(C) 2013 Vladimir Pešić. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 (CC-BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
New records of water mites of the family Torrenticolidae Piersig, 1902 (Acari: Hydrachnidia) from streams in South Korea and the Russian Far East are presented. Detailed descriptions or redescrptions are provided for eight species of the genera Torrenticola Piersig, 1896 and Monatractides K. Viets 1926. Two species are described as new to science: Torrenticola kimichungi sp. n. and Monatractides abei sp. n. Five species are reported as first records from Korea: Torrenticola brevirostris (Halbert, 1911); Torrenticola dentifera Wiles, 1991; Torrenticola recentis Tuzovskij, 2003; Torrenticola ussuriensis (Sokolow, 1934); and Torrenticola turkestanica (Sokolow, 1926). Torrenticola nipponica (Enami, 1940) is reported for the first time from Russia.
Acari, Hydrachnidia, new species, new records, running waters
Water mites of the family Torrenticolidae are presently known from all continents except Antarctica, with more than 400 species described so far (
At present, only one species of the genus Torrenticola Piersig, 1896, i.e. Torrenticola nipponica (Enami, 1940) is known from South Korea (
Water mites were collected by hand netting, sorted on the spot from the living material, preserved in Koenike’s fluid and dissected as described elsewhere (e.g.
In the section ‘Material examined’ collecting site abbreviations derive from the geographical database Pešić. The composition of the material is given as: males/females/deutonymphs. All measurements are given in μm. The following abbreviations are used: asl = above sea level, Cx-I = first coxae, Cxgl-4 = coxoglandularia of fourth coxae (= E4 in
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_brevirostris
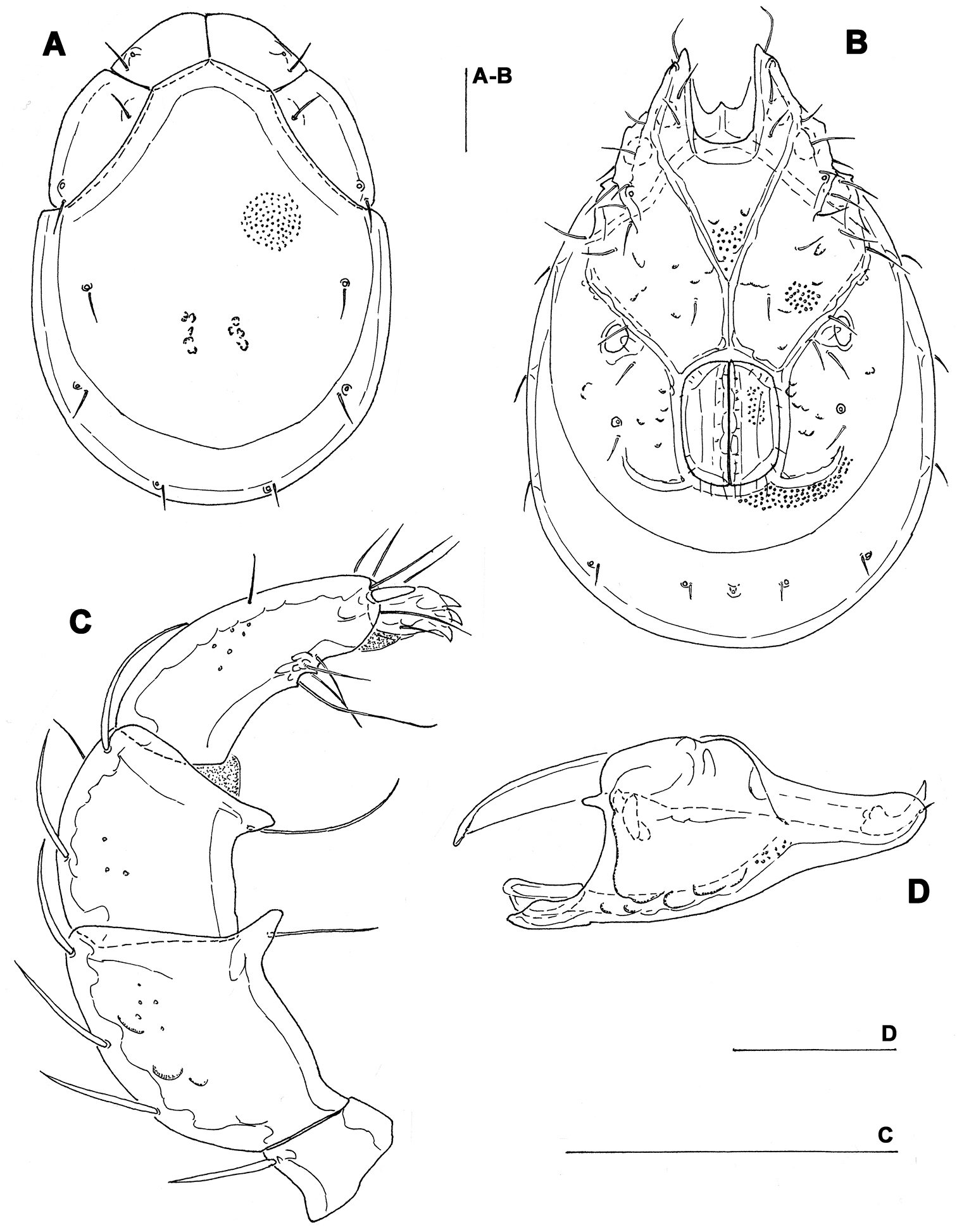
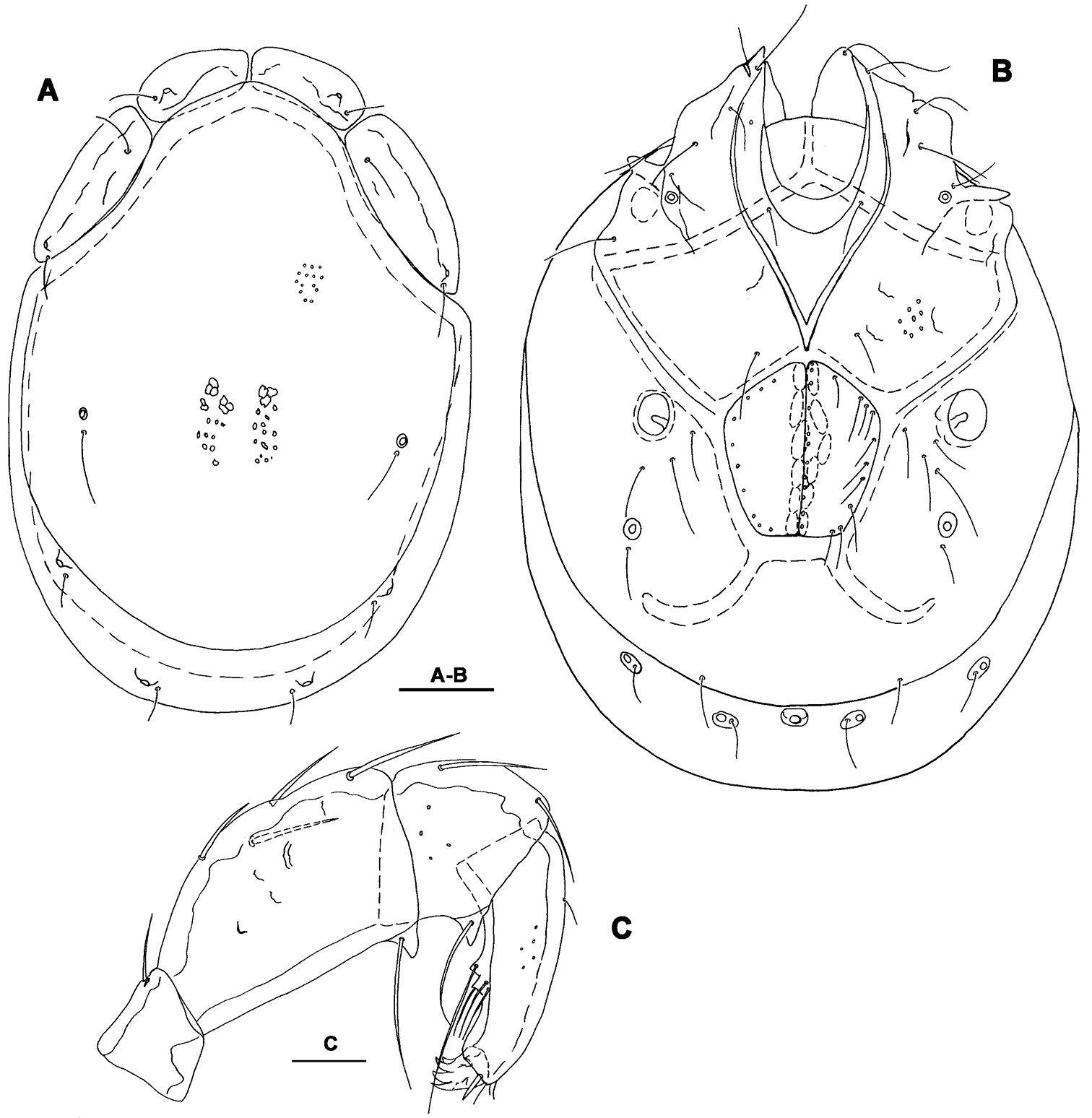
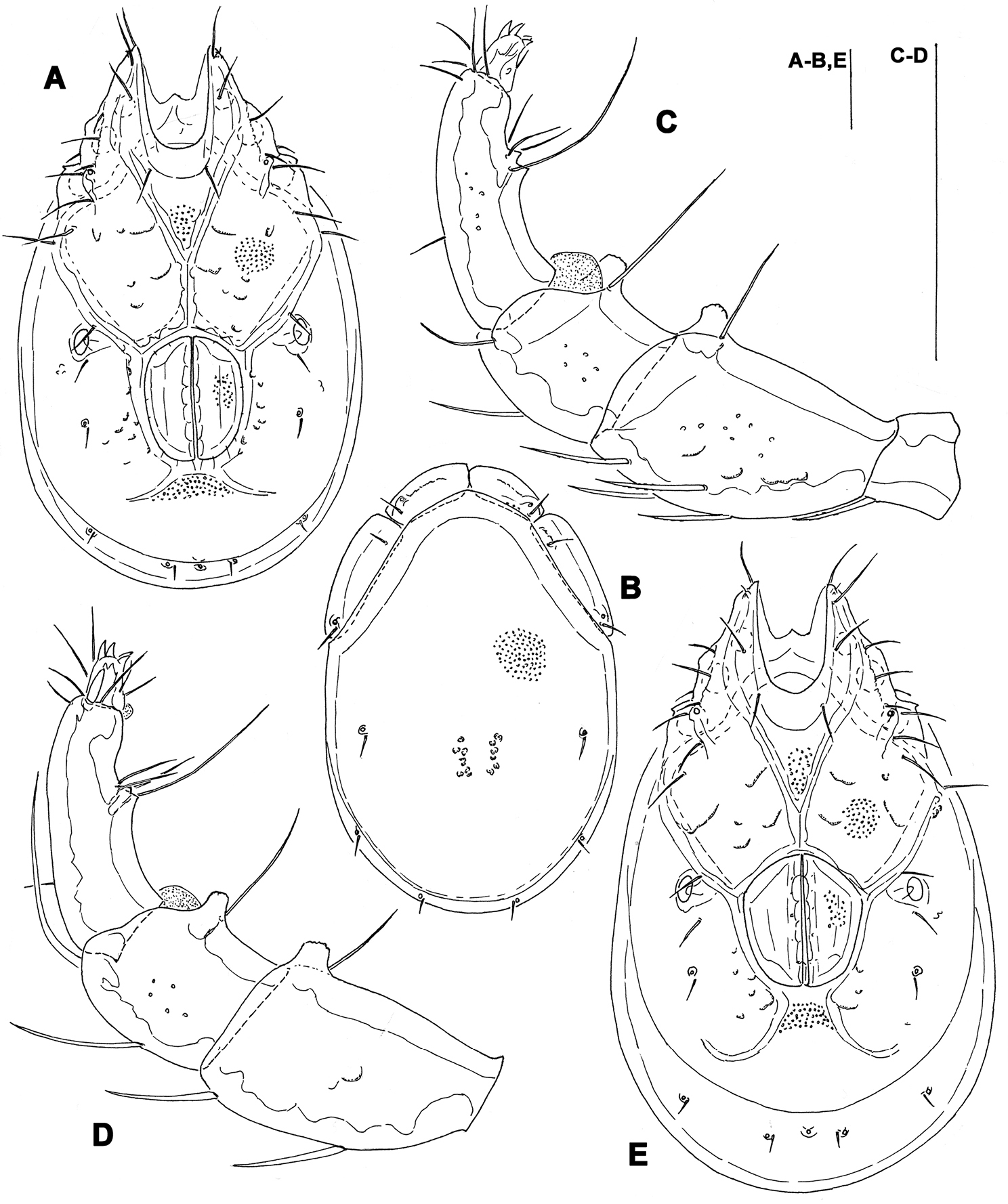
Figs 1, 7ASOUTH KOREA: CR9 Ne myeon Mt, Naebyeansan NP, stream near Naebyeansan Info Center, 35°38'25.623"N, 126°34'53.1438"E, 10.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 1/0/0 (mounted, NIBRIV0000268844).
Male. General features. Idiosoma roundish; Cxgl-4 subapical; posterior suture line of Cx-IV starting at right angle from genital field; excretory pore and Vgl-2 away from the line of primary sclerotization (Fig. 1B); ejaculatory complex conventional in shape (with well developed anterior keel and proximal arms); gnathosomal rostrum shortened, ventrally not evidently set off from gathosomal base (Fig. 1D); P-2 shorter than P-4, P-2 ventral margin slightly convex; P-4 stout, with well developed ventral tubercles (Fig. 1C).
Measurements. Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 1B) L 731, W 500; dorsal shield (Fig. 1A, 7A) L 598, W 441, L/W ratio 1.36; dorsal plate L 544; shoulder plate L 175-177, W 78-83, L/W ratio 2.1-2.3; frontal plate L 130-131, W 66-67, L/W ratio 1.9-2.0; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.34-1.36. Gnathosomal bay L 119, Cx-I total L 284, Cx-I mL 164, Cx-II+III mL 93; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 3.05; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.8. Genital field L/W 152/119, ratio 1.28; ejaculatory complex L 222; distance genital field-excretory pore 127, genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 200. Gnathosoma vL 266; chelicera total L 292; palp total L 296, dL: P-1, 26; P-2, 87; P-3, 66; P-4, 89; P-5, 28; P-2/P-4 ratio 0.98.
Torrenticola brevirostris (Halbert, 1911), male, stream in Naebyeansan NP, Korea: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C palp, medial view D gnathosoma. Scale bars = 100 μm.
The single male specimen examined from a stream in Naebyeansan National Park fits well the original description of Torrenticola brevirostris. The differences are found in a minor idiosoma and gnathosoma dimensions and a more shallow gnathosoma with a relatively less shortened rostrum compared with the populations from the Western Palaearctic (see:
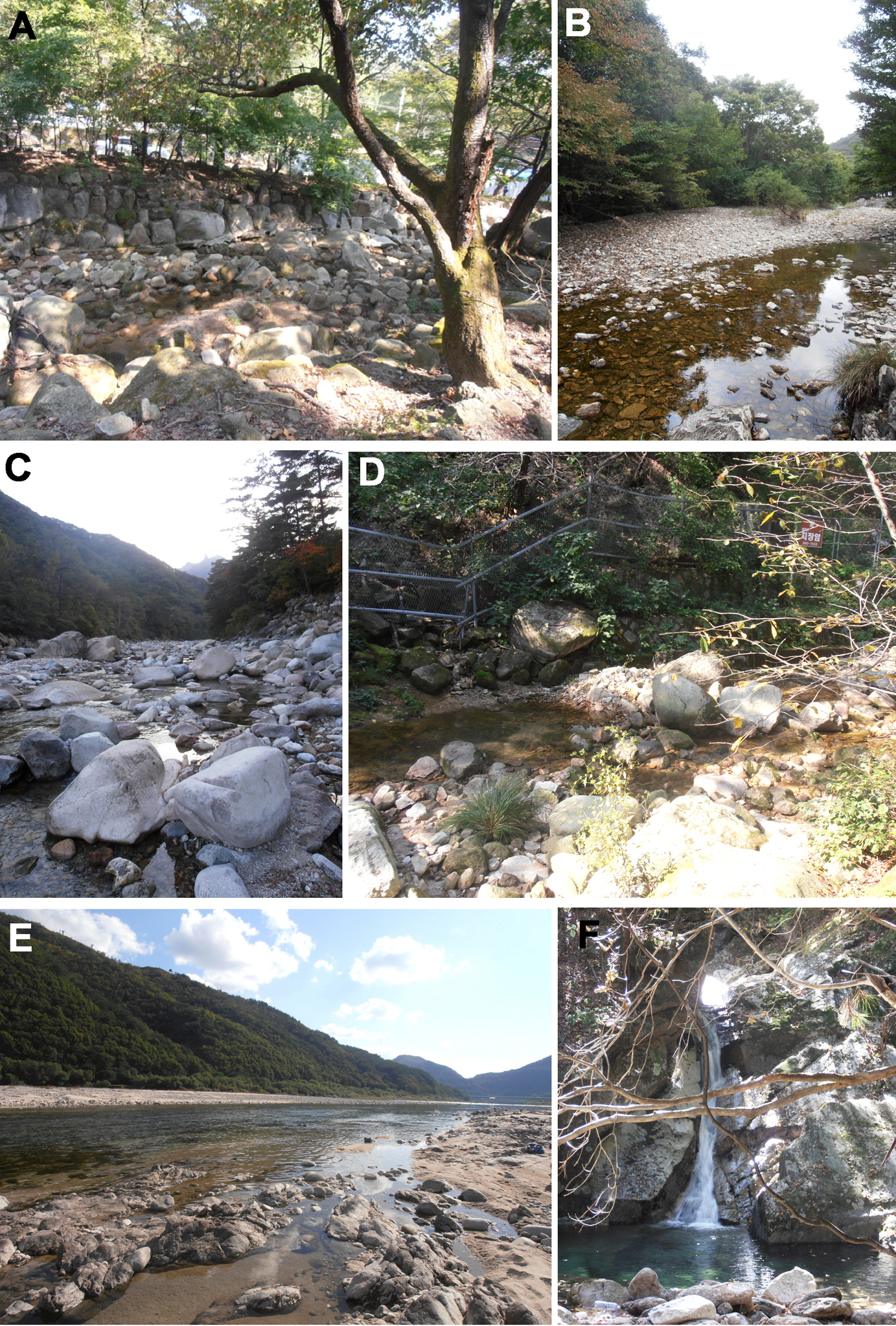
A permanent sandy/bouldary stream, shaded by riparian vegetation (Fig. 14B).
Palaearctic. New for the fauna of Korea.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_dentifera
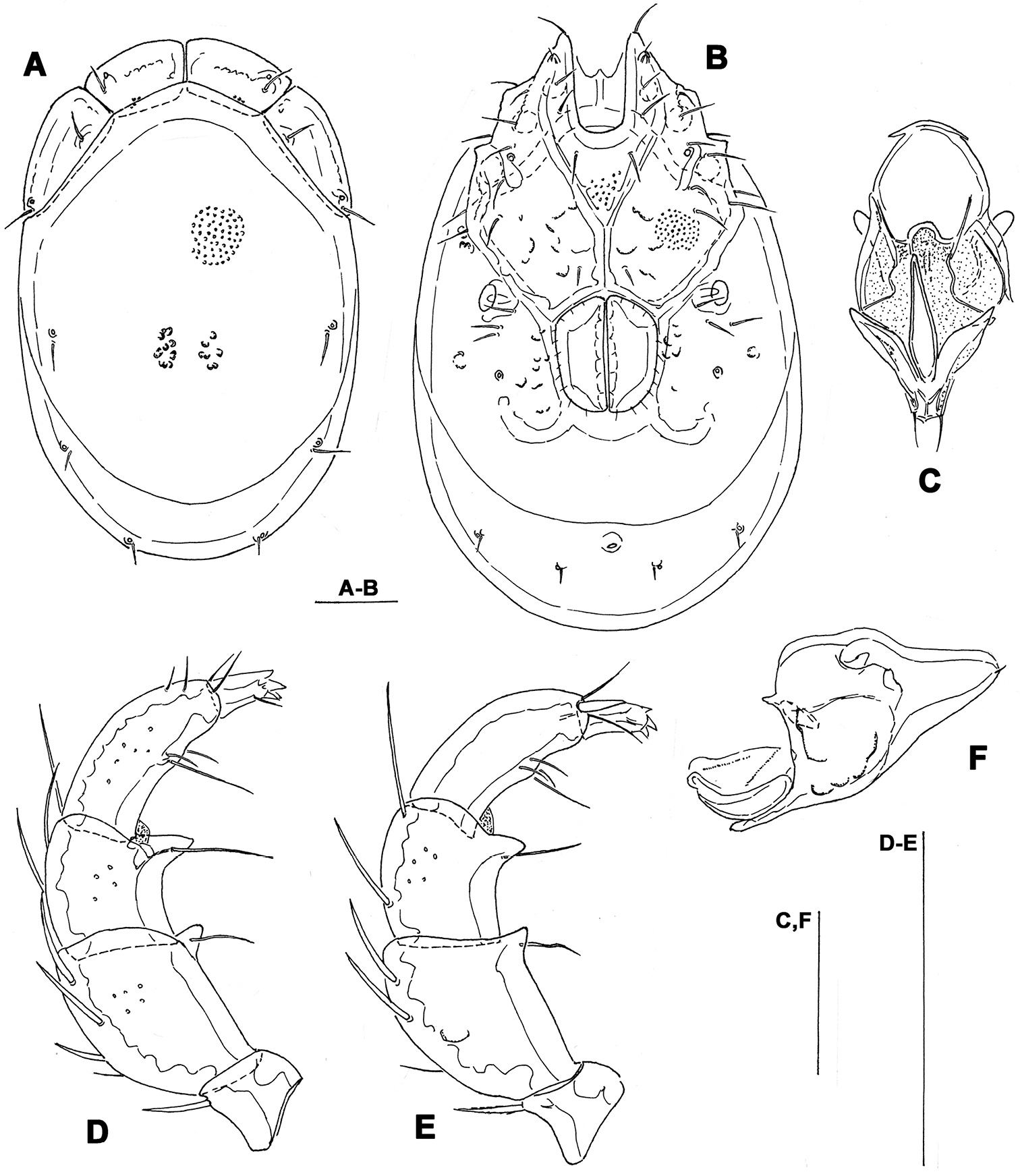
Figs 2, 7BSOUTH KOREA: CR9 Ne myeon Mt, Naebyeansan NP, stream near Naebyeansan Info Center, 35°38'25.623"N, 126°34'53.1438"E, 10.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 1/0/0 (mounted, NIBRIV0000268845).
Male. General features. Idiosoma elongated; frontal platelets anteriorly bulging (Figs 2A, 7B); Cxgl-4 subapical; medial suture line of Cx-II+III relatively long; posterior suture line of Cx-IV weakly curved; excretory pore and Vgl-2 on the line of primary sclerotization near posterior idiosoma margin; ejaculatory complex conventional in shape (Fig. 2D); gnathosoma ventral margin only slightly curved, rostrum well developed (Fig. 2E); P-2 shorter than P-4, ventral margin with a fine denticulation also in proximal half of the segment, distally with a laterally compressed, anteriorly directed hyaline extension; P-3 with a subrectangular, apically serrated ventrodistal projection with a fine denticles; P-4 with long and broadly rounded distal seta (Fig. 2C), ventral tubercles well developed and separated.
Measurements. Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 2B) L 591, W 341; dorsal shield (Figs 2A, 7B) L 472, W 305, L/W ratio 1.55; dorsal plate L 434; shoulder plate L 141-144, W 37-40, L/W ratio 3.6-3.8; frontal plate L 101-108, W 47-48, L/W ratio 2.2-2.3; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.3-1.4. Gnathosomal bay L 81, Cx-I total L 200, Cx-I mL 117, Cx-II+III mL 113; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 1.8; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.04. Genital field L/W 113/95, ratio 1.19; ejaculatory complex L 166; distance genital field-excretory pore 133, genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 161. Gnathosoma vL 247; palp total L 226, dL: P-1, 22; P-2, 62; P-3, 48; P-4, 77; P-5, 17; P-2/P-4 ratio 0.8.
Torrenticola dentifera Wiles, 1991, male, stream in Naebyeansan NP, Korea: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C palp, medial view D ejaculatory complex E gnathosoma. Scale bars = 100 μm.
The single male specimen examined fits the original description of Torrenticola dentifera, which was based on two male specimens from Selangor, Peninsular Malaysia (
A permanent sandy/bouldary stream, shaded by riparian vegetation (Fig. 14B).
Malaysia (
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:B92491ED-F051-4C8B-9381-BFC4668BA2CE
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_kimichungi
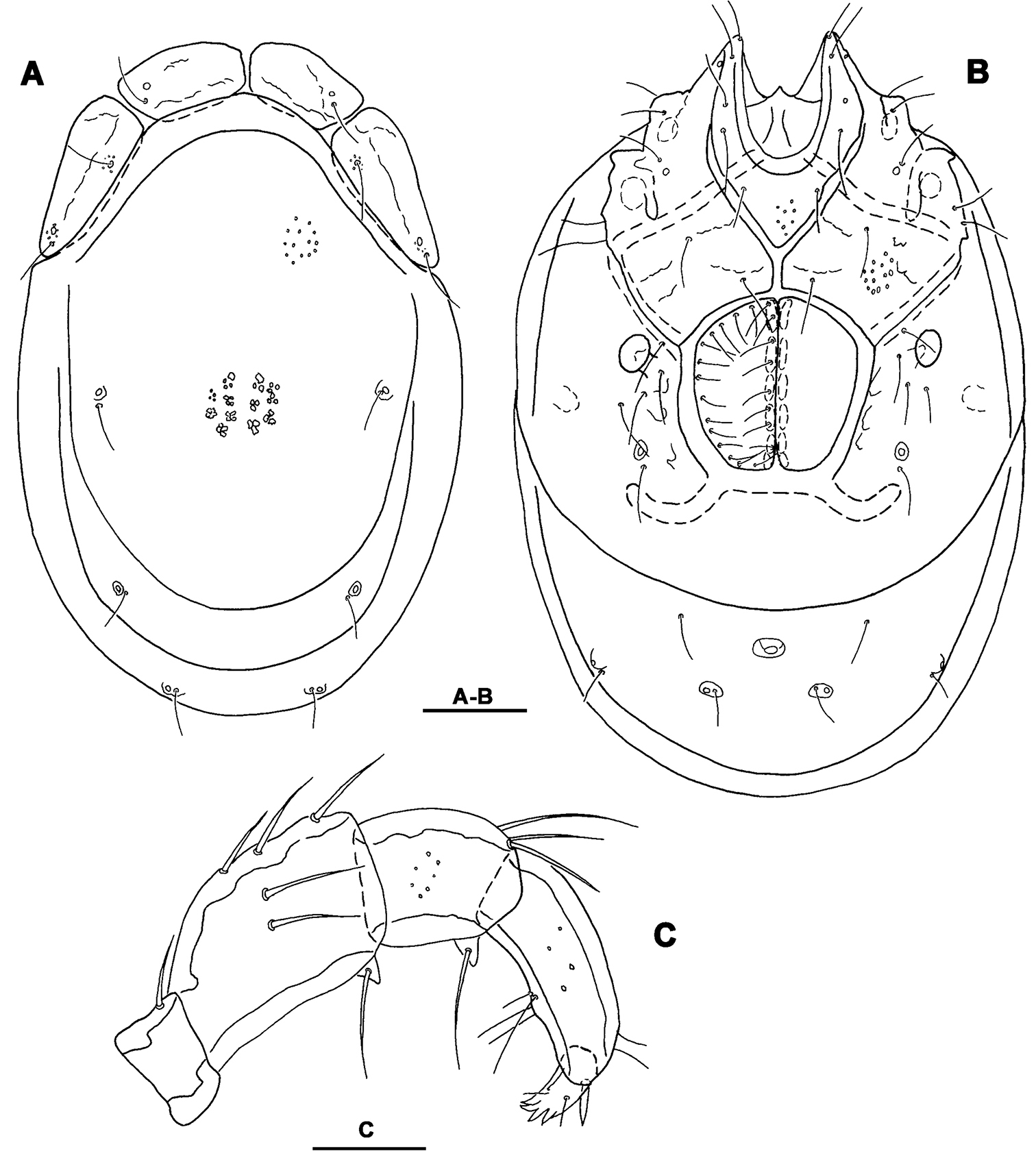
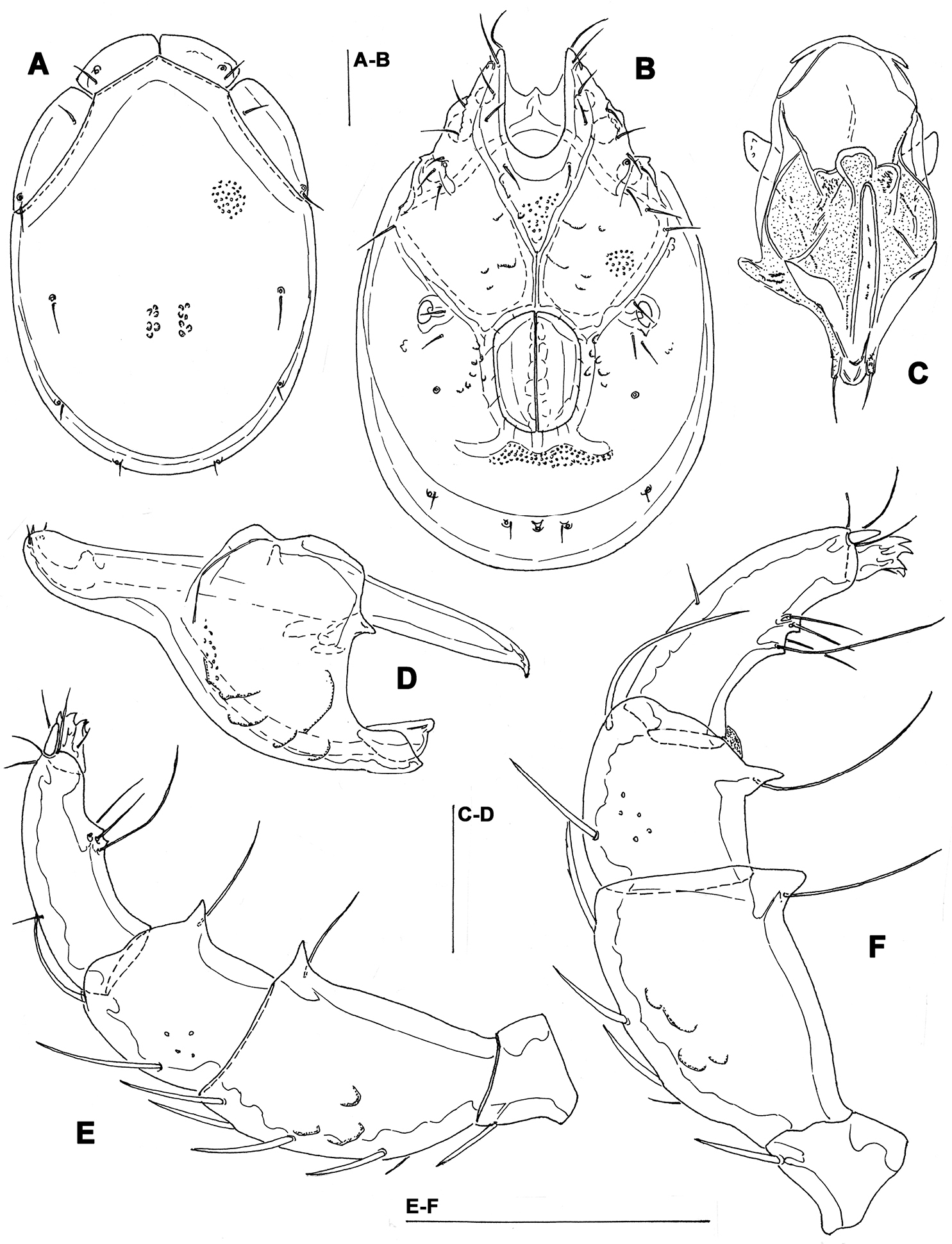
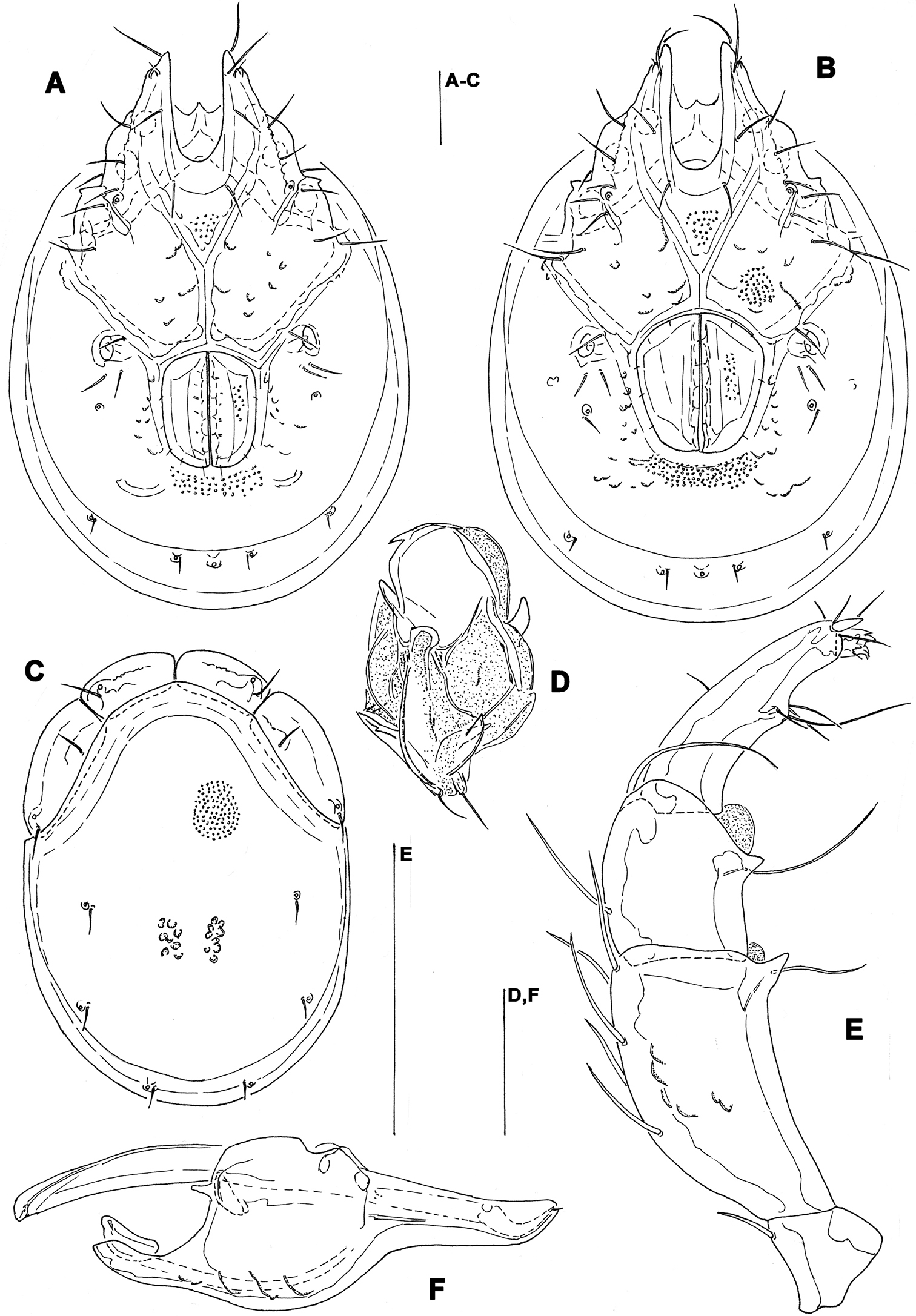
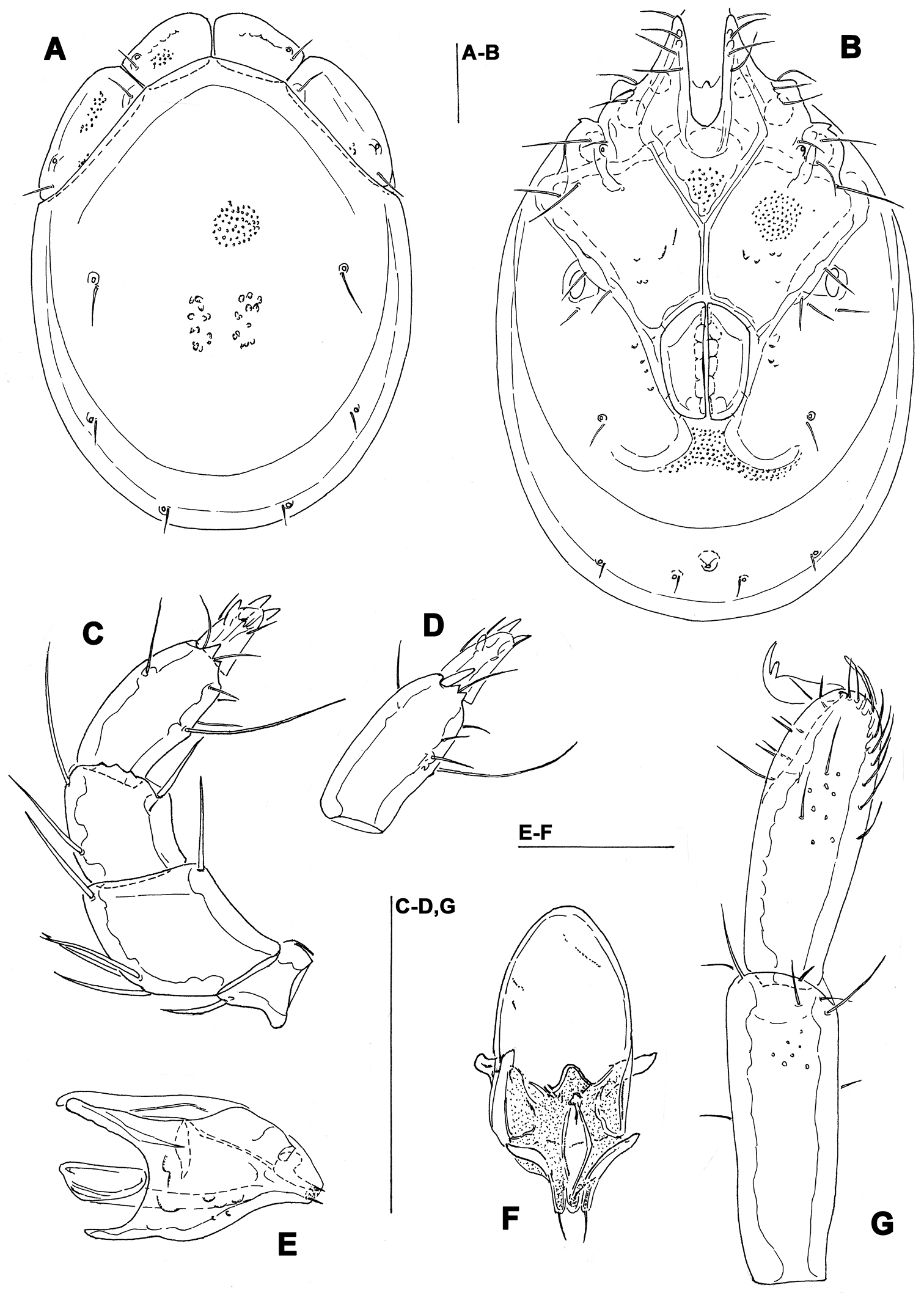
Figs 3, 4, 7C–FHolotype male (NIBRIV0000268846), dissected and slide mounted, SOUTH KOREA: CR4 Seoraksan NP, stream near Temple, 38°10.399'N, 128°29.050'E, 196 m asl., 8.x.2012 Pešić & Karanović. Paratype: same data as holotype, one male (NIBRIV0000268847); RUSSİA, Primory Territory, Partizansky District, Partizanskay River basin, Tigrovaya River, 43°11.401'N, 133°12.660'E; depth 30 cm below the sediment surface; substrate: cobbles, pebbles, sand; 12.vi.2010, Semenchenko & Sidorov, three males (490-492-kas–IBSS), two females (493-494-kas–IBSS), dissected and slide mounted.
Idiosoma elongated (dorsal shield L/W ratio 1.5-1.6); medial suture line of Cx-II+III in male short (L 74-85 μm); suture line of Cx-IV extended posterior to the genital field; excretory pore posterior to the line of primary sclerotization, Vgl-2 posterior to excretory pore; male genital field with maximum width at the anterior margin; gnathosoma deep with a short rostrum; P-4 with ventral setae on flat hump.
General features. Idiosoma elongated; Cxgl-4 subapical; suture line of Cx-IV evident and curved, starting posterior from genital field, laterally curved anteriorly (Figs 3B, 4B); excretory pore posterior to the line of primary sclerotization, Vgl-2 posterior to excretory pore; gnathosoma deep with a short rostrum not evidently set off from gnathosomal base (Fig. 3F); P-2 ventrally slightly convex, ventrodistal projection cone-shaped, pointed towards distal, P-3 with ventrodistal projection slightly larger than projection of P-2, P-4 slightly curved, ventral setae (one long and three short) on flat hump (Figs 3D–E, 4C). Male: Medial suture line of Cx-II+III short; genital field with maximum width at the anterior margin; ejaculatory complex normal in shape (Fig. 3C); P-2 and P-4 almost equal in length.
Measurements. Male (holotype, in parentheses measurements of paratype from South Korea, in square parentheses specimens from Russia, n = 2): Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 3B) L 723 (741) [731-748], W 477 (513) [488-578]; dorsal shield (Figs 3A, 7C–E) L 628 (650) [607-663], W 414 (444) [409-425], L/W ratio 1.52 (1.46) [1.47-1.56]; dorsal plate 575 (596) [554-595]; shoulder plate L 166-169 (163-166) [161-167], W 72-75 (73) [72-79], L/W ratio 2.2-2.3 (2.2-2.3) [2.11-2.24]; frontal plate L 131-134 (127-131) [125-126], W 72 (69-73) [62-72], L/W ratio 1.8-1.9 (1.7-1.9) [1.75- 2.0]; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.24-1.29 (1.27-1.28) [1.28-1.33]. Gnathosomal bay L 122 (125) [112-119], Cx-I total L 231 (244) [231-237], Cx-I mL 109 (119) [118-119], Cx-II+III mL 75 (85) [74-79]; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 3.1 (2.9) [2.91-3.2]; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.45 (1.4) [1.5-1.58]. Genital field L/W 138 (148) [145-152]/122 (125) [112-114], L/W ratio 1.12 (1.18) [1.26-1.36]; ejaculatory complex L 183 (184) [180-200]; distance genital field-excretory pore 166 (163) [152-172], genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 266 (263) [251-257]. Gnathosoma vL 191 (198) [194-211]; chelicera total L 234 (231) [231-232]; palp total L 215 (210) [210-216], dL: P-1, 25 (21) [24-27]; P-2, 62 (61) [59-62]; P-3, 43 (42) [43-46]; P-4, 60 (63) [62-63]; P-5, 25 (23) [19-21]; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.03 (0.97) [0.94-1.0].
Female (from Russia, n = 2). Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 4B) L 800-816, W 544-580; dorsal shield (Figs 4A, 7F) L 714-731, W 476-493, L/W ratio 1.45-1.54; dorsal plate L 650-663; shoulder plate L 174-185, W 72-74, L/W ratio 2.34-2.57; frontal plate L 132-133, W 71-72, L/W ratio 1.83-1.86; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.32-1.4. Gnathosomal bay L 119-132, Cx-I total L 231-244, Cx-I mL 112-113, Cx-II+III mL 39-46; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 5.02-6.25; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 2.43-2.9. Genital field L/W 174-178/162-165, L/W ratio 1.05-1.09; distance genital field-excretory pore 160-198, genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 310-330. Gnathosoma vL 218-264; chelicera total L 244; palp total L 220-228, dL: P-1, 24-27; P-2, 66-70; P-3, 46-48; P-4, 64-65; P-5, 18-20; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.01-1.08.
Torrenticola kimichungi sp. n., male holotype: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C ejaculatory complex D palp, lateral view E palp, medial view F gnathosoma. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Torrenticola kimichungi sp. n., paratype female, Tigrovaya River, Russia: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C palp, lateral view. Scale bars = 100 μm (A–B), 25 μm (C).
The species is named after Drs Il-Hoi Kim and Kyung-Sook Chung in appreciation of their studies of the Korean water mites.
The new species belongs to the group of species characterized by having well-developed finger or peg-like ventrodistal tubercles on P-2 and P-3, the deep gnathosoma with a short rostrum, not evidently set off from gnathosomal base and a relatively short medial suture line of Cx-II+III in male. This group includes the following Asian species of Torrenticola: Torrenticola brevirostris (Halbert, 1911) (Palaearctic), Torrenticola nanshihensis Pešić et al., 2011 (Taiwan), Torrenticola projectura Pešić et al., 2012 (Taiwan), Torrenticola retractipora Lundblad, 1969 (Burma), Torrenticola siamis Pešić & Smit, 2009 (Thailand), and Torrenticola subterranea Imamura, 1957 (Japan). Males of Torrenticola brevirostris and Torrenticola nanshihensis differ in a prominent suture line of Cx-IV starting at a right angle from the genital field, excretory pore on the same level as Vgl-2 and more away from the line of primary sclerotization and P-4 stockier with well developed ventral tubercles (see:
A permanent sandy/bouldery stream with considerably exposure to sunlight (Fig. 14C); the specimens from Russia were collected from interstitial waters.
South Korea, Far East of Russia (present study).
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_nipponica
Figs 5, 6, 7G–ISOUTH KOREA: CR1 Seoul, Dobong stream, 37°41.262'N, 127°01.706'E, 19 m asl., 7.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 2/0/0 (mounted, NIBRIV0000268848). RUSSIA: Primory Territory, Partizansky District, Partizanskay River basin, Tigrovaya River, 43°11.401'N, 133°12.660'E; depth 30 cm below the sediment surface; substrate: cobbles, pebbles, sand; 12.vi.2010, Semenchenko & Sidorov 2/2/0 (mounted, IBSS).
General features. Idiosoma roundish; dorsal shield with colour pattern as illustrated in Figs 7G-I; Cxgl-4 subapical; excretory pore and Vgl-2 slightly away from the line of primary sclerotization; gnathosoma deep, rostrum shorter than depth of gnathosomal base (Fig. 5D); palp robust and compact, P-2 longer than P-4, P-2 and P-3 ventrodistal projection pointed towards distal, P-4 with well developed ventral tubercles bearing one long and three short setae (Figs 5E-F, 6C). Male: Medial suture line of Cx-II+III short; suture line of Cx-IV medially starting from posterior margin of genital field (Fig. 2B); ejaculatory complex normal in shape (Fig. 5C). Female: Suture of Cx-IV curved (Fig. 2C); genital field pentagonal in shape.
Measurements. Male (from South Korea, n = 2; in parentheses specimens from Russia, n = 2) Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 5B) L 694-819 (740-755), W 478-534 (508-544); dorsal shield (Figs 5A, 7G-H) L 584-675 (636-670), W 410-469 (422-476), L/W ratio 1.42-1.44 (1.4-1.5); dorsal plate L 556-643 (594-614); shoulder plate L 178-206 (178-188), W 56-61 (59-60), L/W ratio 3.0-3.4 (2.96-3.18); frontal plate L 113-125 (121-125), W 45-50 (46-47), L/W ratio 2.4-2.5 (2.56- 2.72); shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.56-1.67 (1.46-1.5). Gnathosomal bay L 148-153 (132-141), Cx-I total L 278-294 (284-286), Cx-I mL 129-141 (145-165), Cx-II+III mL 69-91 (79-92); ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 3.2-4.0 (3.1-3.6); Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.55-1.87 (1.57-2.08). Genital field L/W 156-181/117-133 (168-172/125-132), L/W ratio 1.33-1.36 (1.26-1.38); ejaculatory complex L 231 (224-251); distance genital field-excretory pore 131-178 (138-145), genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 183-231 (172-205). Gnathosoma vL 273-303 (277-297); chelicera total L 319-347 (323-343); palp total L 279-316 (284-291), dL: P-1, 34-37 (33-36); P-2, 92-101 (92-95); P-3, 52-63 (51-59); P-4, 82-93 (82-92); P-5, 19-22 (17-18); P-2/P-4 ratio 1.09-1.13 (1.03-1.12).
Female (from Russia, n = 2). Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 6B) L 860-867, W 629-635; dorsal shield (Figs 6A, 7I) L 723-782, W 502-544, L/W ratio 1.44; dorsal plate L 680-731; shoulder plate L 211-214, W 66-73, L/W ratio 2.92-3.2; frontal plate L 128-139, W 59-64, L/W ratio 2.16- 2.17; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.54-1.65. Gnathosomal bay L 168-178, Cx-I total L 303-310, Cx-I mL 132-145, Cx-II+III mL 30-40; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 7.75-10.1; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 3.63-4.4. Genital field L/W 185-195/172-178, L/W ratio 1.04-1.13; distance genital field-excretory pore 208-210, genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 297-310. Gnathosoma vL 330-336; chelicera total L 420; palp total L 341-345, dL: P-1, 41-43; P-2, 115-116; P-3, 65-67; P-4, 100-102; P-5, 18-19; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.13-1.16.
Torrenticola nipponica (Enami, 1940), male, Dobong stream, Korea: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C ejaculatory complex D gnathosoma E–F palp, medial view (E-smaller specimen, F-larger specimen). Scale bars = 100 μm.
Torrenticola nipponica (Enami, 1940), female, Tigrovaya River, Russia: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C palp, lateral view. Scale bars = 100 μm (A–B), 25 μm (C).
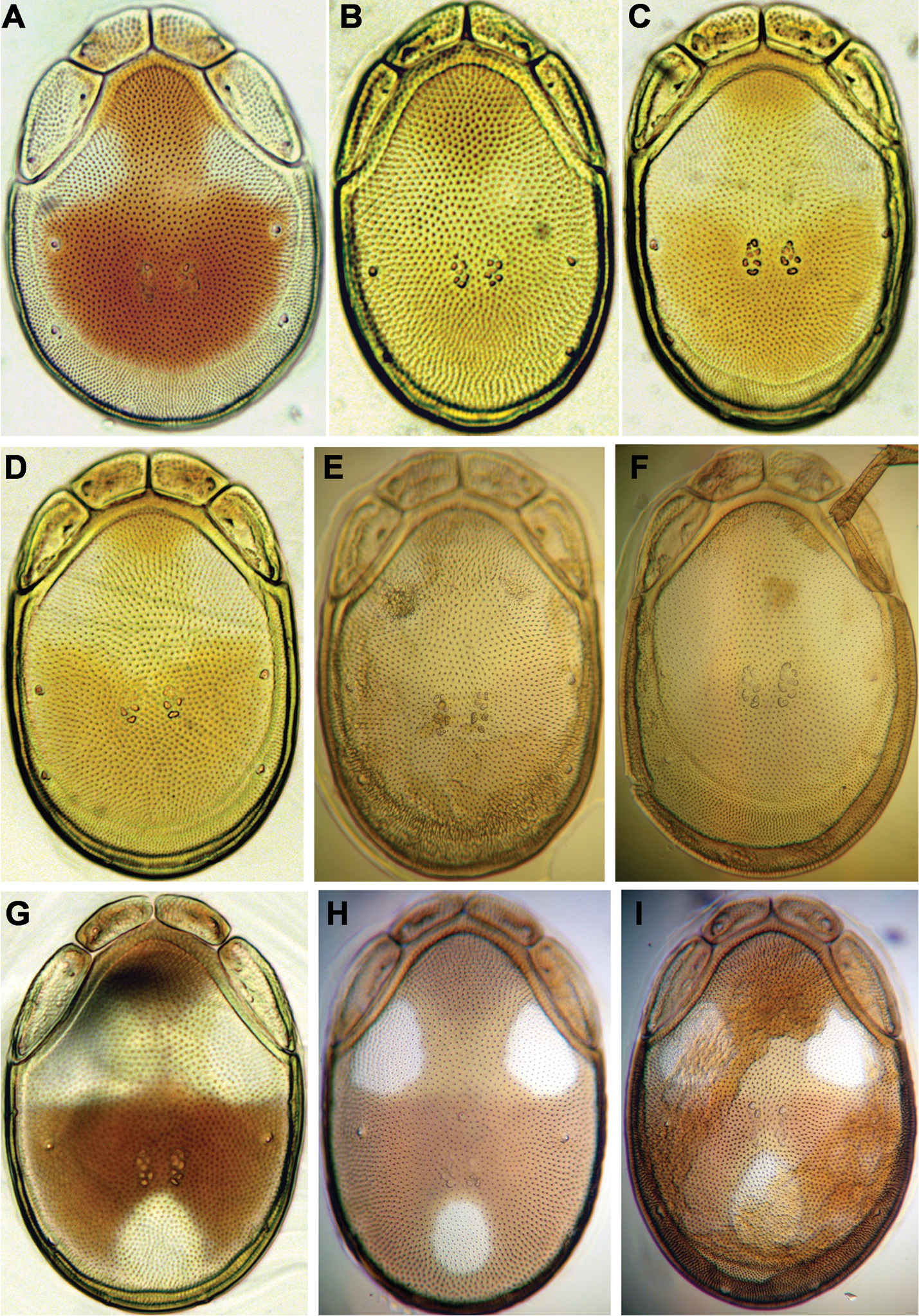
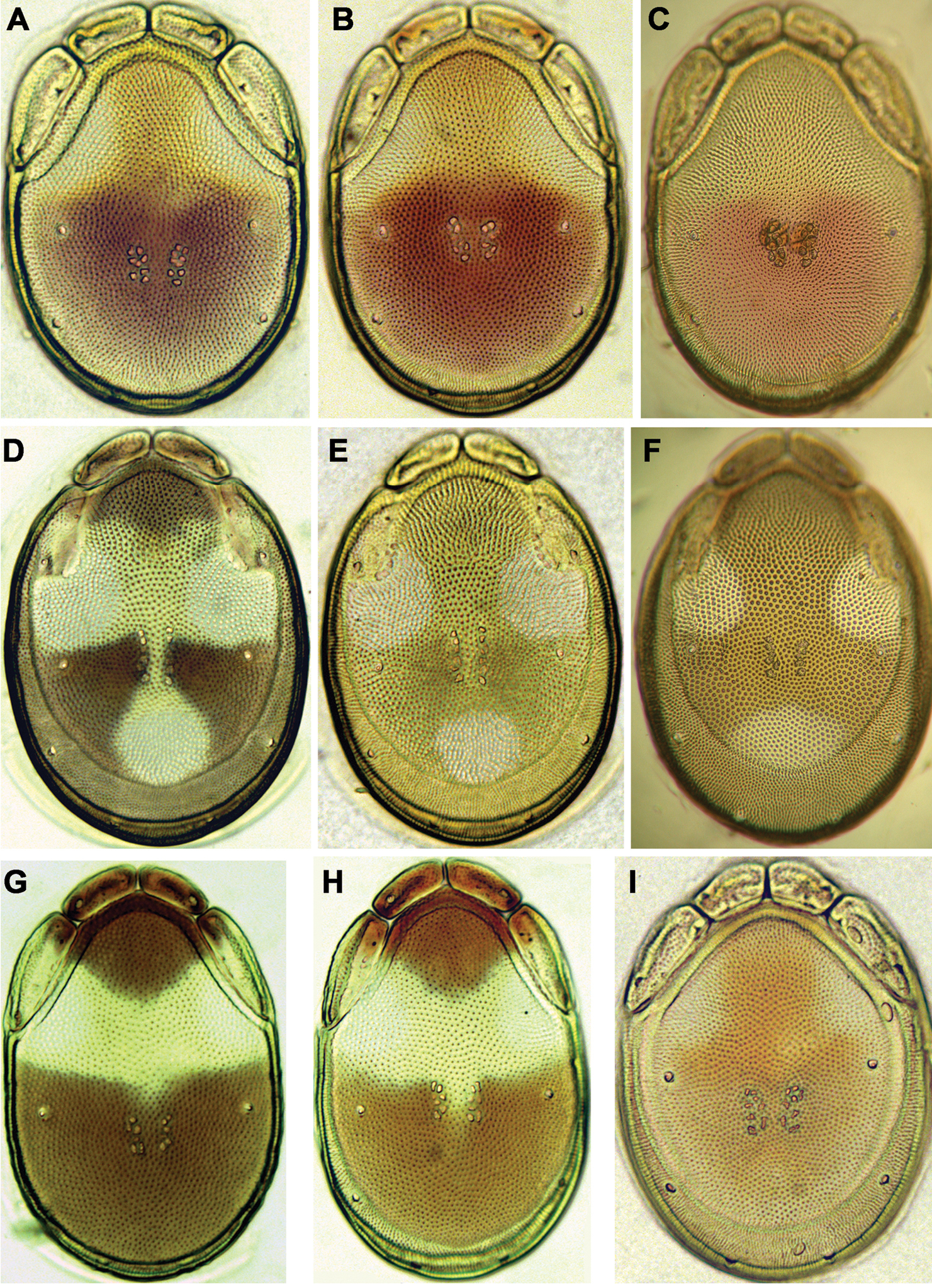
Photographs of dorsal shield: A Torrenticola brevirostris (Halbert, 1911), female, stream in Naebyeansan NP, Korea B Torrenticola dentifera Wiles, 1991, male, stream in Naebyeansan NP, Korea: C–F Torrenticola kimichungi sp. n. (C–D specimens from stream in Seoraksan NP, Korea, E–F specimens from Tigrovaya River, Russia): C maleholotype D–E maleparatypes F femaleparatype G–I Torrenticola nipponica (Enami, 1940) (G specimen from Dobong stream, Korea H–I specimens from Tigrovaya River, Russia): G–H male I female. Photos. V. Pešić (Figs A–D, G), K. Semenchenko (Figs E–F, H–I).
The male specimens from South Korea and Russia fit the description of Torrenticola nipponica (Enami, 1940) which was based on one male and seven females from River Inôzava, Uzi region in Japan (
A permanent shaded sandy/bouldary stream at low elevations (Fig. 14A); the specimens from Russia were collected from interstitial waters.
Japan (Uzi region- Enami, 1940), South Korea (Chindo Island – Chung & Kim 1995; present study). New for the fauna of Russia.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_recentis
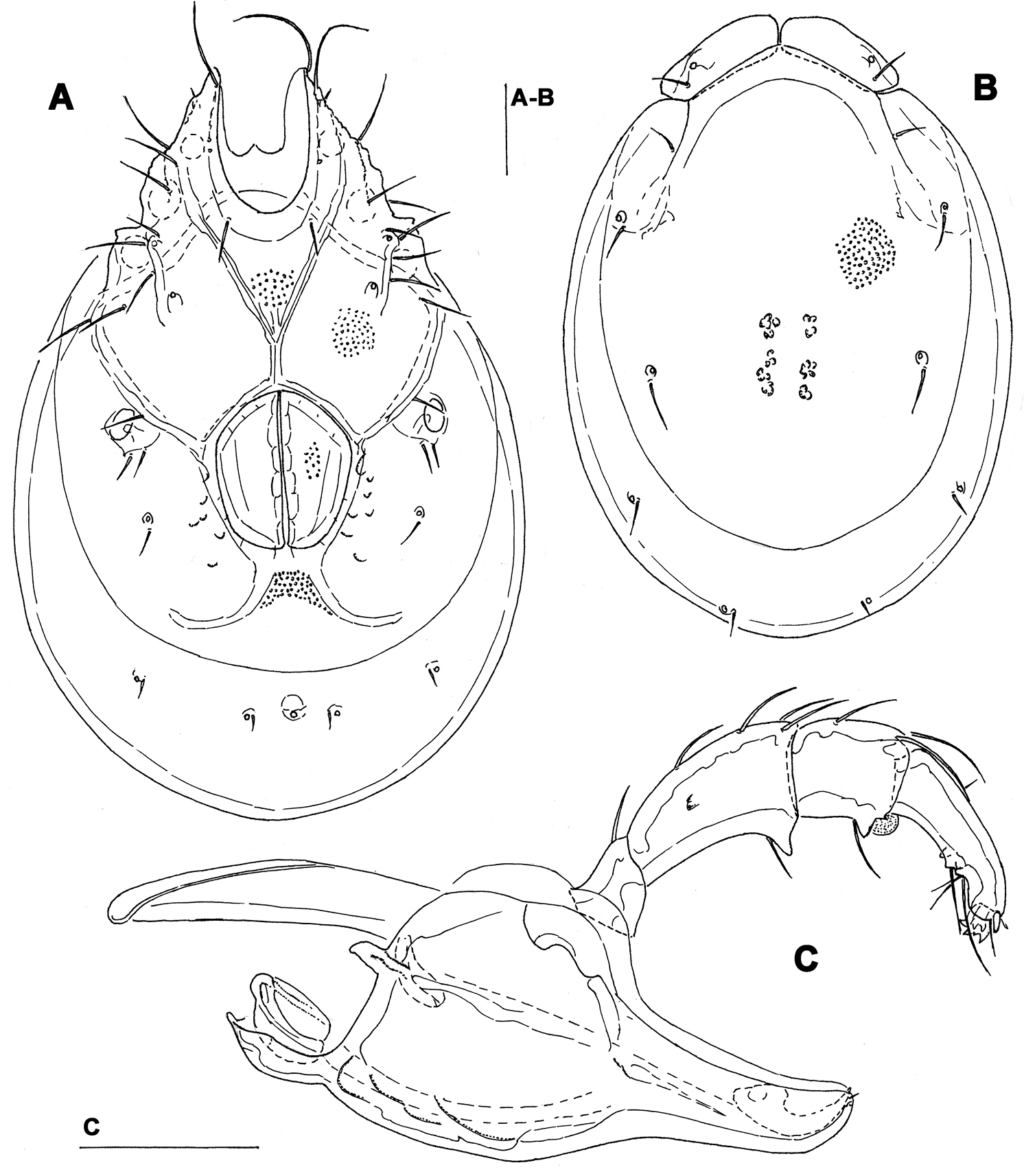
Figs 8, 11A–CSOUTH KOREA: CR1 Seoul, Dobong stream, 37°41.262'N, 127°01.706'E, 19 m asl., 7.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 6/6/0 (1/1/0 mounted, NIBR IV0000268849); CR2 Seoul, Ui-dong stream 37°39.554'N, 127°00.249'E, 114 m asl., 7.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 3[1 juvenile]/0/1; CR4 Seoraksan NP, stream near Temple, 38°10.399'N, 128°29.050'E, 196 m asl., 8.x.2012 Pešić & Karanović 7/2/5; CR7 Odesean NP, stream, 37°49.642'N, 128°42.170'E, 215 m asl., 9.x.2012, Pešić & Karanović 6/6/0 (2/1/0 mounted, NIBRIV0000268850);; CR11 Mudeung Mt., stream, 35°8'50.2584"N, 126°59'18.942"E, 11.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 2/2/1; CR12 JiriSan NP, stream near waterfall, 35°22'47''N, 127°29'10''E, 11.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 4/12[1 juvenile]/0 (1/0/0 mounted); CR14 Duckyu San NP, stream, 35°53'50"N, 127°46'35"E, 11.x.2012, Pešić & Choi 0/2/0. RUSSIA, Primory Territory, Khasansky District, “Kedrovaya Pad National Nature Biosphere Reserve”, Sea of Japan basin, Kedrovaya River, 43°06.056'N, 131°33.310'E; depth 12–50 cm; substrate: boulders, cobbles, pebbles; 8.xi.1993, Tiunova 2/2/0 (IBSS).
General features. Idiosoma roundish; dorsal shield with colour pattern as illustrated in Figs 11A–C; Cxgl-4 subapical; suture line of Cx-IV hardly evident; excretory pore and Vgl-2 only slightly away from the line of primary sclerotization (Fig. 8A); gnathosoma ventral margin strongly curved (Fig. 8F); P-2 longer than P-4, P-2 ventral margin slightly concave, P-4 with well developed ventral protuberance bearing one long and three short setae (Fig. 8E). Male: Medial suture line of Cx-II+III moderately long; genital field subrectangular in shape, ejaculatory complex with small proximal chamber and robust proximal arms (Fig. 8D).
Measurements. Male (from CR1, in parentheses specimen from CR7). Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 7A) L 769 (753), W 556 (522); dorsal shield (Figs 7C, 11A-B) L 631 (613), W 450 (446), L/W ratio 1.4 (1.4); dorsal plate L 589 (575); shoulder plate L 195-202 (188-195), W 78 (70-72), L/W ratio 2.5-2.6 (2.6-2.8); frontal plate L 134-138 (136-138), W 58-63 (55-56), L/W ratio 2.1-2.4 (2.4-2.5); shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.4-1.5 (1.4). Gnathosomal bay L 152 (159), Cx-I total L 292 (306), Cx-I mL 141 (147), Cx-II+III mL 117 (103); ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 2.5 (3.0); Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.2 (1.4). Genital field L/W 161 (150) /129 (125), ratio 1.25 (1.2); ejaculatory complex L 189 (193); distance genital field-excretory pore 131 (134), genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 198 (191). Gnathosoma vL 325 (320); chelicera total L 376 (381); palp total L 298 (285), dL: P-1, 34 (34); P-2, 104 (97); P-3, 55 (52); P-4, 91 (88); P-5, 14 (14); P-2/P-4 ratio 1.14 (1.1).
Female (from CR1). Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 7B) L 825, W 569; dorsal shield (Fig. 11X) L 672, W 488, L/W ratio 1.38; dorsal plate L 631; shoulder plate L 212-213, W 69, L/W ratio 3.1; frontal plate L 142-144, W 56-59, L/W ratio 2.4-2.5; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.5. Gnathosomal bay L 179, Cx-I total L 320, Cx-I mL 141, Cx-II+III mL 47; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 6.8; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 3.0. Genital field L/W 191/176, ratio 1.09; egg (n = 1) maximum diameter 222; distance genital field-excretory pore 163, genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 250. Gnathosoma vL 344; chelicera total L 404; palp total L 318-321, dL: P-1, 39; P-2, 110-112; P-3, 56-57; P-4, 97; P-5, 16; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.13-1.16.
Torrenticola recentis Tuzovskij, 2003 (A, C–F male B female), Dobong stream, Korea: A–B ventral shield C dorsal shield D ejaculatory complex E palp, medial view F gnathosoma and chelicera. Scale bars = 100 μm.
The specimens from South Korea fit the description of Torrenticola recentis, a species described by
Torrenticola elliptica Maglio, 1909, a species similar in general shape of idiosioma and palps, differs from Torrenticola recentis in a more slender idiosoma, a more extended postgenital area in the male and the ejaculatory complex with a large proximal chamber (see:
Running waters at low and middle elevations (Figs 14A, D, F).
Far East of Russia (Primory Territory –
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_ussuriensis
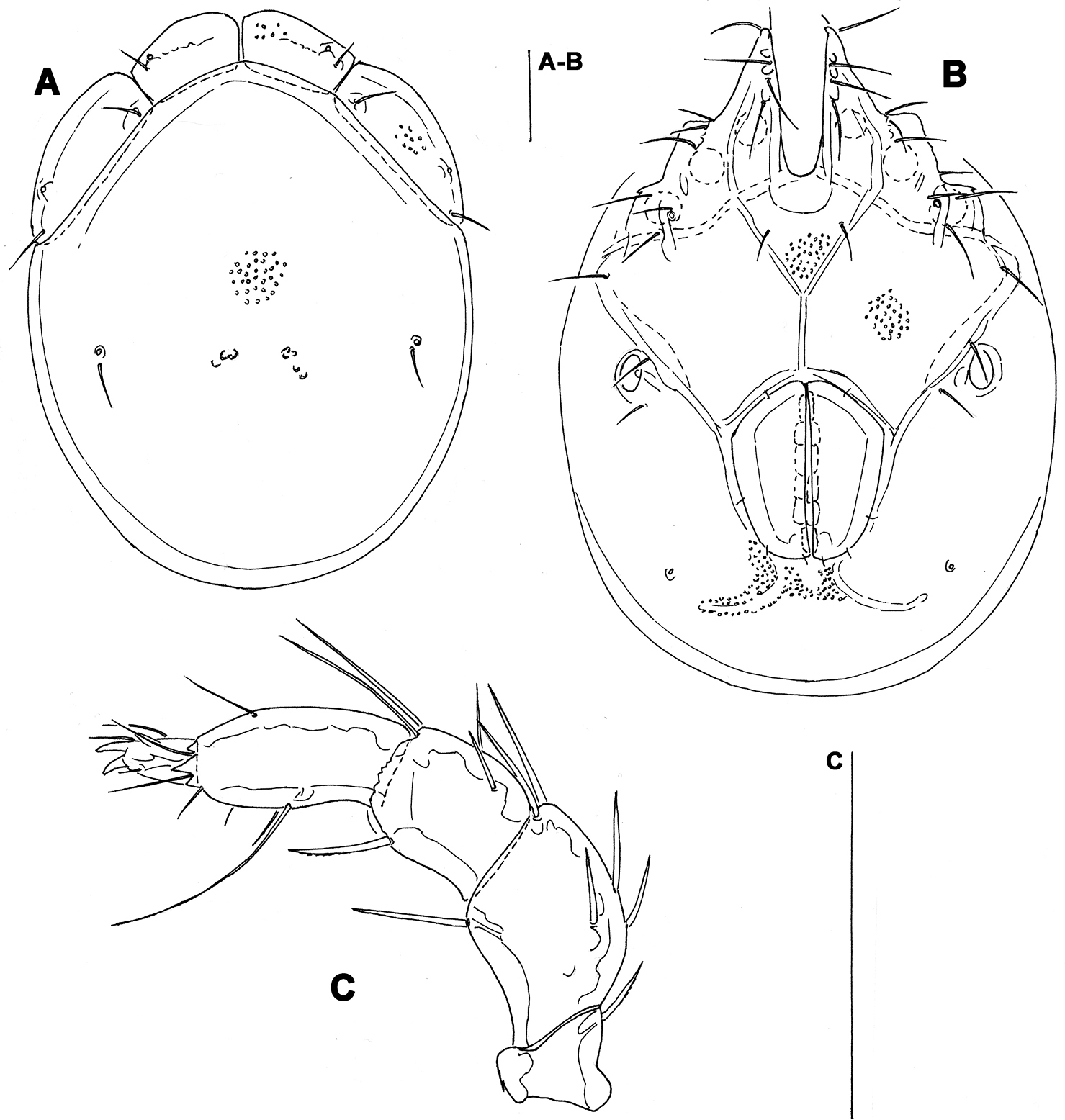
Figs 9, 11D–FSOUTH KOREA: CR3 River Inje, 38°03.961'N, 128°10.516'E, 225 m asl., 8.x.2012 Pešić & Karanović 0/1/0 (mounted, NIBRIV0000268851).
Female. General features. Shoulder platelets fused to the large dorsal plate (Fig. 9B); Cxgl-4 posterior to Cxgl-2 (Fig. 9A), glandular pore Cxgl-4 distanced from Cxgl-2 by 50-55 µm; excretory pore and Vgl-2 clearly posterior to the line of primary sclerotization; suture of Cx-IV curved; P-2 longer than P-4; P-4 with four well developed ventral tubercles (Fig. 9C).
Measurements. Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 9A) L 838, W 569; dorsal shield (Fig. 9B, 11D-E) L 694, W 501, L/W ratio 1.39; dorsal plate L 661; frontal plate L 142-147, W 50, L/W ratio 2.8-3.0; gnathosomal bay L 170, Cx-I total L 313, Cx-I medial L 142, Cx-II+III medial 52; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III medial L 6.1; Cx-I medial L/Cx-II+III medial L 2.7; distance between glandular openings of Cxgl-4 and Cxgl-2 51–54. Genital field L/W 171/150, L/W ratio 1.14; distance genital field–excretory pore 181, genital field–caudal idiosoma margin 305. Gnathosoma vL 359; chelicera total L 434; palp total L 358, dL: P-1, 46; P-2, 114; P-3, 69; P-4, 109; P-5, 20; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.05.
Torrenticola ussuriensis (Sokolow, 1940), female, Inje River, Korea: A ventral shield B dorsal shield C gnathosoma and palp, medial view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Torrenticola ussuriensis was originally described by
A permanent sandy/bouldery river with considerably exposure to sunlight (Fig. 14E).
Far East of Russia (Primory and Khabarovsk Territory, Jewish Autonomous and Amurskaya Area - “Atractides semisutus”
http://species-id.net/wiki/Torrenticola_turkestanica
Figs 10, 11G–HSOUTH KOREA: CR3 River Inje, 38°03.961'N, 128°10.516'E, 225 m asl., 8.x.2012 Pešić & Karanović 1/1/0 (mounted, NIBRIV0000268852).
General features. Idiosoma elongated (dorsal shield L/W ratio 1.5-1.6); dorsal shield with colour pattern as illustrated in Figs 11G-H; Cxgl-4 subapical; gnathosoma ventral margin strongly curved; P-2 ventral margin convex, P-2 and P-3 with a subrectangular, apically serrated ventrodistal projection, P-4 stocky with well developed ventral protuberance bearing one long and three short setae (Figs 10C-D). Male: Medial suture line of Cx-II+III moderately long; genital field subrectangular in shape, ejaculatory complex normal in shape; excretory pore and Vgl-2 located on the margin of primary sclerotization. Female: Posterior suture line of Cx-IV curved and well evident; genital field excretory pore and Vgl-2 away from the line of primary sclerotization.
Measurements. Male: Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 10A) L 700, W 441; dorsal shield (Figs 7B, 11G) L 575, W 375, L/W ratio 1.5; dorsal plate L 541; shoulder plate L 172-174, W 48-56, L/W ratio 3.1-3.6; frontal plate L 106-116, W 44-47, L/W ratio 2.4-2.5; gnathosomal bay L 133, Cx-I total L 270, Cx-I medial L 137, Cx-II+III medial 97; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III medial L 2.8; Cx-I medial L/Cx-II+III medial L 1.4. Genital field L/W 156/122, ratio 1.28; distance genital field–excretory pore 137, genital field–caudal idiosoma margin 169; ejaculatory complex L 212. Gnathosoma vL 283; chelicera total L 323; palp total L 272, dL: P-1, 28; P-2, 88; P-3, 52; P-4, 84; P-5, 20; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.05.
Female. Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 10E) L 781, W 494; dorsal shield (Fig. 11H) L 650, W 409, L/W ratio 1.6; dorsal plate L 610; shoulder plate L 178-189, W 56-64, L/W ratio 3.0-3.2; frontal plate L 127-131, W 52-55, L/W ratio 2.3-2.5; gnathosomal bay L 145, Cx-I total L 297, Cx-I medial L 151, Cx-II+III medial 47; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III medial L 6.3; Cx-I medial L/Cx-II+III medial L 3.2. Genital field L/W 169/151, ratio 1.12; distance genital field–excretory pore 188, genital field–caudal idiosoma margin 272. Gnathosoma vL 372; chelicera total L 316; palp total L 301, dL: P-1, 31; P-2, 99; P-3, 59; P-4, 92; P-5, 20; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.08.
Torrenticola turkestanica (Sokolow, 1926) (A–D male E female), Inje River, Korea: A, E ventral shield B dorsal shield C palp, lateral view D palp, medial view (P-1 missing). Scale bars = 100 μm.
Photographs of dorsal shield: A–C Torrenticola recentis Tuzovskij, 2003 (A, B specimens from Dobong stream, Korea C specimen from River Kedrovaya, Russia): A male C–B female D–F Torrenticola ussuriensis (Sokolow, 1940), female (D specimen photographed immediately after dissection E–F specimens mounted in Hoyer’s medium): D–E specimen from Korea F specimen from Russia G–H Torrenticola turkestanica (Sokolow, 1926), specimens from River Inje, Korea: G male H female I Monatarctides abei sp. n., male holotype. Photos. V. Pešić (Figs A–B, D–E, G–I), K. Semenchenko (Figs C, F).
The specimens examined from River Inje fit the description of Torrenticola turkestanica, a species described based on a single female from Tadjikistan (Sokolow 1926). The only difference with the original description is found in a broader genital field in the type specimen. Later on, populations provisionally assigned to Torrenticola turkestanica, mainly based on the approved non-identity with the alternative species, were reported from Indian Himalayas (
Torrenticola japonica Imamura, 1953, a species described based on a single female from a stream in Shinjô-mura in Japan (
A permanent sandy/bouldery river with considerable exposure to sunlight (Fig. 14E).
Tadjikistan (Sokolow 1926), Indian Himalayas (
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:F9C4384E-4673-4FC9-B098-A002FCDD1CDA
http://species-id.net/wiki/Monatractides_abei
Figs 12, 13, 11IHolotype male (NIBRIV0000268853), dissected and slide mounted, SOUTH KOREA, CR2 Seoul, Ui-dong stream, 37°39.554'N, 127°00.249'E, 114 m asl., 7.x.2012, Pešić & Choi. Paratypes: SOUTH KOREA, CR1 Seoul, Dobong stream, 37°41.262'N, 127°01.706'E, 19 m asl., 7.x.2012, Pešić & Choi, one female (NIBRIV0000268854), dissected and slide mounted; RUSSIA, Primory Territory, Partizansky District, Partizanskay River basin, Tigrovaya River, 43°11.401'N, 133°12.660'E; depth 30 cm below the sediment surface; substrate: cobbles, pebbles, sand; 12.vi.2010, Semenchenko & Sidorov, one female (497-kas–IBSS), dissected and slide mounted.
Lateral margins of dorsal shield nowhere subparallel; distal margins of P-3 with several pointed extensions; genital field in male with slightly protruding anteriolateral angles; medial suture line of Cx-II+III in female relatively long (L 90–105 μm).
General features. Lateral margins of dorsal shield nowhere subparallel (Fig. 12A, 11I); three pairs of knob-like protrusions on the lateral margin of gnathosomal bay; suture line of Cx-IV distinct, originating from lateral edge of genital field, laterally curved anteriorly; excretory pore away from the line of primary sclerotization, Vgl-2 posterior to excretory pore; ejaculatory complex (Fig. 12F): proximal chamber large, proximal horns reduced; P-2 equal in length, or only slightly shorter than P-4; distal margins of P-3 with several pointed extensions; ventral seta on P-4 relatively long and away from distal edge (Figs 12C-D). Male. Medial suture line of Cx-II+III moderately long, genital field with slightly protruding anteriolateral angles. Female: Similar to the male; the short postgenital area and caudal position of the excretory pore in the specimen from Korea are due to the obviously juvenile age (indicated by weak sclerotization and absence of eggs); medial suture line of Cx-II+III relatively long.
Measurements. Male: Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 12B) L 775, W 538; dorsal shield (Fig. 12A, 11I) L 663, W 488, ratio 1.36; dorsal plate L 606; shoulder plate L 191-194, W 75, ratio 2.5-2.6; frontal plate L 122-123, W 75, ratio 1.6; shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.6. Gnathosomal bay L 143, Cx-I total L 264, Cx-I mL 120, Cx-II+III mL 99; ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 2.7; Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.2. Genital field L/W 147/115, ratio 1.28; ejaculatory complex L 197; distance genital field-excretory pore 191, genital field-caudal idiosoma margin 264. Gnathosoma vL 152; chelicera total L 181; palp total L 199, dL: P-1, 23; P-2, 54; P-3, 40; P-4, 54; P-5, 28; P-2/P-4 ratio 1.0; dL of I-Leg-5-6 (Fig. 9G): 99, 97.
Female (from CR2, in parentheses specimen from Russia). Idiosoma (ventral view: Fig. 13B) L 725 (800), W 544 (612); dorsal shield (Fig. 13A) L 625 (680), W 488 (476), L/W ratio 1.28 (1.43); dorsal plate L 575 (620); shoulder plate L 203-206 (204), W 70-76 (74), L/W ratio 2.7-2.9 (2.76); frontal plate L 125-127 (114), W 69-70 (79), ratio 1.8 (1.43); shoulder/frontal plate L ratio 1.6 (1.79). Gnathosomal bay L 159 (132), Cx-I total L 283 (257), Cx-I mL 123 (118), Cx-II+III mL 90 (105); ratio Cx-I L/Cx-II+III mL 3.1 (2.45); Cx-I mL/Cx-II+III mL 1.4 (1.1). Genital field L/W 191 (145) /160 (112), ratio 1.19 (1.28); distance genital field-excretory pore (205), genital field-caudal idiosoma margin (277). Gnathosoma vL 162 (198); chelicera total L 202 (200); palp total L 209, dL: P-1, 28; P-2, 56 (54); P-3, 39 (40); P-4, 58 (54); P-5, 28 (19); P-2/P-4 ratio 0.97 (1.0); dL of I-Leg-4-6: 114 (103), 105 (100), 104 (94).
Monatractides abei sp. n., male holotype: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C palp, lateral view D P-4 and -5, medial view E gnathosoma and chelicera F ejaculatory complex G I–Leg-5 and -6. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Monatractides abei sp. n., paratype female, Dobong stream, Korea: A dorsal shield B ventral shield C palp, lateral view. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Photographs of selected sampling sites. A CR1 (Dobong stream, sampling site of Torrenticola recentis, Torrenticola nipponica and Monatractides abei sp. n.) B CR9 (stream in Naebyeansan NP, sampling site of Torrenticola brevirostris and Torrenticola dentifera);] C CR4 (stream in Seoraksan NP, type locality of Torrenticola kimichungi sp. n. and sampling site of Torrenticola recentis) D CR2 (Ui-dong stream, type locality of Monatractides abei sp. n. and sampling site of Torrenticola recentis) E Inje River (sampling site of Torrenticola ussuriensisis and Torrenticola turkestanica) F CR12 (stream in JiriSan NP, sampling site of Torrenticola recentis). Photos. V. Pešić.
The species is named after Dr Hiroshi Abe in appreciation of his studies on water mites.
Monatractides abei sp. n. is apparently closely related to Monatractides madritensis (K. Viets, 1930), known from the Western Palaearctic, due to the presence of an elongated ventral seta on P-4 and the similar shape of the ejaculatory complex. Males of Monatractides madritensis differ in a more slender idiosoma with subparallel lateral margins of the dorsal shield, and a slender genital field with more protruding anterior margins of the genital flaps forming a more acute angle (see:
The specimens of Monatractides abei sp. n. was collected in two sandy/bouldary streams, shaded by riparian vegetation (Fig. 14A, D); the specimens from Russia were collected from interstitial waters.
South Korea, Far East of Russia (present study).
We are indebted to Dr Hiroshi Abe (Nixon University, Fujisawa), Dr Hiroshi Kajihara (Hokkaido University, Sapporo) and Dr Hirotsugu Ono (National Museum of Nature and Science, Tokyo) for information on the type material from the collections of Masasi Enami and Taiji Imamura. The senior author thanks Ms. Hye-Ryen Choi and Dr Tomislav Karanovic (both from the Hanyang University, Seoul) for their assistance with the field work. We express deep gratitude to D.A. Sidorov and T.M. Tiunova (Institute of Biology and Soil Science, Russia) for collecting some of the material examined in this study. This study was undertaken with financial support of the discovery project of endemic species in Korea [Invertebrate part excluding insect] sponsored by NIBR Korea (NIBR No. 2013-02-001), and by the Presidium of FEBRAS grants 13-III-B-06-047, and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research grant 09-04-98544. We are thankful to an anonymous referee for the careful work and valuable comments.