0.621 | 1.942 | 0.871 | 0.779 | 0.824 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||||
| 0.529 | 1.254 | 1.267 | 0.472 | 1.119 |
Asklepia marchantaria Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.077 | 0.109 | 0.032 | 0.027 | 0.067 | 0.028 | 0.018 | 0.055 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 2.599–2.828 | 2.675 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 1.324–1.582 | 1.457 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 0.500–0.578 | 0.529 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 1.108–1.238 | 1.185 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 7 | 1.114–1.523 | 1.382 | |||||
Asklepia marituba Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| SBL | MW | ABL | HL | PL | EL | WH | WP | WE |
| 2.732 | 1.574 | 2.924 | 0.433 | 0.605 | 1.694 | 0.820 | 0.768 | 0.787 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | PL/LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||||
| 0.521 | 1.268 | 1.398 | 0.488 | 1.069 |
Asklepia pakitza Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.033 | 0.022 | 0.057 | 0.006 | 0.030 | 0.007 | 0.017 | 0.011 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 2.635–2.683 | 2.659 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 2 | 1.399–1.430 | 1.414 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 0.540–0.545 | 0.542 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.308–1.370 | 1.338 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.39–1.713 | 1.538 | |||||
Asklepia paraguayensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.135 | 0.105 | 0.019 | 0.027 | 0.094 | 0.049 | 0.048 | 0.053 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 4 | 2.478–2.769 | 2.574 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 4 | 1.264–1.506 | 1.362 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 4 | 0.517–0.544 | 0.527 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 4 | 1.617–1.779 | 1.693 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 4 | 1.365–1.447 | 1.397 | |||||
Asklepia pulchripennis (Bates, 1871), comb. n.
| SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 2.718 | 1.366 | 0.402 | 0.584 | 1.732 | 0.769 | 0.700 | 0.683 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP / LH | WP/TW | WH/WP | |||
| 0.563 | 1.198 | 1.454 | 0.512 | 1.099 |
Asklepia samiriaensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 2.436 | 1.274 | 0.396 | 0.537 | 1.503 | 0.728 | 0.613 | 0.637 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/LP | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||
| 0.571 | 1.141 | 1.357 | 0.962 | 0.481 | 1.188 |
Asklepia stalametlitos Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| SBL | MW | LH | LP | LE | WH | WP | WE |
| 2.815 | 1.467 | 0.430 | 0.597 | 1.788 | 0.818 | 0.751 | 0.733 |
| WH/TW | WP/LP | LP/LH | WP/LP | WP/TW | WH/WP | ||
| 0.557 | 1.258 | 1.388 | 1.024 | 0.512 | 1.089 |
Asklepia surinamensis Zamorano & Erwin, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.156 | 0.138 | 0.036 | 0.029 | 0.098 | 0.040 | 0.046 | 0.069 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 2.541–2.992 | 2.843 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.214–1.584 | 1.459 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 0.518–0.599 | 0.551 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.340–1.385 | 1.369 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.042–1.169 | 1.105 | |||||
Asklepia vigilante Erwin & Zamorano, sp. n.
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.277 | 0.081 | 0.065 | 0.182 | 0.040 | 0.061 | 0.063 | 0.040 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 2.589–3.259 | 2.867 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.397–1.598 | 1.506 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 0.505-0.565 | 0.508 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.146–1.265 | 1.209 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 6 | 1.307–1.552 | 1.436 | |||||
Table with measures and ratios for adults of species of Peruphorticus gulliveri Erwin & Zamorano gen. n., sp. n. All measures are in millimeters. Apparent body length (ABL) is provided in the description. Means provided are “harmonic means.”
| Standard deviation | |||||||
| SBL | MW | LP | LE | LH | WP | WH | WE |
| 0.245 | 0.274 | 0.038 | 0.059 | 0.196 | 0.045 | 0.074 | 0.137 |
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 36 | 5.281–6.146 | 5.803 | |||||
| Total length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 36 | 2.3–3.6 | 2.685 | |||||
| Width of head/Total width | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 36 | 0.366–0.533 | 0.484 | |||||
| Pronotum: Width (at widest part)/Length | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 36 | 1.805–2.377 | 2.085 | |||||
| Length of pronotum / Length of head | |||||||
| Specimens | N | Range | Mean | ||||
| 36 | 1.340–1.757 | 1.496 | |||||