(C) 2012 Chun-Cai Yan. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 (CC-BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
Two new species, Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n. and Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n. are described and illustrated as males and Chinese males of Olecryptotendipes lenzi are re-examined. A key to all known males of Olecryptotendipes is provided.
Chironomidae, Olecryptotendipes, new species, key, China
Based on the morphology of the males in the Russian Far East, Cryptotendipes lenzi Zorina, 2001 and Cryptotendipes secundus Zorina, 2003 were described by
The males of Olecryptotendipes are characterized by Y-shaped anal tergite bands; posterior part of tergite IX elongated with setae; superior volsella with sclerotized part and membranous ridge, with dorsal and ventral setae, microtrichia absent or present ventrally and weak inferior volsella (
In the present paper, two new species are recorded. Prof. Ole Sæther and Dr. M. Spies have checked the specimens. The two new species don’t belong to the genera Cryptotendipes Lenz, 1941 and Chernovskiia Sæther, 1977 because of the presence of sclerotized superior volsella and lobate inferior volsella. In addition, the species of the genus Cryptotendipes lack an inferior volsella and the margin of the gonostylus is usually with an expansion. Species of the genus Chernovskiia are also without lobate inferior volsella, but with foot-shaped superior volsella, which also present in species of genera Paracladopelma Harnisch, 1923 and Beckidia Kieffer, 1913. The Y-shaped anal tergite bands (Figs 2, 8), the shoulder-like margin of tergite IX (Figs 2, 8), the sclerotized superior volsella (Figs 4, 10) and lobate inferior volsella (Figs 3, 9) show them to belong to the genus Olecryptotendipes (O. Sæther and M. Spies, pers. comm.). However, we have no specimens of larvae and pupae which are important to place the species properly.
The larvae of Olecryptotendipes inhabit sandy substrate in rivers (
Distribution in China for the genus Olecryptotendipes. A Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n. B Olecryptotendipes lenzi Zorina C Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n.
Two new species, Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n. and Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n., are described and illustrated based on material from China and a key to the males of Olecryptotendipes is provided.
Material and methodsThe terminology follows
The type material and other material studied are housed in the College of Life Science, Department of Biology, Nankai University, Tianjin, China (BDN).
Taxonomy Amended generic diagnosisBased on
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:843E24C2-A4C2-4BDF-B681-582F6CBF1692
http://species-id.net/wiki/Olecryptotendipes_exilis
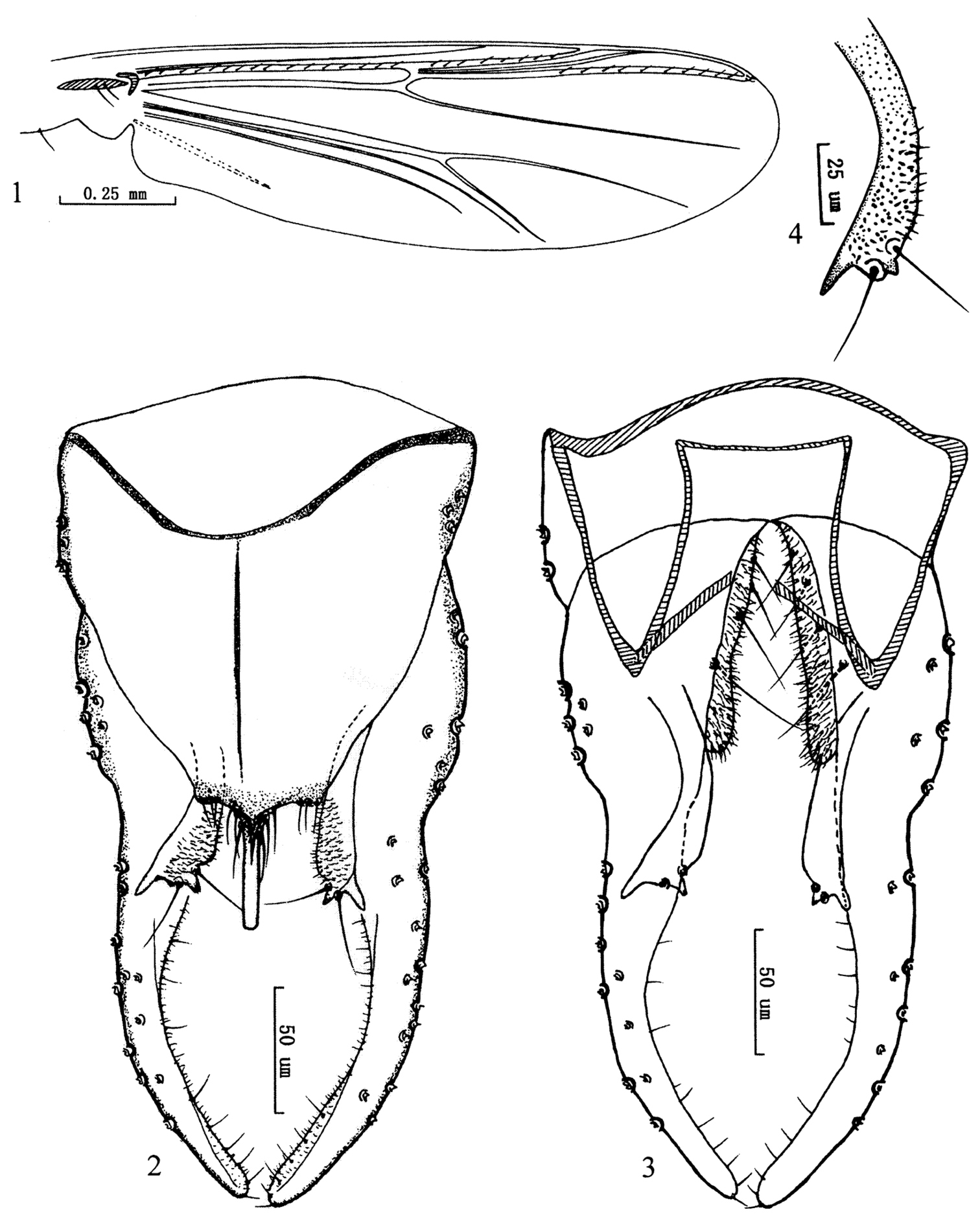
Figs 1–4The species is separated by the slender posterolateral projection of the superior volsella and the lobate inferior volsella, the posterolateral weak lobes of the anal tergite, and the parallel-sided anal point.
Male imago (n=2). Total length 2.70−2.94 mm. Wing length 1.38−1.50 mm. Total length / wing length 1.96. Wing length / length of profemur 1.92−2.08.
Coloration. Thorax and legs dark brown. Abdomen with tergite I–V yellowish brown and tergite VI–VIII and hypopygium dark brown.
Head. AR 1.97−2.02. Ultimate flagellomere 590−600 mm long. Frontal tubercles absent. Temporal 13−15 setae, including 4 inner verticals, 5−6 outer verticals and 4−5 postorbitals. Clypeus with 13 setae. Tentorium 103−110 mm long, 28−30 mm wide. Palpomere lengths (in mm): 36−38, 38−40, 118−120, 140−145, 203−210. Palp segment 5th / 3rd 1.72−1.75.
Thorax. Antepronotals with 6−7 setae, dorsocentrals 8−10, acrostichals 8, prealars 3. Scutellum with 12−13 setae.
Wing (Fig. 1). VR 1.19−120, R with 16−18 setae, R1 with 8−10 setae, R4+5 with 10−11 setae. Brachiolum 2 setae. Squama with 2−3 setae.
Legs. Front tibia with 3 subapical setae, 113−120, 138−144 and 141−150 µm long, spurs of mid tibia 30−35 and 37−46 µm long excluding comb, comb with 32−36 teeth, 10 µm long; spurs of hind tibia 28−30 and 38−47 µm long excluding comb, comb with 42−48 teeth, 10−12 µm long. Ta1 of mid legs with only 1 sensilla chaetica, sensilla chaetica absent in hind legs. Lengths (in µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 1.
Lengths (µm) and proportion of legs of Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n., male (n=2).<br/>
| Fe | ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 | ta4 | ta5 | LR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | 680−720 | 500−520 | 920−1080 | 490−515 | 380−410 | 310−320 | 150−160 | 1.84−1.08 |
| p2 | 630−650 | 530−550 | 340−365 | 190−220 | 120−135 | 70−80 | 60−70 | 0.64−0.66 |
| p3 | 700−720 | 710−725 | 480−495 | 250−260 | 220−230 | 110−115 | 90−95 | 0.68 |
Hypopygium (Figs 2−4). Tergite IX with weak lobes bearing 3−4 setae at each side of base of anal point. Laterosternite IX with 3 setae. Anal point 45−50 mm long, 5−6 mm wide, originating from caudal margin of anal tergite, completely parallel-side. Anal tergite bands Y-shaped. Phallapodeme 75−82 mm long. Transverse sternapodeme 56−60 mm long. Superior volsella (Fig. 4) slightly curved, with apical, partially sclerotized beak-like protrusion and slender spur-like posterolateral projection, bearing two long setae beside the beak-like protrusion, and covered with microtrichia in inner parts. Inferior volsella with a moderately blunt caudal projection, covered with microtrichia, and not reaching beyond margin of anal tergite. Gonocoxite 98−104 mm long, with 4 strong inner marginal setae. Gonostylus 168−175 mm long, slightly swollen at base, curved medially, moderately slender to apex, bearing 17−20 setae along inner margin. HR 0.58−0.59; HV 1.61−1.68.
Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n., male. 1 wing. 2 hypopygium (dorsal view ) 3 hypopygium (ventral view) 4 superior volsella.
Holotype ♂ (BDN No. 1291). CHINA: Hainan Province, Ledong Li Nationality Autonomous County, Jianfengling Nature Conservation area, 18°14'45.96"N, 109°30'42.69"E, 21.iv.1985, X. Wang. Paratype 1♂ (BDN No. 03578), same data as holotype.
From Latin exilis, slender, in reference to the slender posterolateral projections of superior volsella.
The species was collected in a subtropical mountain area in Hainan province in Oriental China.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Olecryptotendipes_lenzi
China, Xinjiang Autonomous Region: 13♂♂, Kaba Altay, Baihualin Nature Conservation area, 48°03'39.05"N, 86°25'7.04"E, 15−16.vii.2002, Tang HQ, sweep net.
Based on
This species is distributed in the Russian Far East and northwestern China.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:A177BD2D-75F5-43F5-A269-E0FA3D9B22DC
http://species-id.net/wiki/Olecryptotendipes_melasmus
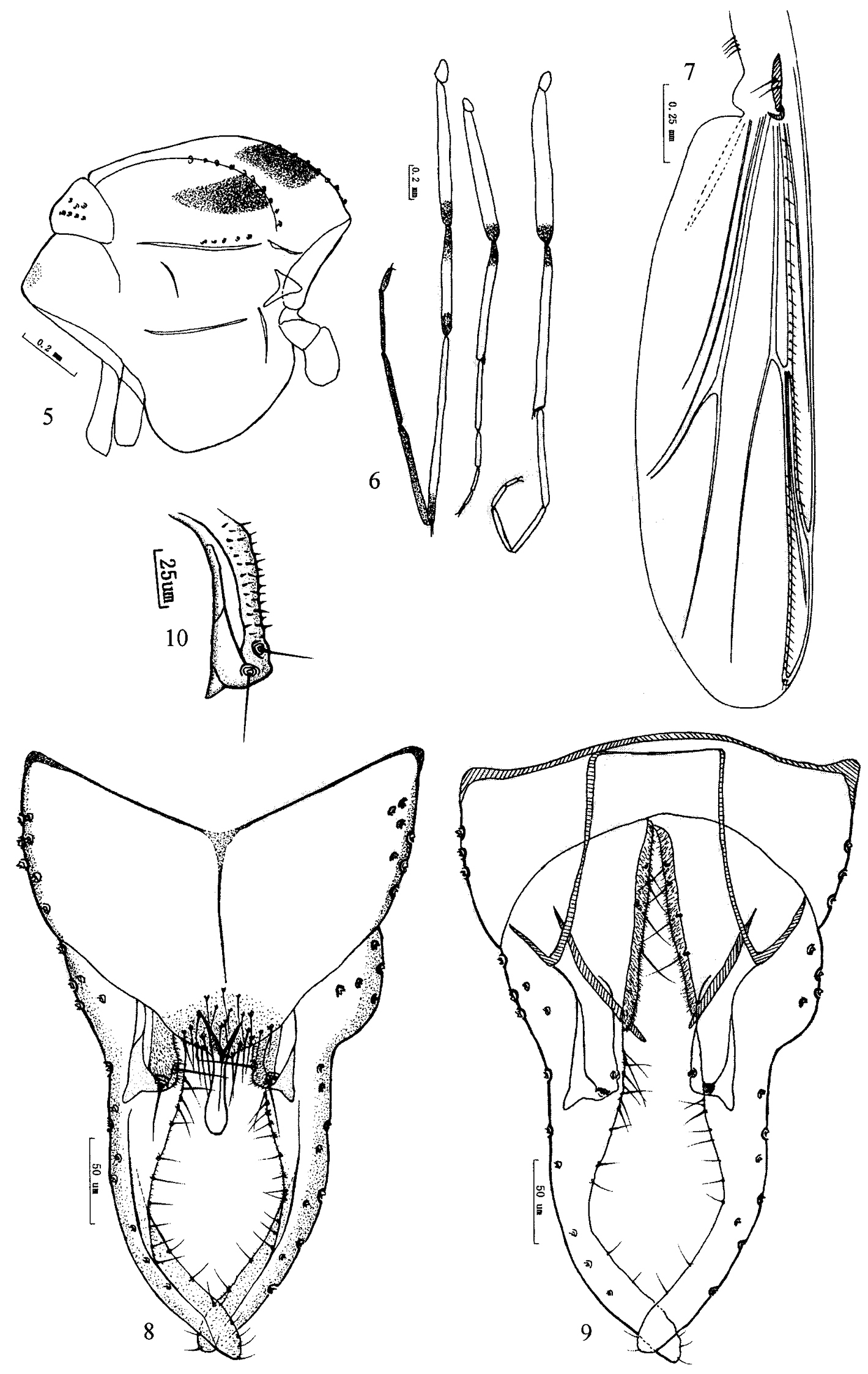
Figs 5–10The species can be separated by the blackish brown spots on thorax and legs, the distally swollen anal point and the gonostylus with basal weak expansion.
Male imago (n=2). Total length 3.13–3.60 mm. Wing length 1.50–1.88 mm. Total length / wing length 1.91–2.09. Wing length / length of profemur 2.05–2.14.
Coloration. Thorax (Fig. 5) yellowish brown, with median black brown vittae. Femur of front leg yellowish green with distal parts dark brown, tibia dark brown except for median parts yellowish green, tarsi dark brown with basal 3/4 of ta1 yellowish green; femora and tibia of mid and hind legs yellowish green with distal parts of femora and basal parts of tibia dark brown, ta1 to ta5 lightly brown (Fig. 6). Abdomen yellowish green to brown, with tergite I–V yellowish green, tergite VI–VIII and hypopygium yellowish brown.
Head. AR 1.94–2.24. Ultimate flagellomere 620–760 mm long. Frontal tubercles absent. Temporal 13–15 setae, including 4–5 inner verticals, 4–6 outer verticals and 4–5 postorbitals. Clypeus with 13–21 setae. Tentorium 113–120 mm long, 27–37 mm wide. Palpomere lengths (in mm): 37–40, 39–45, 133–172, 133–158, 193–223. Palp segment 5th / 3rd 1.30–1.45.
Thorax. Antepronotum with 2 setae, dorsocentrals 8–10, acrostichals 4–7, prealars 4–5. Scutellum with 12–15 setae.
Wing (Fig. 7). VR 1.15–1.20, R with 12–16 setae, R1 with 11–16 setae, R4+5 with 18–25 setae. Brachiolum 2 setae. Squama with 3–4 setae.
Legs. Front tibia with 3 subapical setae, 113–135, 133–150 and 145–170 µm long, spurs of middle tibia 28–30 and 35–37 µm long excluding comb, comb with 22–34 teeth, 10–11 µm long; spurs of hind tibia 30–32 and 42–43 µm long excluding comb, comb with 34–45 teeth, 10–12 µm long. Sensilla chaetica of mid and hind legs absent. Lengths (in µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 2.
Lengths (µm) and proportion of legs of Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n., male (n=2).<br/>
| Fe | Ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 | ta4 | Ta5 | LR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 730–880 | 500–650 | 1100 (1) | 580 (1) | 430 (1) | 350 (1) | 150 (1) | 1.69 (1) |
| P2 | 640–800 | 530–700 | 330–410 | 180–220 | 120–150 | 70–85 | 60 | 0.59–0.62 |
| P3 | 760–910 | 720–940 | 470–580 | 280–340 | 220–270 | 120–140 | 70–80 | 0.62–0.65 |
Hypopygium (Figs 8–10). Tergite IX with weak shoulder-like corners, bearing 13–20 setae at base of anal point. Laterosternite IX with 4–7 setae. Anal point originating from anterior of caudal margin of anal tergite in dorsal view, constricted basally, swollen apically, 43–50 mm long, 8–10 mm wide at base, 9–12 mm wide at apex. Anal tergite bands Y-shaped. Phallapodeme 68–80 mm long. Transverse sternapodeme 44–70 mm long. Superior volsella (Fig. 10) curved basally, straight distally, with large posterolateral projection, which is constricted medially forming a sharp angle, longitudinal membranous ridge present, bearing two long setae in distinct pits; covered with microtrichia in inner parts of superior volsella. Inferior volsella with reduced lobate caudal projection. Gonocoxite 85–100 mm long, with 4 strong inner marginal setae. Gonostylus 150–190 mm long, slightly swollen at base, concave medially, with rounded apex, bearing 8–20 setae along basal inner margin, and 10–14 setae along distal inner margin. HR 0.53–0.57; HV 1.89–2.09.
Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n., male. 5 thorax 6 leg 7 wing. 8 hypopygium (dorsal view) 9 hypopygium (ventral view) 10 superior volsella.
Holotype ♂ (BDN No. 04250). CHINA: Shaanxi Province, Baoji City, Feng County, Qinling, Dongyu, 33°54'42.03"N, 106°31'21.10"E, 30. vii. 1994, sweep net, W. Bu. Paratype (BDN No. 20598). CHINA: 1♂, Fujian Province, Jianning County, 26°49'51.25"N, 116°50'45.90"E, 25. ix. 2002, light trap, Z. Liu.
From Greek, melasma, spot, in reference to the dark brown spots on the thorax and legs.
The species is known from Palaearctic and Oriental China (Shaanxi Province; Fujian Province).
Male diagnosis: Based on the variation in Chinese material (Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n., Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n.), the generic description given by
Based on the description and figures of
| 1 | Acrostichals absent; R and R1 without setae; superior volsella lacking microtrichia ventrally | Olecryptotendipes secundus (Zorina) |
| – | Acrostichals present; R and R1 with setae; superior volsella with microtrichia ventrally | 2 |
| 2 | Anal point swollen distally; thorax with dark brown spots | Olecryptotendipes melasmus sp. n. |
| – | Anal point parallel-sided, thorax without dark brown spots | 3 |
| 3 | Inferior volsella absent, gonostylus parallel-sided | Olecryptotendipes lenzi (Zorina) |
| – | Inferior volsella lobe-like, gonostylus swollen at base, moderately slender to apex | Olecryptotendipes exilis sp. n. |
We want to thank Dr. M. Spies (Zoologische Staatssammlung München, Germany) and Prof. Ole Sæther (University of Bergen, Norway) for checking the specimens and providing lots of input on various levels of this work. Mr. Bingchun Ji and Mrs. Yufen Li made the slide preparations. Financial support received from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grants No. 31101653, 30870329 and Fauna of China (FY120100); the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (20090226);Tianjin City High School Science & Technology Fund Planning Project (20090608) and Tianjin Normal University Talent Introduction Foundation (5RL104) are thankfully acknowledged.