(C) 2012 Kipling Will. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 (CC-BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
Lesticus finisterrae (Carabidae: Pterostichini) sp. n. (type locality: Finisterre Range, Papua New Guinea), is described and characters to differentiate it from other “Trigonotomi” species are given. A key to the genera of pterostichine-like Harpalinae of the island, including all genera of Morionini, Cratocerini, Drimostomatini, Abacetini, Loxandrini and Pterostichini, is provided. The genus Rhytisternus (Pterostichini) is for the first time reported from New Guinea, represented by the likely adventive species Rhytisternus laevis (Macleay). The previously unknown male of Stegazopteryx ivimkaensis Will (Drimostomatini) is described.
New Guinea, Carabidae
Darlington reported 667 species of Carabidea from New Guinea in his treatment of the fauna (1971) and a search of the Zoological Record for new species and new records suggests that the total is now easily greater than 700 species. Given the complexity of island’s geological history (
One area poorly covered by Darlington’s study was the Finisterre Range along the northeastern coast of Papua New Guinea, extending approximately from Madang in the north to Lae in the south. This area was previously recognized as a unique area of endemism (
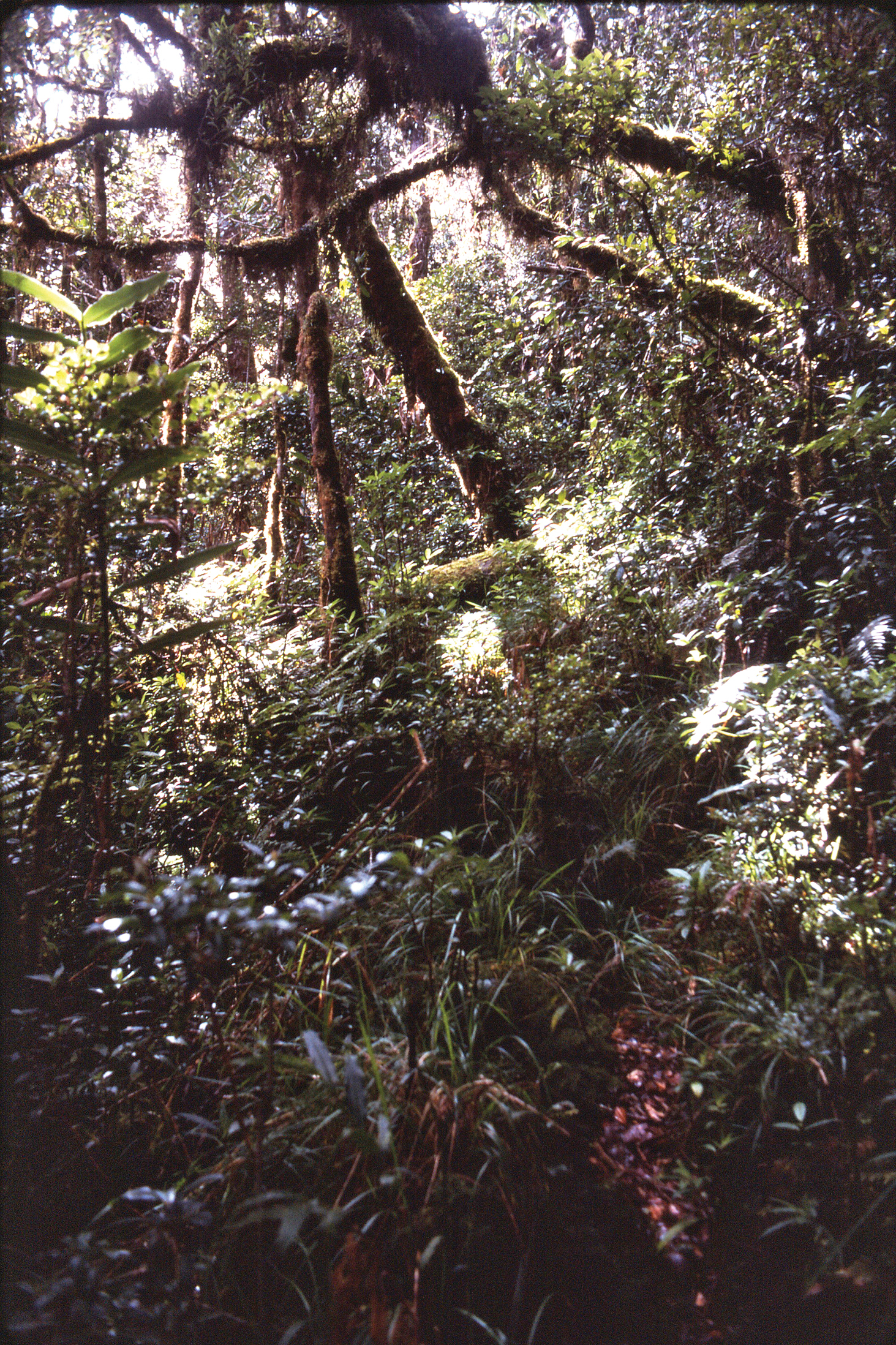
The forest canopy was between 10 and 20 meters tall, dense, with a lush coating of mosses and other epiphytes on tree trunks, branches, logs and stones on the forest floor. A low and fairly dense understory obscured most of the forest floor and made collecting difficult. Consequently, a few pitfall traps were installed in this cool and relatively dark habitat (Fig. 1). After two nights in the ground, the traps were collected and their contents examined. Only a single carabid beetle was found in the catch and the specimen was distinctly different from anything that has been described. Subsequent comparative microscopic study and dissection have confirmed this conclusion.
The genus Lesticus Dejean in New Guinea was treated by
View within upper montane moss forest habitat at 3050m elevation, Finisterre Range, Papua New Guinea. The pitfall trap in which the unique holotype of Lesticus finisterrae sp. n. was collected was located in the shaded area just below the middle of the figure.
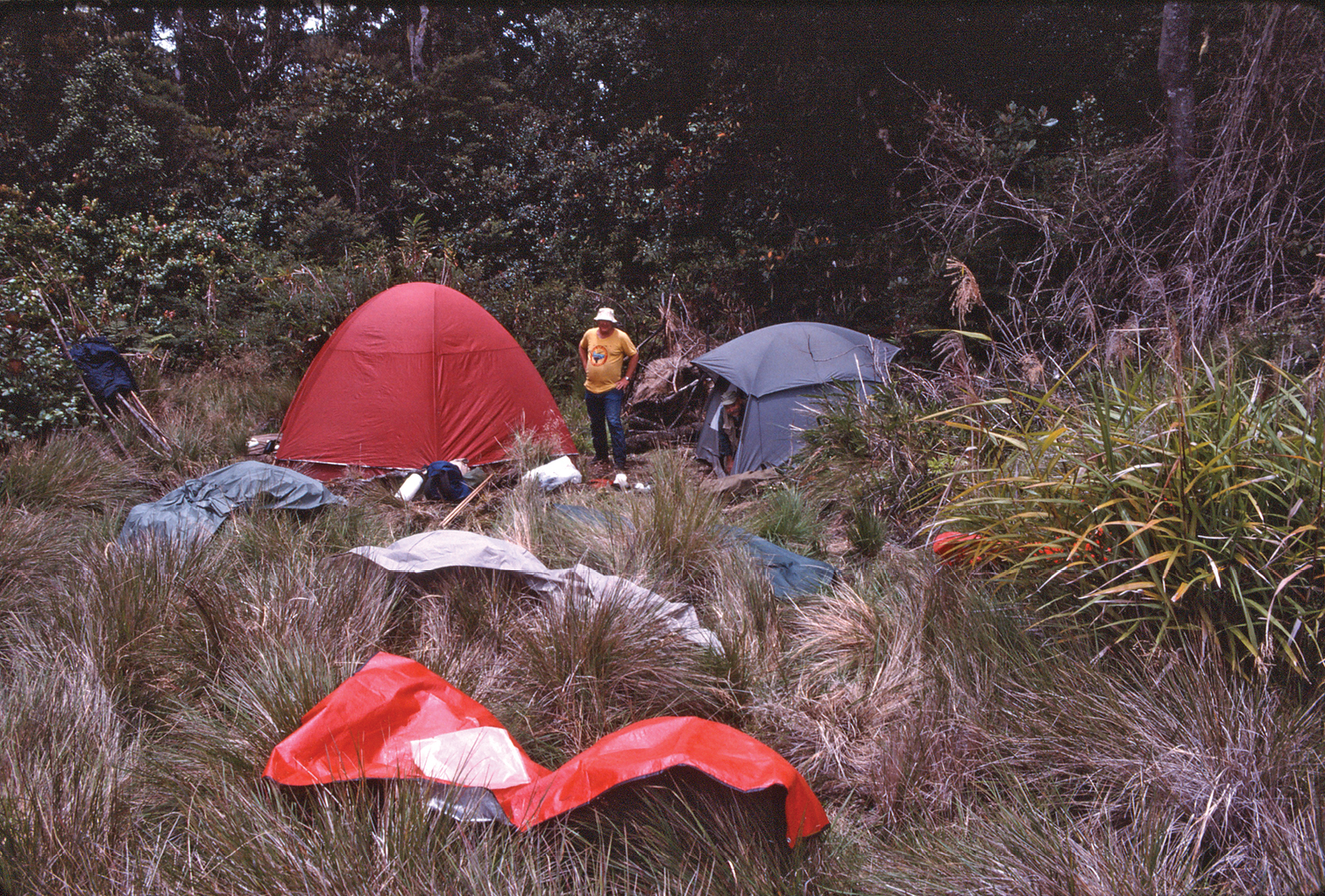
Grassland/upper montane moss forest ecotone at 3050m elevation in the Finisterre Range, Papua New Guinea. The holotype of Lesticus finisterrae sp. n. was collected in a pitfall trap placed approximately 20m inside the forest edge.
Methods and terms follow
Comparative material and specimens studied to develop the key are deposited in the following institutional collections: Australian National Insect Collection (ANIC), Canberra, ACT; California Academy of Science (CASC), San Francisco, CA; Essig Museum of Entomology (EMEC), Berkeley, CA; Institute Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, (IRSNB), Bruxelles; Museum of Comparative Zoology (MCZ), Harvard University, Cambridge, MA; The Natural History Museum, London (NHM); Nationaal Natuurhistorische Museum (NNM), Leiden, Netherlands; Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle (MNHN), Paris; Queensland Museum (QM), Brisbane; Bohart Museum of Entomology (UCDC), Davis, CA; and Zoologische Staatssammlung (ZMS), München.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:52A9C3D7-A304-4D05-83DC-D1E385182B6F
Male. “PAPUA NEW GUINEA, Madang/Morobe Province border, Finisterre Range, Teptep area, 3.5 air km WNW of Kewieng No.4 village, 3050 m, 28 March 1989 stop #89-50// D. H. Kavanaugh, G. E. Ball & N. D. Penny collectors, Cal. Acad. Sci. Specimen//Papua New Guinea Expedition – 1989// California Academy of Sciences Type No. 18684//HOLOTYPE Lesticus finisterrae Will & Kavanaugh [red label]”. Deposited CASC.
Finisterre Range, Papua New Guinea. 5.99778°S, 52280°W.
This species shares with other Lesticus species sharply hooked mandibular apices, relatively broad mentum, extremely wide gula (nearly the width of the mentum) and has the general form of a modified species of the Lesticus chloronotus group. It is distinguished from all other species of Lesticus, including the New Guinea species covered in Darlington’s keys and descriptions (1962, 1971) and
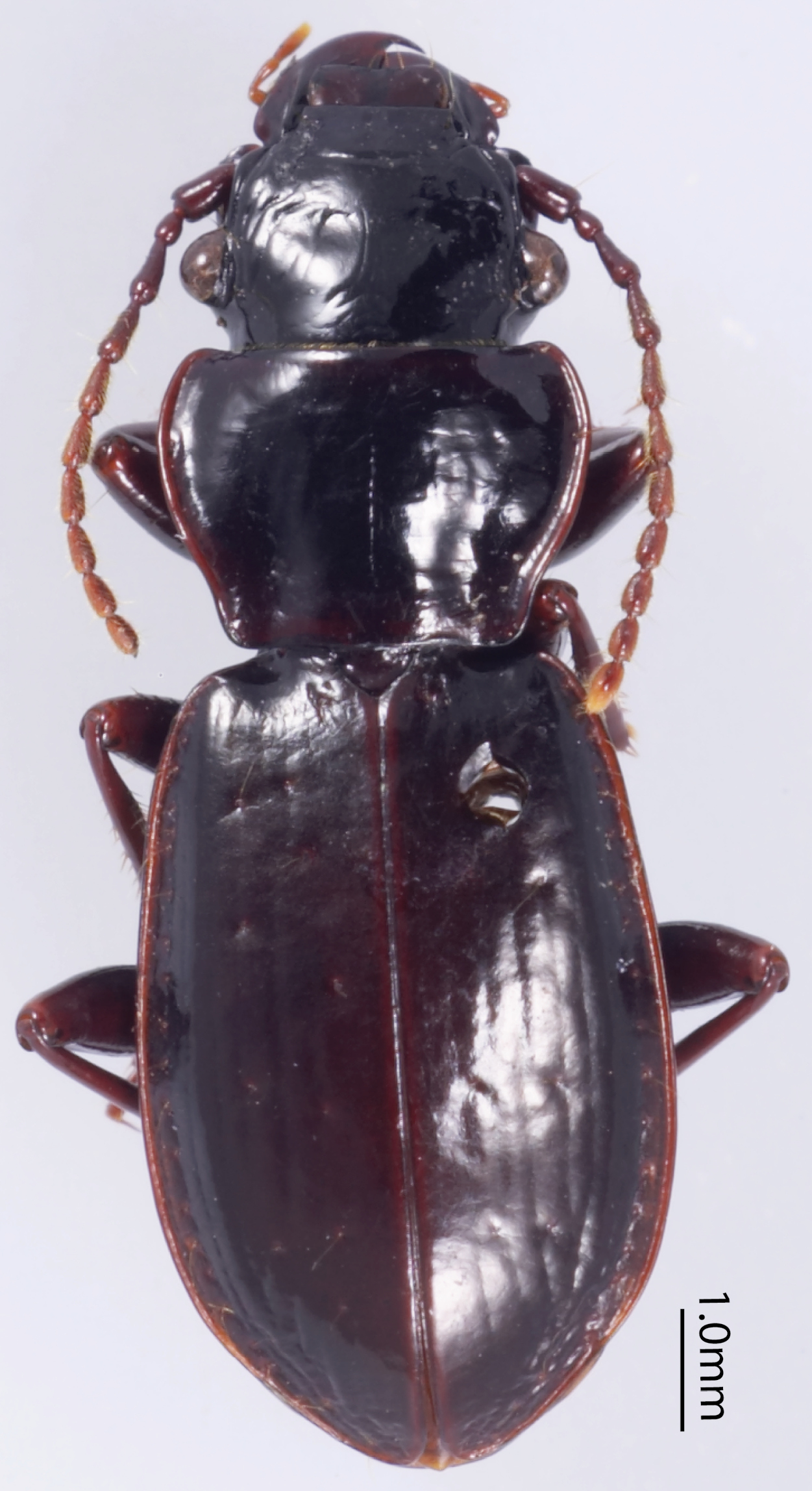
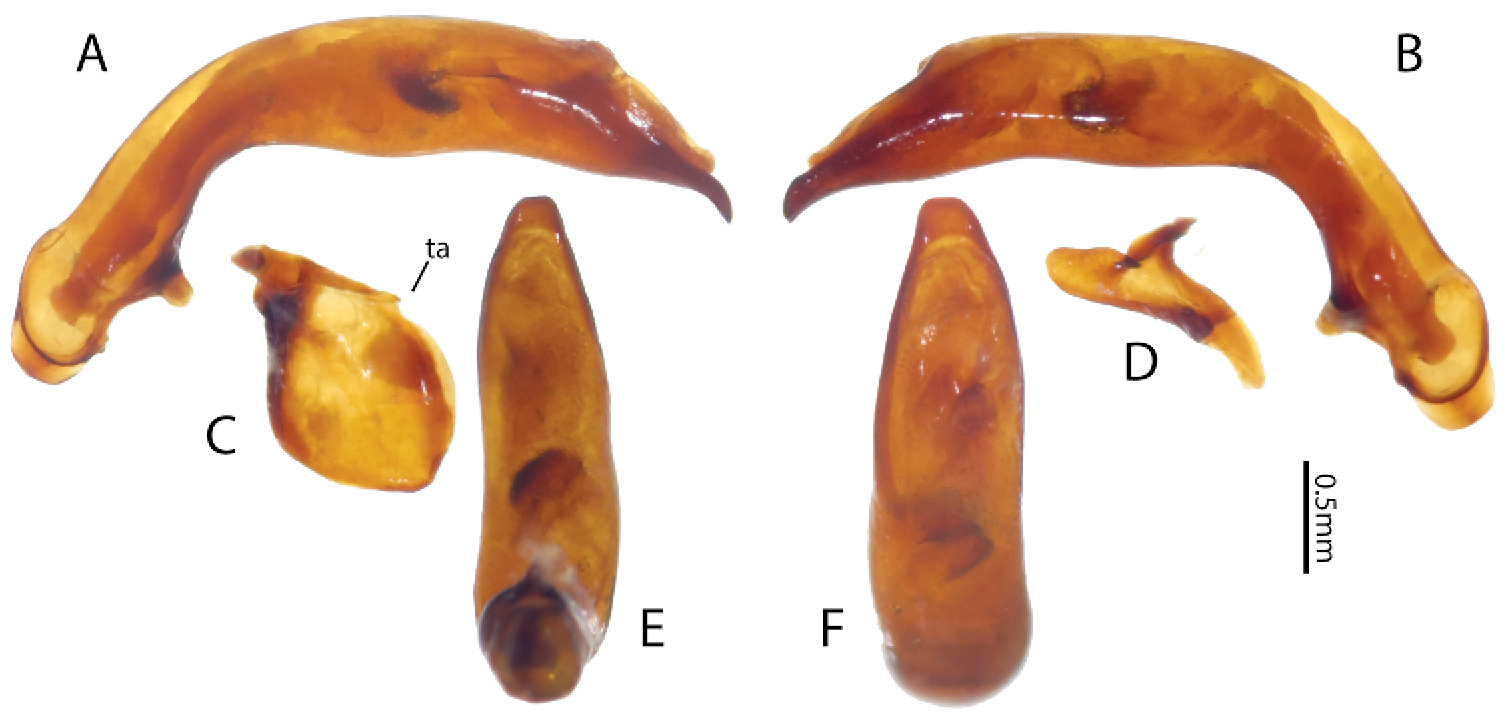
(Fig. 3), Size. Overall length (sbl) 20.0mm, greatest width over elytra 8.5mm. Color. Dorsal and ventral surfaces black to brunneous. Legs, mouthparts, and antennae slightly paler, lateral margins of pronotum and lateral and sutural areas of elytra margins piceous to rufopiceous. Luster. Dorsally and ventrally shiny. Iridescence. Elytra and ventral surface of body without spectral iridescence. Head. Dorsal microsculpture absent, entire surface with micropunctulae, clypeal-ocular sulci impression absent, shallowly rugose above eyes, with broad, shallow paramedial depressions, ocular ratio (greatest width over eyes/width between eyes at level of anterior supraorbital setae) 1.29, eyes moderately large size, very prominently “bulging”. Labrum with anterior margin slightly emarginate, with six setae of which medial four setae equally distributed in medial half, distance from outermost medial seta to lateral seta about twice distance between medial setae. Antenna overall length moderately long, antennomere 11 just reaching beyond pronotal base. Thorax. Pronotum transverse, lateral margin sinuate near base, medial and basal setae touching lateral marginal bead; basal impressions obsolete; anterior angles scarcely produced; microsculpture not visible at 50× magnification; entire surface covered with minute punctulae. Elytral striae extremely shallow, scarcely impressed or absent; base of elytra not margined; humeri prominent but rounded; parascutellar punctures present at base of striae 1; interval 1 with two punctures at apex; interval 3 with three (right) or six (left) punctures; interval 5 with three (right) or four (left) punctures; interval 7 with one puncture near apex; interval 9 with 20 evenly spaced punctures; elytral microsculpture visible at 50× as irregular isodiametric mesh of microlines; entire surface with micropunctulae. Male protaromeres 1–3 expanded with squamose setae ventrally. Tarsomere 5 on all legs ventral setose. Metatrochanter without setae. Metacoxa with single lateral seta. Abdomen. Abdominal ventrites smooth, glabrous except for very shallowly impressed transverse sulcus on last ventrite. Male with two setae on last ventrite. Aedeagus (Fig. 4) with small, dissimilar conchoid parameres; right paramere with large dorsal process (Fig. 4D); left paramere with a minute transverse apophysis (Fig. 4C). Median lobe with apex truncate; ostium dorsal; endophallus with small median sclerite.
Dorsal habitus of Holotype of Lesticus finisterrae.
Male genitalia of holotype of Lesticus finisterrae. Median lobe. A left lateral B right lateral E ventral and F dorsal views. Parameres. C left D right. ta transverse apophysis.
The specific epithet finisterrae refers to the type locality, the Finisterre Range. Additionally, Finisterre is a contraction that derives from the Latin Finis Terrae, meaning “End of the Earth”, an appropriate metaphor for this remote and entomologically little-known region. Although terrae is the genitive form, the contraction is treated as a noun in apposition since the “end of the Earth” is used as the name for the location.
Only a single specimen of Lesticus finisterrae is known. It was collected in an unbaited pitfall trap placed in upper montane moss forest at an elevation of 3050 meters. The area was near the upper limit of forest growth and adjacent to open grassland (Fig. 2). Under the forest canopy, a fairly dense understory of low vegetation was present (Fig. 1).
“Trigonotomi” sensu
Below is a revised key to the genera of “pterostichites” of New Guinea based on the key by
| 1 | Front tibia fossorial, outer apical angle strongly produced; bodyform parallel-sided; antennae moniliform. | Morion Latreille [Morionini] |
| – | Front tibia with outer apical angle not produced; (other characters variable) | 2 |
| 2 | Small, compact; antennae moniliform; elytron with basal pore (if present) at base of 3rd stria | 3 |
| – | Size and form variable; antennae usually not moniliform; elytron with basal pore (if present) near or inside base of 2nd stria | 5 |
| 3 | Elytron without basal pore; anteriolateral prothoracic setae almost on anterior angles | Brachidius Chaudoir [Cratocerini] |
| – | Elytron with basal pore at base of 3rd stria; anteriolateral prothoracic setae about 2/5 prothoracic length behind anterior angles | 4 |
| 4 | Elytra ovoid or elongate-ovoid, apex broadly rounded | Caelostomus Macleay [Drimostomatini] |
| – | Elytra elongate-rectangular, bluntly truncate at the apex | Stegazopteryx [Drimostomatini] |
| 5 | Antennomere 2 attached to 1 more eccentrically than usual; mentum transverse; metacoxal anterior sulcus sinuate; (small, 4.7–6.8mm, in New Guinea hydrophilic species) | Abacetus Dejean [Abacetini] |
| – | Antennomere 2 attached to 1 less eccentrically; (other characters variable, but never in combination as above) | 6 |
| 6 | Four basal antennomeres glabrous; size very large, length (in New Guinea) about 50mm or more | Catadromus Macleay [Pterostichini] |
| – | Three basal antennomeres glabrous; size much smaller | 7 |
| 7 | Abdominal ventrites 4–6 with transversely impressed sulci or margined at base, at least toward sides | 8 |
| – | Abdomen with ventral segments not thus impressed or margined, or only ventrite 6 with a very shallowly impressed sulcus | 11 |
| 8 | Elytron with 10th interval absent or not distinct from margin | Prosopogmus Chaudoir [Pterostichini] |
| – | Elytron with a distinct 10th interval at least posteriorly | 9 |
| 9 | Elytra with 3rd intervals impunctate; proepisterna longitudinally strigate | 10 |
| – | Elytra with 3rd intervals with setigerous punctures; parascutellar striae present (except when other striae obsolete); proepisterna not strigate (but often punctate) | Lesticus (in part) [Pterostichini] |
| 10 | Metepisternum short, flight wing reduced | Rhytiferonia Darlington [Pterostichini] |
| – | Metepisternum elongate, flight wing full (in New Guinea) | Rhytisternus laevis (Macleay) [Pterostichini] |
| 11 | Small size, broad (prothoracic width/length c. 1.55-1.71), compact (superficially similar to Brachidius but with antennae less stout and basal pore of elytron present, at base stria 2) | Cosmodiscus Sloane [Abacetini] |
| – | Size small to large, but never so broad and compact | 12 |
| 12 | Elytra with 3rd interval punctate; parascutellar striae absent or nearly so | 13 |
| – | Elytra with 3rd interval impunctate; parascutellar striae variable | 17 |
| 13 | Antennae subgeniculate, first antennomere moderately longer than 2 and 3 together | Homalonesiota Maindron [Loxandrini] |
| – | Antennae not at all geniculate, first antennomere shorter than 2 and 3 together | 14 |
| 14 | Metepisterna scarcely longer than wide | 15 |
| – | Metepisterna clearly longer than wide | 16 |
| 15 | Elytra without plica. Mentum with prominent epilobes. Mentum tooth prominent, acuminate-entire | Haploferonia Darlington [Loxandrini] |
| – | Elytra with plica. Mentum transverse, epilobes not prominent. Mentum tooth broad and emarginate | Lesticus (in part) [Pterostichini] |
| 16 | Prothorax not cordate | Loxandrus Leconte [Loxandrini] |
| – | Prothorax cordate | Nebrioferonia Straneo [Loxandrini] |
| 17 | Very small (4.0–4.5 mm.); parascutellar stria lacking | Tiferonia Darlington [Abacetini] |
| – | Larger; parascutellar stria present | 18 |
| 18 | Flight wings usually (not always) fully developed; body proportions normal, head not relatively very large | Platycaelus Blanchard [Pterostichini] |
| – | Flight wings atrophied; head very large | Analoma Darlington [Pterostichini] |
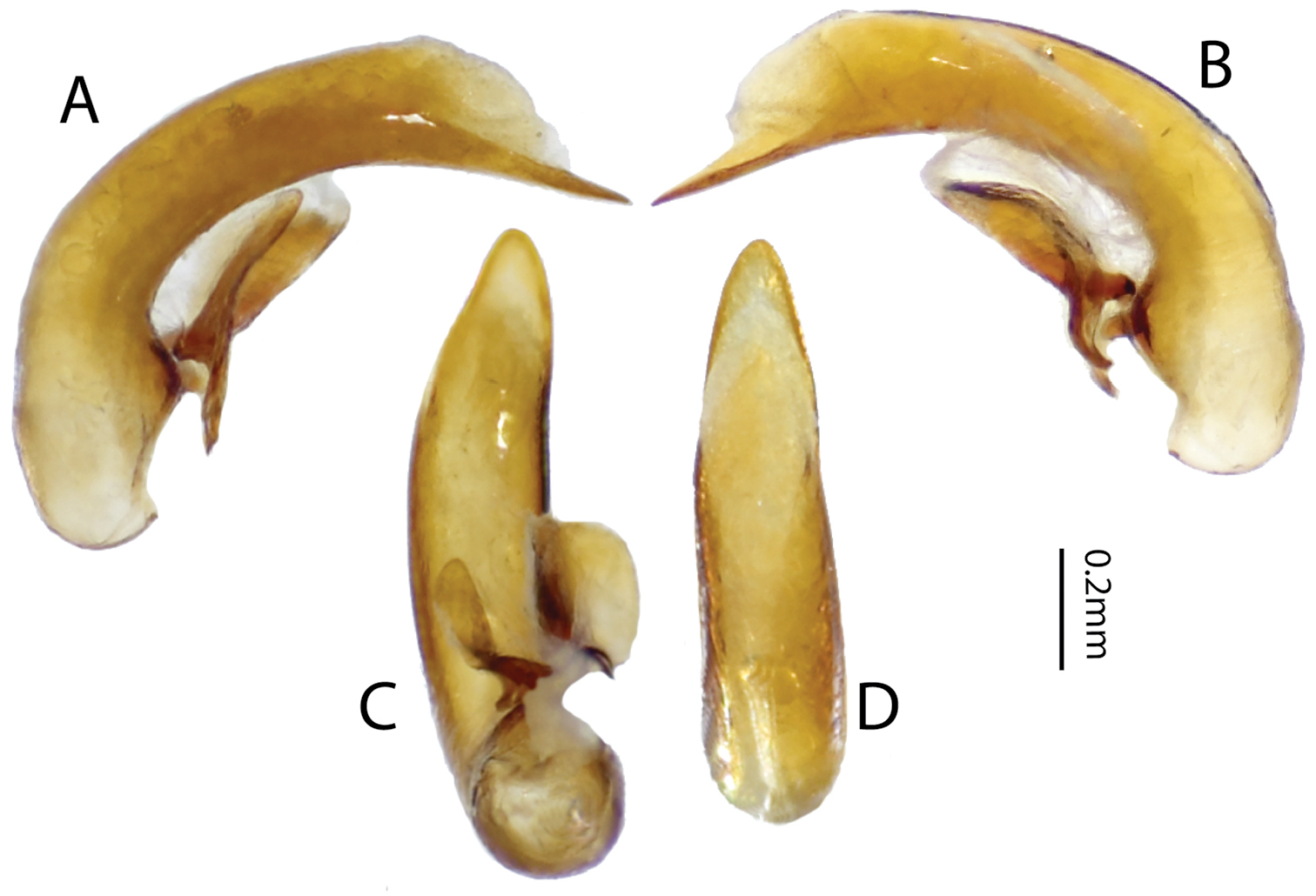
Male genitalia of Stegazopteryx ivimkaensis. Median lobe. A left lateral B right lateral C ventral and D dorsal views.
A male specimen labeled “INDONESIA W-PAPUA 130km SE Kalmana, Omba (=Yamor) river 10–20km from coast, 4°05'49"S, 134°54'09"E, 10–20m, 09.–11.II.2011 leg. A. Skale (008).” Specimen deposited ZSM.
This specimen record extends the range of this species into eastern West-Papua. This specimen, the two female syntype specimens and the further records below, are all from elevations of 120m and below. This species is now known to range across nearly all of New Guinea. The examined male specimen is consistent with the description: of the genus based on females as given by Will (2004), with the following additions. sbl=5.4mm, greatest width of elytra 2.3mm. Secondary sexual characters- male protarsi not expanded but with spatulate setae ventrally on tarsomeres 1-3. Last ventrite with one pair of setae. Aedeagus right side up in repose. Right paramere larger and conchoid, left paramere small, peg-like. Median lobe of adeagus simple, no evident sclerotized structure on the endophallus (Fig. 5).
Additional locality records (not examined, Martin Baehr, in litt.). PAPUA NEW GUINEA Canopy Mission, Madang Province, Baiteta, Light, Leg. Olivier Missa: 1 male- AR 53, 30-V-1996; 1 male, 1 female- T 2, 31-V-1993; 1 female, X G, 24-IV-1996; 1 female, M 2, 30-IV-1996. One male and two females deposited IRSNB, one male and one female ZSM.
A female specimen labeled “New Guinea, Weam, Aug 1962// H. Olmus collector”. Deposited ANIC. This species is distributed across northern Australia and it has not been previously reported from New Guinea. It is likely a recent accidental introduction or dispersal. We have only seen this single individual from New Guinea and it is unknown if the species is established.
Fieldwork in Papua New Guinea in 1989 was generously supported by a ten-week fellowship provided by the Christensen Fund for work based at the Christensen Research Institute in Madang. We thank Martin Baehr for providing the records of Stegazopteryx and facilitating loans of other important specimens.