(C) 2012 Xiaolong Lin. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 (CC-BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
Two new species of Bryophaenocladius Thienemann, 1934, Bryophaenocladius mucronatus sp. n. and Bryophaenocladius parictericus sp. n. are described and illustrated as males. A key to male imagines of the genus from China is presented.
Chironomidae, Bryophaenocladius, new species, key, China
The genus Bryophaenocladius was erected by Thienemann in 1934 with Orthocladius muscicola Kieffer, 1906 as type species. To date, more than 100 species have been recorded all over the world (
The adult males of most Bryophaenocladius species can be recognized by strong and decumbent acrostichals beginning close to antepronotum; wing membrane without setae, but with coarse punctation visible at 40x magnification, squama with one to several setae; tibial spurs strongly developed, with well developed, but not divergent lateral denticles; hind tibial comb well developed; sensilla chaetica absent; tergite IX distinctive, with strongly pigmented, semi-circular band running around posterior margin; anal point projecting from setose area, large, semicircular to triangular; virga consisting of simple spines; gonostylus often distinctly broadened, strong megaseta (
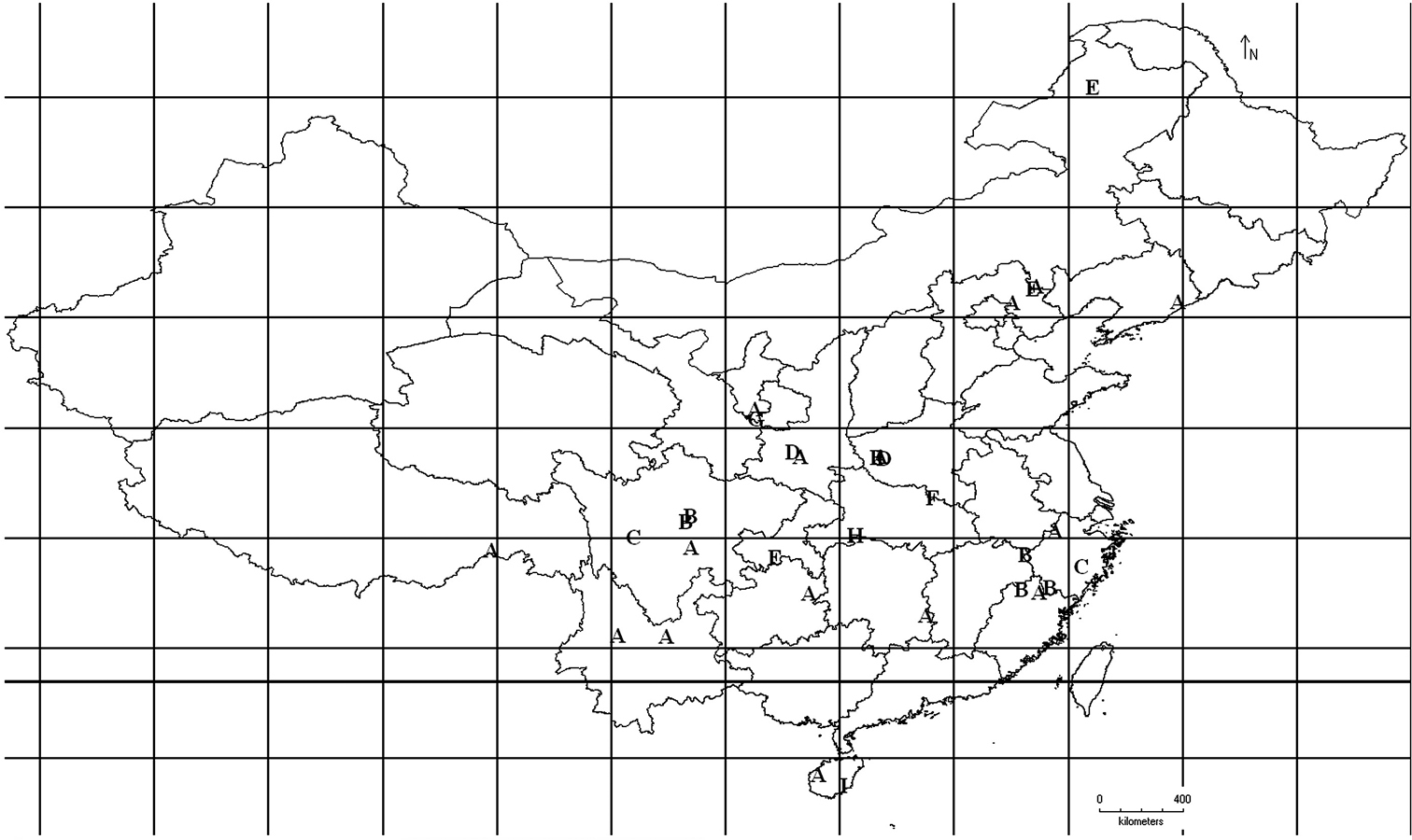
After examinzing the type specimen of Bryophaenocladius bicolor Wang, Sæther & Andersen, 2001 and the specimens of Bryophaenocladius ictericus (Meigen, 1830) collected from Canada, China and Sweden, two new species from oriental China are described. A key to male imagines of Bryophaenocladius from China and a distribution map of genus Bryophaenocladius in China is presented (Fig. 1).
Distribution in China for the genus Bryophaenocladius A Bryophaenocladius cuneiformis Armitage, 1987 B Bryophaenocladius mucronatus sp. n. C Bryophaenocladius parictericus sp. n. D Bryophaenocladius parimberbus Du & Wang, 2010 E Bryophaenocladius propinquus (Brundin, 1947) F Bryophaenocladius scanicus (Brundin, 1947). G Bryophaenocladius vernalis (Goetghebuer, 1921) H Bryophaenocladius wufengensis Du & Wang, 2010 I Bryophaenocladius xinglongensis Du & Wang, 2010.
The morphological nomenclature follows
| 1 | Third palpomere with apical projection | 2 |
| – | Third palpomere without apical projection | 4 |
| 2 | Squama with setae; AR>1.0 | 3 |
| – | Squama bare; AR<1.0 | Bryophaenocladius parictericus sp. n. |
| 3 | Inferior volsella unobvious | Bryophaenocladius xinglongensis Du & Wang, 2010 |
| – | Inferior volsella obvious | Bryophaenocladius cuneiformis Armitage, 1987 |
| 4 | Squama bare | 5 |
| – | Squama setose | 6 |
| 5 | Crista dorsalis absent; inferior volsella obvious | Bryophaenocladius vernalis (Goetghebuer, 1921) |
| – | Crista dorsalis present; inferior volsella unobvious | Bryophaenocladius parimberbus Du & Wang, 2010 |
| 6 | Anal point broad | 7 |
| – | Anal point slender | 8 |
| 7 | Inferior volsella finger-shaped | Bryophaenocladius propinquus (Brundin, 1947) |
| – | Inferior volsella almost rectangular | Bryophaenocladius scanicus (Brundin, 1947) |
| 8 | Pseudospurs present on ta1, ta2 of mid and hind legs | Bryophaenocladius mucronatus sp. n. |
| – | Pseudospurs absent | Bryophaenocladius wufengensis Du & Wang, 2010 |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:09174531-D113-4061-B288-6627445DFCAF
http://species-id.net/wiki/Bryophaenocladius_mucronatus
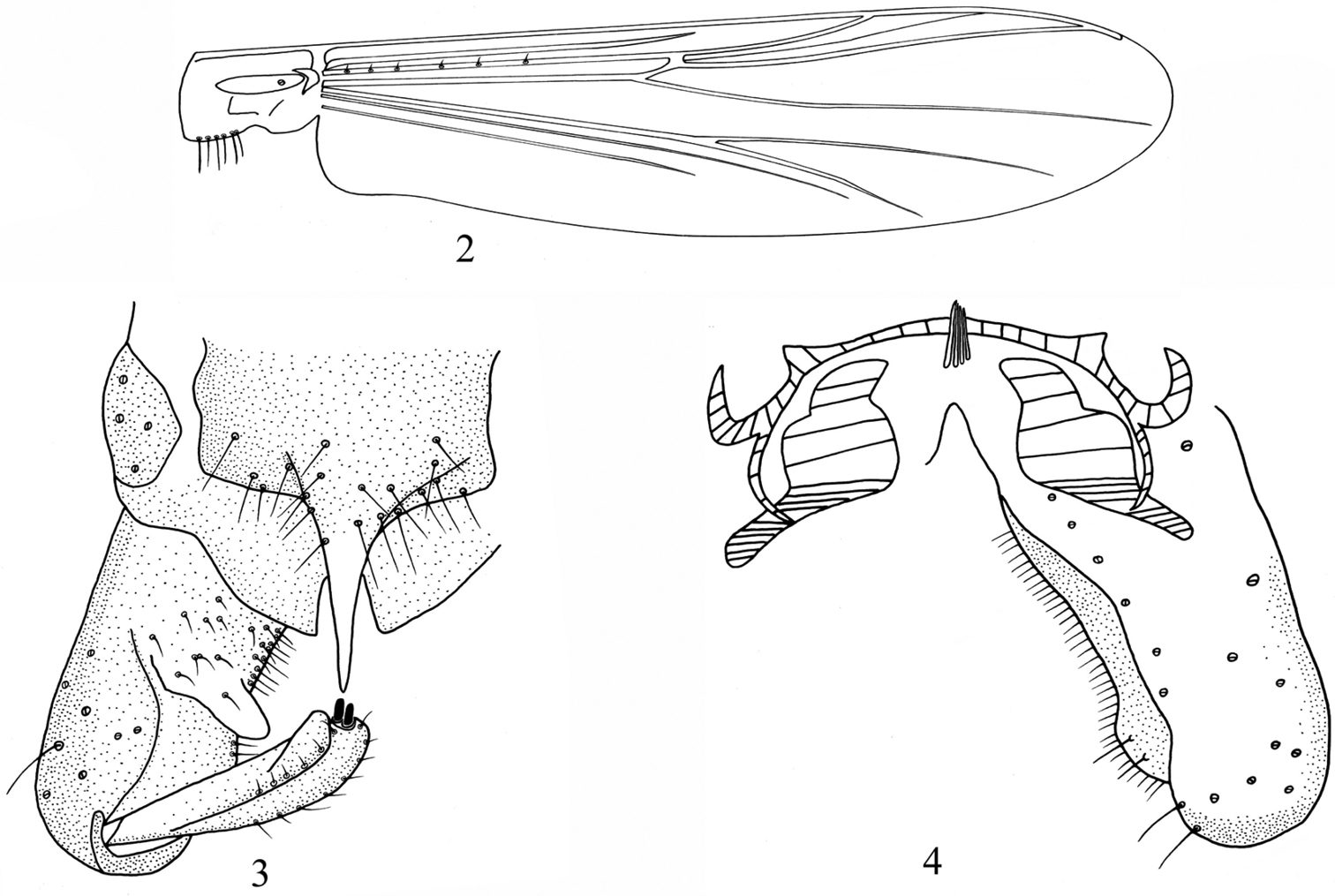
Figures 2–4The male imago can be distinguished from known species of the genus by the following combination of characters: third palpomere without apical digitiform projection; squama with 1–7, 4 setae; pseudospurs present on ta1 and ta2 of mid and hind legs; anal point hyaline, slender with pointed apex; tergite IX columnar; inferior volsella thumb-shaped, with 0–5, 3 setae.
Male imago (n = 29). Total length 2.20–3.00, 2.51 mm. Wing length 1.33–1.76, 1.55 mm. Total length/wing length 1.43–1.90, 1.65. Wing length/length of profemur 2.50–3.34, 2.75.
Coloration.Dark brown.
Head. AR 1.13–1.43, 1.26. Ultimate flagellomere 415–455, 430 μm long. Temporal setae 7–11, 9 including 2–4, 3 inner verticals; 4–6, 5 outer verticals and 1–2, 2 postorbitals. Clypeus with 2–5, 3 setae. Tentorium 105–150, 130 μm long, 18–25, 20 μm wide. Stipes 105–110, 108 μm long, 7–10, 8 μm wide. Palpomere lengths (in μm): 20–50, 35; 30–95, 47; 55–110, 80; 60–100, 80; 100–125, 113. L: 5th/3rd 1.40–1.82, 1.56. Third palpomere without apical digitiform projection.
Wing (Fig. 2). Anal lobe developed. Coarse punctation easily visible at 40x magnification. VR 1.16–1.33, 1.26. Costa extension 40–63, 48 μm long. Brachiolum with 1–3, 2 setae. R with 3–6, 4 setae; R4+5 with 0–1, 0 seta. Remaining veins bare. Squama with 1–7, 4 setae.
Thorax. Antepronotum with 3–8, 4 lateral setae. Dorsocentrals 5–13, 9; acrostichals 3–10, 7; prealars 2–5, 3. Scutellum with 2–8, 4 setae.
Legs. Spur of fore tibia 16–65, 45 μm long; spurs of mid tibia 20–40, 33 μm and 12–27, 20 μm long; spurs of hind tibia 42–58, 50 μm and 11–40, 23 μm long. Lateral denticles appressed to main shaft. Hind tibial comb with 6–16, 13 spines. Pseudospurs present on ta1 and ta2 of mid and hind legs, 18–23, 20 μm long. Width at apex of fore tibia 23–38, 30 mm, of mid tibia 25–35, 27 mm, of hind tibia 30–40, 35 mm. Lengths (in μm) and proportions of legsas in Table 1.
Lengths (in μm) and proportions of legs of Bryophaenocladius mucronatus sp. n.
| P1 | P2 | P3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| fe | 500–594, 553 | 588–650, 622 | 580–690, 643 |
| ti | 620–783, 723 | 570–704, 661 | 648–810, 765 |
| ta1 | 370–450, 415 | 240–324, 288 | 300–450, 415 |
| ta2 | 220–270, 240 | 140–190, 170 | 160–250, 220 |
| ta3 | 160–200, 180 | 105–135, 123 | 135–200, 173 |
| ta4 | 105–130, 118 | 60–90, 75 | 80–110, 95 |
| ta5 | 80–100, 86 | 60–95, 80 | 75–100, 88 |
| LR | 0.52–0.63, 0.57 | 0.42–0.48, 0.45 | 0.46–0.59, 0.55 |
| BV | 2.59–2.62, 2.61 | 3.37–3.57, 3.47 | 3.13–3.28, 3.19 |
| SV | 2.96–3.10, 3.03 | 4.32–4.58, 4.47 | 3.16–3.51, 3.31 |
| BR | 2.17–2.86, 2.41 | 2.22–3.00, 2.47 | 3.33–4.35, 3.81 |
Hypopygium (Figs 3–4). Anal point hyaline, slender, with pointed apex, 45–90, 70 μm long, 25–35, 30 μm wide. Anal point length/width: 2.14–2.71, 2.45. Tergite IX columnar, with 10–22, 15 setae, laterosernite IX with 4–8, 6 setae. Phallapodeme 45–85, 70 μm long. Transverse sternapodeme arcuate with developed oral projection, 68–100, 88 μm long. Gonocoxite 175–212, 190 μm long. Gonostylus 68–100, 87 μm long with 1–2, 1 megaseta, 8–13, 10 μm long. Crista dorsalis low. Inferior volsella thumb-shaped, 23–35, 27 μm long, with 0–5, 3 setae. Virga 10–25, 16 μm long, composed of 1–9, 5 spines. HR 1.95–2.36, 2.12. HV 2.59–3.00, 2.71.
Holotype: ♂ (BDN. I4B20), China, Zhejiang Province: Quzhou City, Kaihua County, Gutian Mountain, 29°14'35"N, 118°06'41"E, 18.iv.2011, Lin XL, sweeping net. Paratypes (28♂♂): 2♂♂, as holotype; 1♂, Zhejiang Province, Lishui City, Qinyuan County, 27°45'08"N, 119°12'26"E, 15.iv.1994, Wu H, sweeping net; Fujian Province: 11♂♂, Wuyi Mountain, 27°38'22"N, 117°56'56"E, 26.iv.1993, Wang XH, sweeping net; Sichuan Province: 7♂♂, Wenchuan County, 30°59'27"N, 103°26'44"E, 14.vii.1987, Li XZ, sweeping net; 7♂♂, Wolong National Nature Reserve, 30°45'23"N, 103°13'55"E, 27.vii.1987, Li XZ, sweeping net.
The species name is from Latin mucronatus, pointed, referring to the shape of apex of anal point.
The present new species resembles to Bryophaenocladius bicolor Wang, Sæther & Andersen, 2001 in the shape of anal point, but it can be separated from Bryophaenocladius bicolor in the following combination of characters in Table 2.
Differences between Bryophaenocladius mucronatus sp.n. and Bryophaenocladius bicolor Wang, Sæther & Andersen, 2001.
| Bryophaenocladius mucronatus sp. n. | Bryophaenocladius bicolor Wang, Sæther & Andersen, 2001 | |
|---|---|---|
| Finger-shaped extension on third palpomere | absent | present |
| Seta on R1 | bare | 4–5 setae |
| LR1 | 0.52–0.63, 0.57 | 0.76–0.82, 0.80 |
| Pseudospurs | present on ta1, ta2 of mid and hind legs | absent |
| Crista dorsalis | present | reduced |
Female and immature stages unknown.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:125AC1CD-0CD6-46B4-AACF-D43C1084EFA6
http://species-id.net/wiki/Bryophaenocladius_parictericus
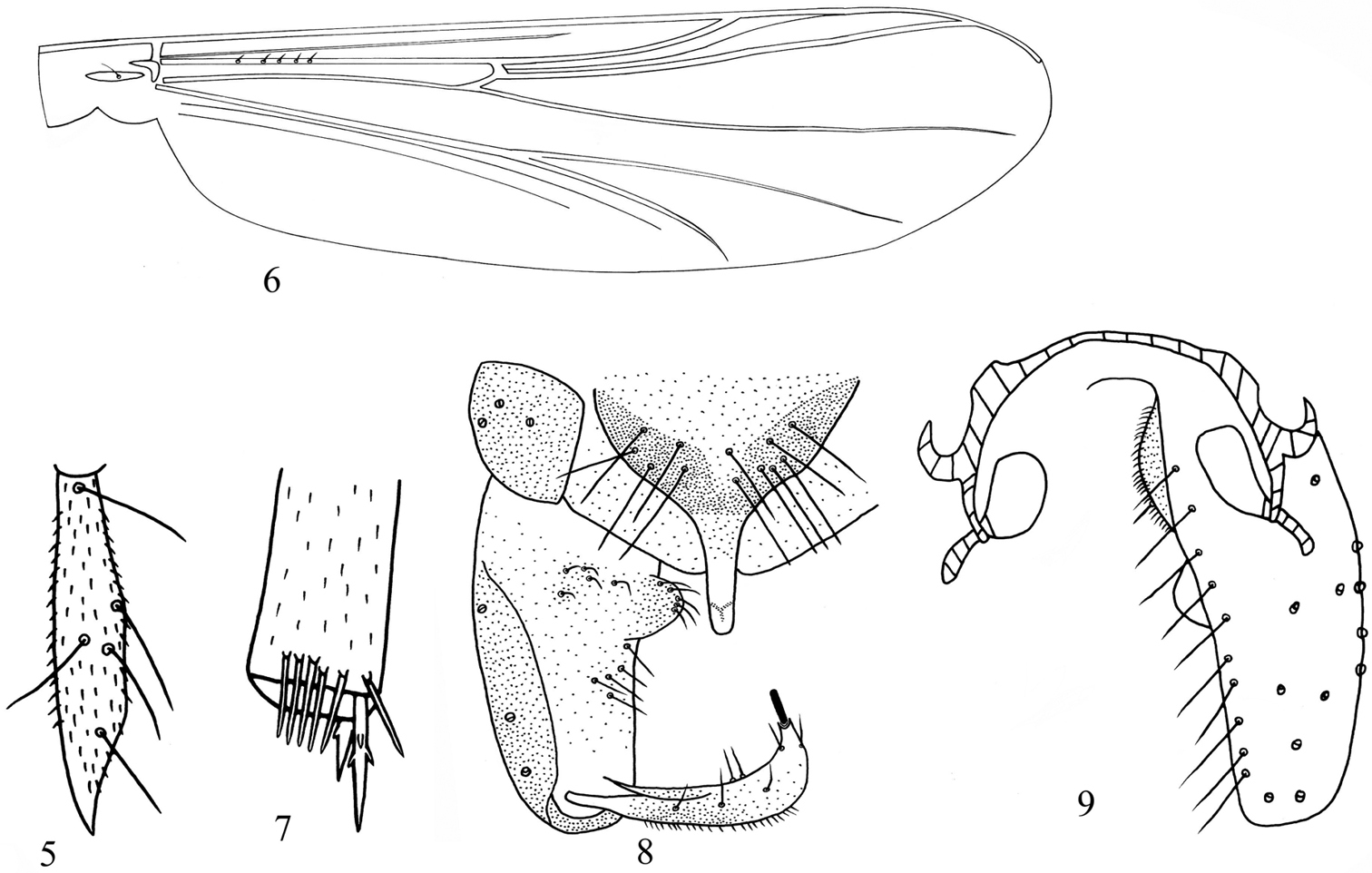
Figs 5–9The male imago can be distinguished from known species of the genus by the following combination of characters: AR 0.52–0.55; third palpomere with apical digitiform projection; Costa extension 115–143, 122 μm long; squama bare; mid tibia comb with 3–7, 5 spines; anal point hyaline, slender with blunt apex; crista dorsalis absent; inferior volsella bubble-shaped, with 8–12, 9 setae.
Male imago (n = 6). Total length 2.65–3.08 2.76 mm. Wing length 1.63–2.48, 2.22 mm. Total length/wing length 1.10–1.46, 1.26. Wing length/length of profemur 2.78–3.19, 3.03.
Coloration. Dark brown.
Head (Fig. 5). AR 0.52–0.55 (n = 2). Ultimate flagellomere 230–245 (n = 2) μm long. Temporal setae 3–9, 7 including 2–7, 4 inner verticals; 0–4, 2 outer verticals and 0–2, 1 postorbital. Clypeus with 4–7, 5 setae. Tentorium 109–148, 129 μm long, 15–25, 20 μm wide. Stipes 80–100, 90 μm long, 5–8, 6 μm wide. Palpomere lengths (in μm): 16–25, 20; 35–52, 41; 90–143, 114; 42–65, 57; 60–80, 71. L: 5th/3rd 0.76–0.80, 0.78. Third palpomere with apical digitiform projection.
Wing (Fig. 6). Anal lobe not developed. Coarse punctation easily visible at 40x magnification. VR 1.02–1.23, 1.17. Costa extension 115–143, 122 μm long. Brachiolum with 1 seate. R with 5–9, 7 setae. Remaining veins bare. Squama bare.
Thorax. Antepronotum with 2–5, 3 lateral setae. Dorsocentrals 8–10, 9; acrostichals 6–7, 7; prealars 2–4, 3. Scutellum with 3–7, 6 setae.
Legs (Fig. 7). Spur of fore tibia 40–58, 48 μm long; spurs of mid tibia 30–42, 38 μm and 21–32, 25 μm long; spurs of hind tibia 40–63, 52 μm and 21–32, 28 μm long. Lateral denticles appressed to main shaft. Mid tibial comb with 3–7, 5 spines; hind tibial comb with 9–14, 12 spines. Mid and hind legs without tarsal pseudospurs. Width at apex of fore tibia 35–45, 40 mm, of mid tibia 33–38, 36 mm, of hind tibia 40–48, 45 mm. Lengths (in μm) and proportions of legs in Table 3.
Lengths (in μm) and proportions of legs of Bryophaenocladius parictericus sp. n.
| P1 | P2 | P3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| fe | 510–893, 718 | 600–914, 798 | 620–977, 735 |
| ti | 710–1134, 916 | 660–987, 873 | 770–1260, 994 |
| ta1 | 360–670, 558 | 320–504, 427 | 400–683, 611 |
| ta2 | 240–389, 322 | 170–263, 232 | 220–315, 282 |
| ta3 | 180–273, 235 | 140–189, 176 | 180–284, 233 |
| ta4 | 100–147, 132 | 70–105, 98 | 80–126, 115 |
| ta5 | 70–108, 96 | 70–95, 87 | 70–105, 95 |
| LR | 0.51–0.64, 0.58 | 0.45–0.51, 0.48 | 0.52–0.58, 0.54 |
| BV | 2.68–2.92, 2.84 | 3.22–3.68-3.47 | 3.25–3.35, 3.30 |
| SV | 3.24–3.39, 3.31 | 3.94–4.11, 4.01 | 3.31–3.48, 3.39 |
| BR | 2.14–2.67, 2.33 | 2.00–2.14, 2.09 | 1.50–2.11, 2.01 |
Hypopygium (Figs 8–9). Anal hyaline, slender with blunt apex, 40–55, 48 μm long, 15–20, 18 μm in width. Anal point length/width: 2.22–2.75, 2.51. Tergite IX with 6–13, 9 setae, laterosernite IX with 3–5, 4 setae. Phallapodeme 48–91, 77 μm long. Oral projection of transverse sternapodeme vestigial, 75–96, 85 μm long. Gonocoxite 170–221, 194 μm long. Gonostylus slightly curved, 80–101, 92 μm long. Megaseta 13–21, 18 μm long. Crista dorsalis absent. Inferior volsella bubble-shaped, 18–27, 22 μm long, with 8–12, 9 setae. Virga absent. HR 1.88–2.50, 2.08. HV 2.62–3.48, 3.02.
Holotype: ♂ (BDN. K7A22), China, Zhejiang Province: Taizhou City, Xianju County, Shenxianju Scenic Area, 28°42'14"N, 120°36'25"E, 14.iv.2011, Lin XL, sweeping net. Paratypes (5♂♂): 1♂, as Holotype; Sichuan Province: 4♂♂, Yajiang County, 30°01'52"N, 101°00'52"E, 10.vi.1996, 3050 meters above sea level, Wang XH, sweeping net.
Named in closing to the species Bryophaenocladius ictericus (Meigen, 1830).
The present new species resembles to Bryophaenocladius ictericus (Meigen, 1830) in the shape of inferior volsella, but it can be separated by following combination of characters in Table 4.
Differences between Bryophaenocladius parictericus sp. n. and Bryophaenocladius ictericus (Meigen, 1830)
| Bryophaenocladius parictericus sp. n. | Bryophaenocladius ictericus (Meigen, 1830) | |
|---|---|---|
| Antennal ratio (AR) | 0.52–0.55 | 1.19–1.73, 1.56 |
| Finger-shaped extension on third palpomere | present | absent |
| Length of Costal extension | 115–143, 122 μm | 64–105, 98 μm |
| Length of megaseta | 13–21, 18 μm | 7–14, 11 μm |
| Gonostylus | bended | straight |
| Virga | absent | present |
Female and immature stages unknown.
Financial support from the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Y3100486, Y3110395), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, grant No. 30570207, J0630963), Fauna of China (FY120100) and the Science Foundation of Taizhou University (No. 2012QN18) are acknowledged with thanks. We also thank Jing Du for discussing some questions on the taxonomy of Bryophaenocladius.