Three new species of Potamothrix Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902 (Oligochaeta: Tubificinae), Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n., Potamothrix paramoldaviensis sp. n. and Potamothrix parabedoti sp. n., are reported from Fuxian Lake of Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Potamothrix praeprostatusdiffers from its allies by its prostate glands joining atria in its proximal to middle portion, and spermathecal chaetae. Potamothrix paramoldaviensis is distinguishable from its allies by having penial chaeta but no penes, and differs from Potamothrix moldaviensisby its homogenous atrium. Potamothrix parabedoti is distinctive in the position of its reproductive organs, and differs from Potamothrix bedoti by its homogenous atrium. Hitherto, 34 freshwater oligochaete species have been recorded in Yunnan Province, including nine endemic species from the plateau lakes.
Potamothrix, Naididae, Tubificinae, taxonomy, new species, Yunnan Province, China
The existence of unique faunae in ancient lakes of Yunnan Province, Southwest China has been recognized in several studies (
Being the deepest lake on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, the Fuxian Lake (24°17'–37'N, 102°49'–57'E) is located in the eastern part of Yunnan Province, and it discharges into the upper reaches of Nanpanjiang River. The lake covers an area of 211 km2 at its surface water-level of 1721 m ASL, attaining a maximum depth of 155 m and a shoreline development (DL) of 1.72. For other characteristics of the lake, the reader may refer to our three previous accounts (
Lake sediment samples were collected with a weighted Petersen grab (1/16 m2) and cleaned with a 250 µm sieve. Large worms were manually sorted in a white porcelain dish and small ones were sorted under a dissecting microscope. Specimens were all preserved in 10% formalin.
Preserved specimens were examined first in temporary glycerine mounts, then stained with borax carmine, dehydrated in an alcohol series, cleared in xylene and mounted in Canada balsam. Measurements of body and chaeta were made from the glycerine mounts. Other observations were made on the permanent mounts. Drawings were made using a camera lucida. Types and other specimens were deposited in Institute of Hydrobiology (IHB), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Wuhan, China.
Abbreviation used in the figuresRoman numerals = segment number; at = atrium; mu = muscle; pc = penial chaeta; pe = penis; pr = prostate gland; ps = penial sac; sa = spermathecal ampulla; sc = spermathecal chaeta; scs = spermathecal chaeta sac; sd = spermathecal duct; sf = sperm funnel; sz = spermatozeugmata; vd = vas deferens.
TaxonomyPotamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovský and Mrázek, 1902
Hair chaetae present or absent, dorsal chaetae bifid and always pectinated, or only bifids. Ventral chaetae bifids. No coelomocytes. Vas deferens very short, entering atrium apically; atrium tubular, long. Prostate gland small, attached to proximal part of atrium by a short stalk, or no prostate gland. No ejaculatory duct. Penis with or without cuticular sheath. Spermatozeugmata present. Modified spermathecal chaetae present or absent.
The genus Potamothrix, established by
Principal distinguishing characteristics of the species of Potamothrix
| No | Species | Chaetae | Length ratio of vd/at | Prostate gland | Atrium | Penis | Distribution | References | |||
| Hair | Dorsal bifid | Spermathecal | Penial | ||||||||
| 1 | Potamothrix alatus Finogenova, 1972 | present | pectinated | present | absent or unmodified | 1:33–35 | present | tripartite | present | Russia |
|
| 2 | Potamothrix bavaricus (Oschmann, 1913) | present | pectinated | present | unmodified | 1:8–9 | absent | tripartite | present | Holarctic, Australia, New Zealand |
|
| 3 | Potamothrix bedoti (Piguet, 1931) | present | pectinated | present | unmodified | 1:25–30 | absent | tripartite | present | Europe, North America, China |
|
| 4 | Potamothrix caspicus (Lastočkin, 1937) | absent | bifid | absent, or 2–3 bifids | absent or unmodified | 1:22–26 | present | bipartite | present | Russia |
|
| 5 | Potamothrix cekanovskajae Finogenova, 1972 | absent | bifid | absent, or 4–5 bifids | unmodified | 1:28–31 | absent | bipartite | present | Caspian Sea |
|
| 6 | Potamothrix danubialis (Hrabĕ, 1941) | absent | bifid | present | absent or unmodified | 1:15–17 | present | bipartite | present | Russia |
|
| 7 | Potamothrix hammoniensis (Michaelsen, 1901) | present | pectinated | present | absent or unmodified | 1:40–45 | present | bipartite | present | Holarctic |
|
| 8 | Potamothrix heuscheri (Bretscher, 1900) | present | pectinated | present | unmodified | 1:20 | absent | tripartite | present | Europe, Israel |
|
| 9 | Potamothrix isochaetus (Hrabĕ, 1931) | absent | bifid | present | - | - | present | - | present | Europe |
|
| 10 | Potamothrix manus Finogenova, 1972 | absent | bifid | present | unmodified | 1:14–17 | absent | bipartite | present | Caspian Sea |
|
| 11 | Potamothrix marzeki (Hrabĕ, 1941) | absent | bifid | absent, or 1–2 bifids | absent or unmodified | 1:22–24 | present | bipartite | present | Russia, Czech |
|
| 12 | Potamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902 | absent | bifid | present | unmodified | 1:20–32 | absent | tripartite | present | Holarctic |
|
| 13 | Potamothrix ochridanus (Hrabĕ, 1931) | present | bifid | absent | unmodified | - | present | - | present | North America, Serbia |
|
| 14 | Potamothrix orientalis (Černosvitov, 1938) | present | bifid | present | - | - | absent | - | - | North America |
|
| 15 | Potamothrix postojnae Karaman, 1974 | present | pectinated | absent | - | - | present | homo-geneous | - | Slovenia |
|
| 16 | Potamothrix prespaensis (Hrabĕ, 1931) | present | bifid | present | - | - | absent | - | present | Serbia |
|
| 17 | Potamothrix svirenkoiLastočkin, 1937 | present | bifid | present | - | - | present | - | - | Europe, Russia |
|
| 18 | Potamothrix thermalis (Pop, 1968) | present | pectinated | present | unmodified | 1:20 | present | tripartite | present | Romania |
|
| 19 | Potamothrix tudoranceai Šporka, 1994 | present | pectinated | present | - | 1:34 | absent | homo-geneous | present | Africa |
|
| 20 | Potamothrix vejdovskyi (Hrabĕ, 1941) | present | bifid | present | absent or unmodified | 1:30–33 | present | bipartite | present | Europe, North America |
|
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:A45887B2-F06C-4F6C-B66E-A6F65DACD01B
IHB YAN 20021205b, mature specimen mounted in Canada balsam, and stained with borax carmine.
East of Lichang (24°32'04"N, 102°51'43"E) in Fuxian Lake, eastern Yunnan, China; depth 113 m, bottom temperature 13.5°C, dissolved oxygen at bottom 5.2 mg/L, total nitrogen in water 0.164 mg/L, total phosphorus in water 0.037 mg/L, fine clay; Dec 11, 2002, coll. Y. Cui and X. Liu.
“prae” and “prostatus” are Latin for “proximal” and “prostate”, respectively. The specific name refers to the prostate glands proximally attached to atria.
One complete specimen 7.6 mm long, diameter at XI about 0.8 mm, 27 segments. Prostomium conical. Clitellum inconspicuous.
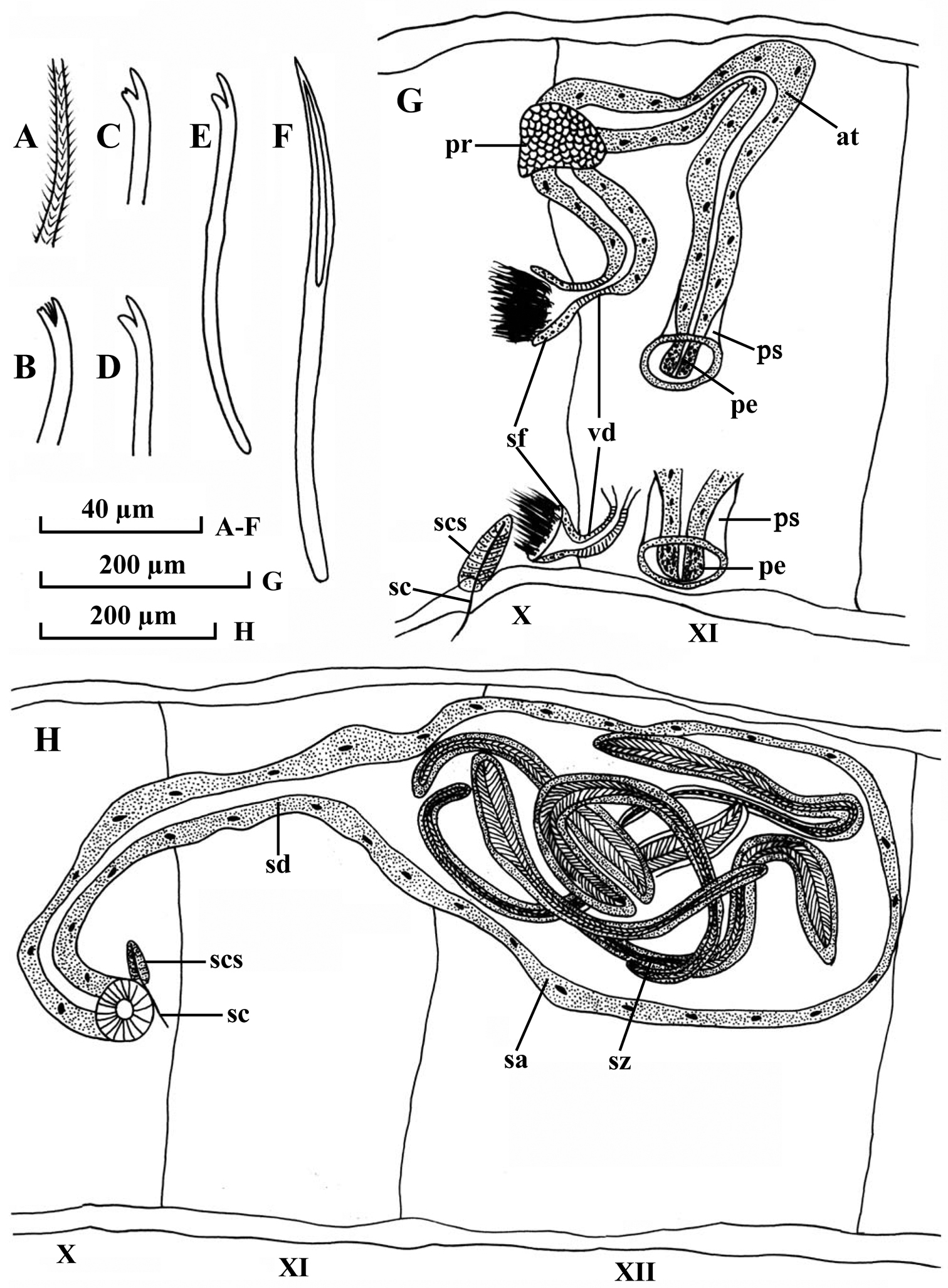
Dorsal chaetae (Fig. 1C–D) of II–IV bifid only, 7–10 per bundle, 135–148 µm long, 3.0–3.5 µm thick, upper tooth longer and thinner than lower, lower tooth occasionally bifurcated. Dorsal bundles of V–X with 5–8 hair chaetae and 5–7 bifid chaetae; plumose hair chaetae (Fig. 1A), 240–420 µm long, 2.6–3.2 µm thick basally; pectinate bifid chaetae (Fig. 1B), 120–140 µm long, 2.8–3.2 µm thick, with 1–2 intermediate teeth, upper tooth slightly longer and thinner than lower tooth (usually bifurcated), or equally long. Dorsal bundles in posterior segments with 1–4 hair chaetae and 2–6 bifid chaetae, shorter and thinner than those of anterior segments, hair chaetae 280–320 µm long, bifid chaetae 90–110 µm long, 2.6–2.8 µm thick. Ventral chaetae (Fig. 1D–E) bifid, 6–8 per bundle anteriorly, 140–150 µm long, 3.0–3.5 µm thick; 2–4 (5) per bundle in postclitellar segments, 80–110 µm long, 2.4–3.2 µm thick, all with teeth similar to the ones in dorsal chaetae in II-IV. Spermathecal chaetae (Fig. 1F, H, sc) one per bundle in middle to posterior of X, entally embedded in glandular sacs, about 145–160 µm long, 4.0 µm thick, with ectal part grooved. Penial chaetae absent. Male pores paired in line with ventral chaetae, anterior to middle of XI. Spermathecal pores paired in line with ventral chaetae, posterior to middle of X, immediately anterior to spermathecal chaetae.
Pharyngeal glands in II–III. Chloragogen cells from VI onwards. No coelomocytes. Male genitalia (Fig. 1G) paired. Vasa deferentia (Fig. 1G, vd) 38–65 µm long, 16–22 µm wide, entering atria apically. Atria (Fig. 1G, at) 690 µm long, 28–80 µm wide, tubular and rather homogenous throughout, with thin outer muscular layer and thick inner epithelium. Prostate glands (Fig. 1G, pr) small, proximally attached to atria, and far from vasa deferentia. Soft part of penis (Fig. 1G, pe) small, 38–54 µm long, 22–44 µm wide, cylindrical, enclosed in penial sacs. Penial sacs (Fig. 1G, ps) 65–80 µm long, 54–80 µm wide, with muscular layer 3–4 µm thick.
Spermathecae (Fig. 1H) in X–XII, ducts (Fig. 1H, sd) 470–490 µm long, 38–65 µm wide, ampullae (Fig. 1H, sa) elongated, 520–540 µm long, maximally 300–315 µm wide. Spermatozeugmata (Fig. 1H, sz) 5–8 in each ampulla, about 300–460 µm long.
Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n., A hair B distal end of dorsal bifid from V C distal end of dorsal bifid from III D distal end of ventral chaeta from V E ventral chaeta from III F spermathecal chaeta G lateral view of male ducts in segments X–XI H lateral view of spermatheca in segments X–XII. Scale bars: A–F 40 µm; G–H 200 µm.
Known only from its type locality, Yunnan Province, China; freshwater lake, 113 m depth, water temperature less than 14 °C, fine clay.
According to short vasa deferentia, long tubular atria, each with a small prostate gland, and lack of ejaculatory ducts, the new species fits more closely the definition of Potamothrix Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902 than that of any other described tubificine genus (
Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n. differs from its allies by its prostate glands joining atria in their proximal to middle portion. With regard homogenous atria with prostate glands, the new species is similar to Potamothrix postojnae Karaman, 1974, Potamothrix scleropenis Cui & Wang, 2005, Potamothrix aductus Cui & Wang, 2012, and Potamothrix paramoldaviensis sp. n. However, these species differ from Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n. in thatPotamothrix postojnae has no spermathecal chaeta (
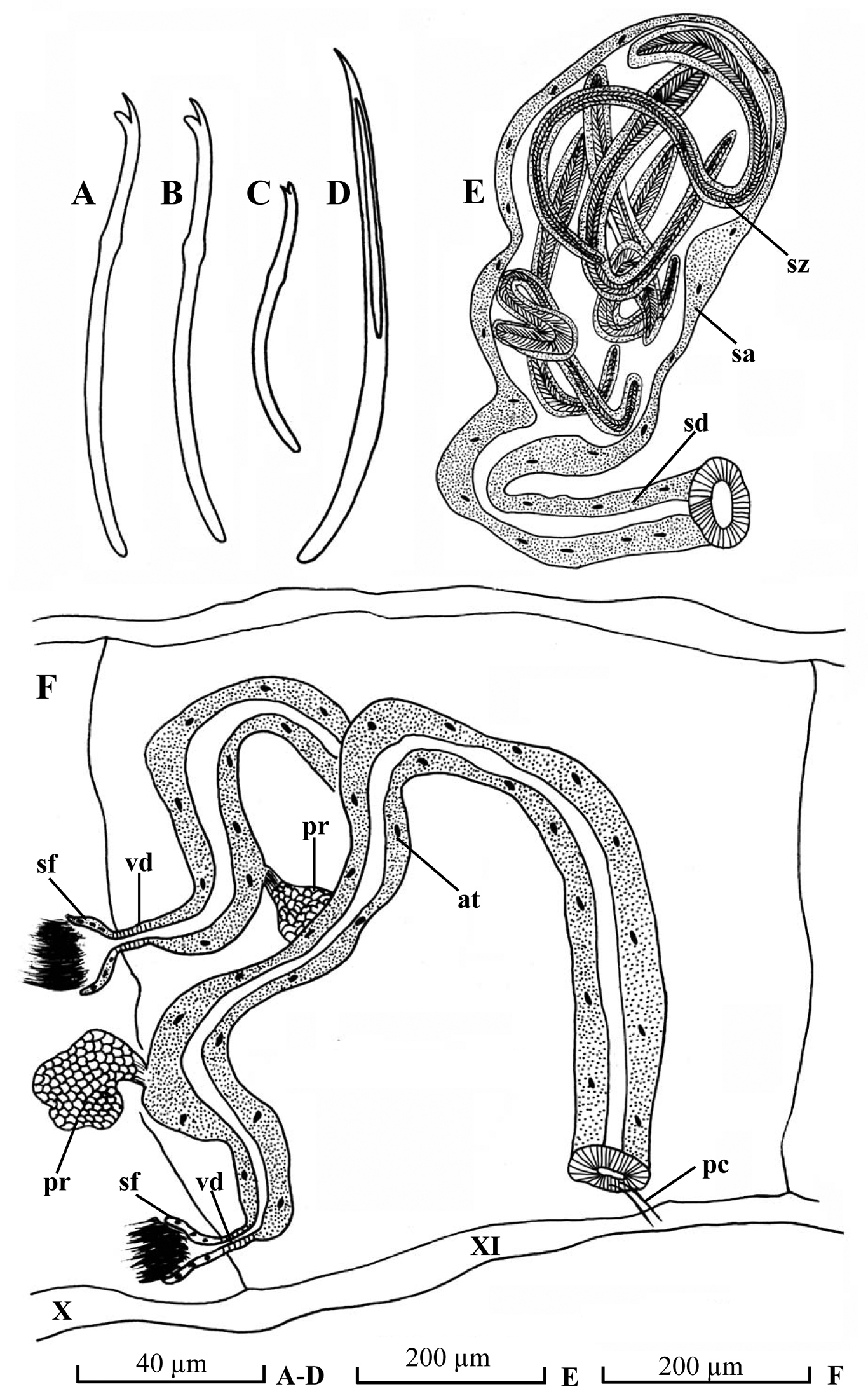
Potamothrix paramoldaviensis sp. n., A dorsal chaeta from III B ventral chaeta from VII C penial chaeta D spermathecal chaeta E spermatheca F lateral view of male ducts in segments X–XI. Scale bars: A–D 40 µm; E–F 200 µm
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:9FE88E3F-B244-443B-9E5D-0DB70AB4559B
IHB YAN 20020812i, mature specimen mounted in Canada balsam, and stained with borax carmine.
East of Gushan Island (24°24'05"N, 102°52'45"E) in Fuxian Lake, eastern Yunnan, China; depth 78 m, bottom temperature 15.9 °C, dissolved oxygen at bottom 9.6 mg/L, total nitrogen in water 0.155 mg/L, total phosphorus in water 0.0234 mg/L, fine clay; Aug 8, 2002, coll. Y. Cui and X. Liu.
Named “paramoldaviensis” for its resemblance with Potamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902 in terms of its male genitalia.
Specimen incomplete, length > 4.4 mm, diameter at XI about 0.7 mm, segments > 13. Clitellum inconspicuous.
Chaetae (Fig. 2A–B) all bifid, 4–6 per bundle dorsally, 3–6 per bundle ventrally, 80–120 µm long, 2.0–2.6 µm thick, upper tooth longer and thinner than lower. Spermathecal chaetae (Fig. 2D) one per bundle in posterior to middle of X, entally embedded in glandular sacs, 145–160 µm long, 4.0–4.5 µm thick, with curved ental part, and grooved ectal part. Penial chaetae (Fig. 2C, F, pc) slightly different to other ventral chaetae, 1–2 per bundle in postero-XI, 70–74 µm long, 2.0–2.4 µm thick, upper tooth as long as, but thicker than lower tooth. Male pores paired in line with ventral chaetae in postero-XI, immediately anterior to penial chaetae. Spermathecal pores paired in line with ventral chaetae in posterior to middle of X, immediately anterior to spermathecal chaetae.
Pharyngeal glands in II–III. Chloragogen cells from VI onwards. No coelomocytes. Male genitalia (Fig. 2F) paired. Vasa deferentia (Fig. 2F, vd) very short, 27–38 µm long, 16–20 µm wide, entering atria apically. Atria (Fig. 2F, at) 1050–1130 µm long, 38–90 µm wide, tubular and rather homogenous throughout, with thin outer muscular layer and thick inner epithelium. Prostate gland small, attached proximally to atrium. Penis absent.
Spermathecae ducts (Fig. 2E, sd) 345–360 µm long, 38–70 µm wide, ampullae (Fig. 2H, sa) pear-shaped, 420–430 µm long, maximally 230–250 µm wide. Spermatozeugmata (Fig. 2H, sz) 6–9 in each ampulla, about 300–640 µm long.
Known only from its type locality, Yunnan Province, China; freshwater lake, 78 m depth, water temperature less than 16 °C, fine clay.
According to very short vasa deferentia, long tubular atria each with a small prostate gland, and lack of ejaculatory ducts, the new species fits more closely the definition of Potamothrix Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902 than that of any other described tubificine genus (
This new speciesresembles Potamothrix moldaviensisin some aspects of the male organs (
The new species is distinguishable from other species from the Yunnan lakes in the characteristics of some somatic chaetae. For instance, hair chaetae and pectinate bifid chaetae are present in Potamothrix scleropenis Cui & Wang, 2005, Potamothrix rhytipeniatus Cui & Wang, 2012, Potamothrix aductus Cui & Wang, 2012, Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n. and Potamothrix parabedoti sp. n., but hair chaetae are absent in Potamothrix paramoldaviensis; the spermathecal chaetae of these six species are dissimilar; slightly modified penial chaetae are present in Potamothrix scleropenis and Potamothrix paramoldaviensis, but are absent in the other three species (Table 2).
Comparison of six species of Potamothrix from Yunnan Lakes.
| Species | Potamothrix aductus Cui & Wang, 2012 | Potamothrix parabedoti sp. n. | Potamothrix paramoldaviensis sp. n. | Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n. | Potamothrix rhytipeniatus Cui & Wang, 2012 | Potamothrix scleropenis Cui & Wang, 2005 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hair chaetae | forward VII, plumose | forward III or V, plumose | absent | forward V, plumose | forward II, smooth | forward VI, plumose |
| Pectinate bifid chaetae | associated with hairs | associated with hairs | absent | associated with hairs | present | associated with hairs |
| Ventral chaetae | bifid | bifid | bifid | bifid, lower prong usually secondarily branched | bifid | bifid, lower prong usually secondarily branched |
| Spermathecal chaetae | ||||||
| Penial chaetae | absent | absent | present | absent | absent | present |
| Length ration of vd/at | 1:12-16 | 1:11-20 | 1:30-42 | 1:10-18 | 1:14-30 | 1:3 |
| Prostate glands | present | absent | present | present | absent | absent |
| Male ducts | homogenous | homogenous | homogenous | homogenous | bipartite | homogenous |
| Penial sheath | absent | absent | absent | absent | absent | present |
| Habitats | Freshwater lake, 70-110 m depth, <15°C, fine clay | Freshwater lake, 70-120 m depth, <15 °C, fine clay. | Freshwater lake, 78 m depth, <16°C, fine clay | Freshwater lake, 113 m depth, < 14°C, fine clay | Freshwater lake, 5 m depth, 18°C, mud | Freshwater lake, 74 m depth, <15°C, fine clay |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:07854E46-F521-4B90-B580-D6862D494E1D
IHB YAN 20021205c, mature specimen mounted in Canada balsam, and stained with borax carmine.
IHB YAN20021205c, East of Lichang (24°32'04"N, 102°51'43"E) in Fuxian Lake, eastern Yunnan, China; depth 113 m, bottom temperature 13.5 °C, dissolved oxygen at bottom 5.2 mg/L, total nitrogen in water 0.164 mg/L, total phosphorus in water 0.037 mg/L, fine clay; Dec 11, 2002, coll. Y. Cui and X. Liu.
IHB YAN20021012b, East of Gushan Island (24°24'05"N, 102°52'45"E) in Fuxian Lake, eastern Yunnan, China; depth 76 m, bottom temperature 14.8 °C, dissolved oxygen at bottom 8.7 mg/L, total nitrogen in water 0.163 mg/L, total phosphorus in water 0.0203 mg/L, fine clay; Oct 8, 2002, coll. Y. Cui and X. Liu. IHB YAN20021009c, North of Dasazui (24°22'58"N, 102°49'49"E) in Fuxian lake, eastern Yunnan, China; depth 87 m, bottom temperature 14.7 °C, dissolved oxygen at bottom 8.7 mg/L, total nitrogen in water 0.165 mg/L, total phosphorus in water 0.022 mg/L, fine clay; Oct 8, 2002, coll. Y. Cui and X. Liu.
Named “parabedoti” for its resemblance with Potamothrix bedoti (Piguet, 1913) in terms of male genitalia.
Two complete specimen 8.9–19.8 mm long (Holotype: 8.9 mm), with 36–131 segments (Holotype: 36), diameter at XI about 0.8 mm. Prostomium conical. Clitellum inconspicuous.
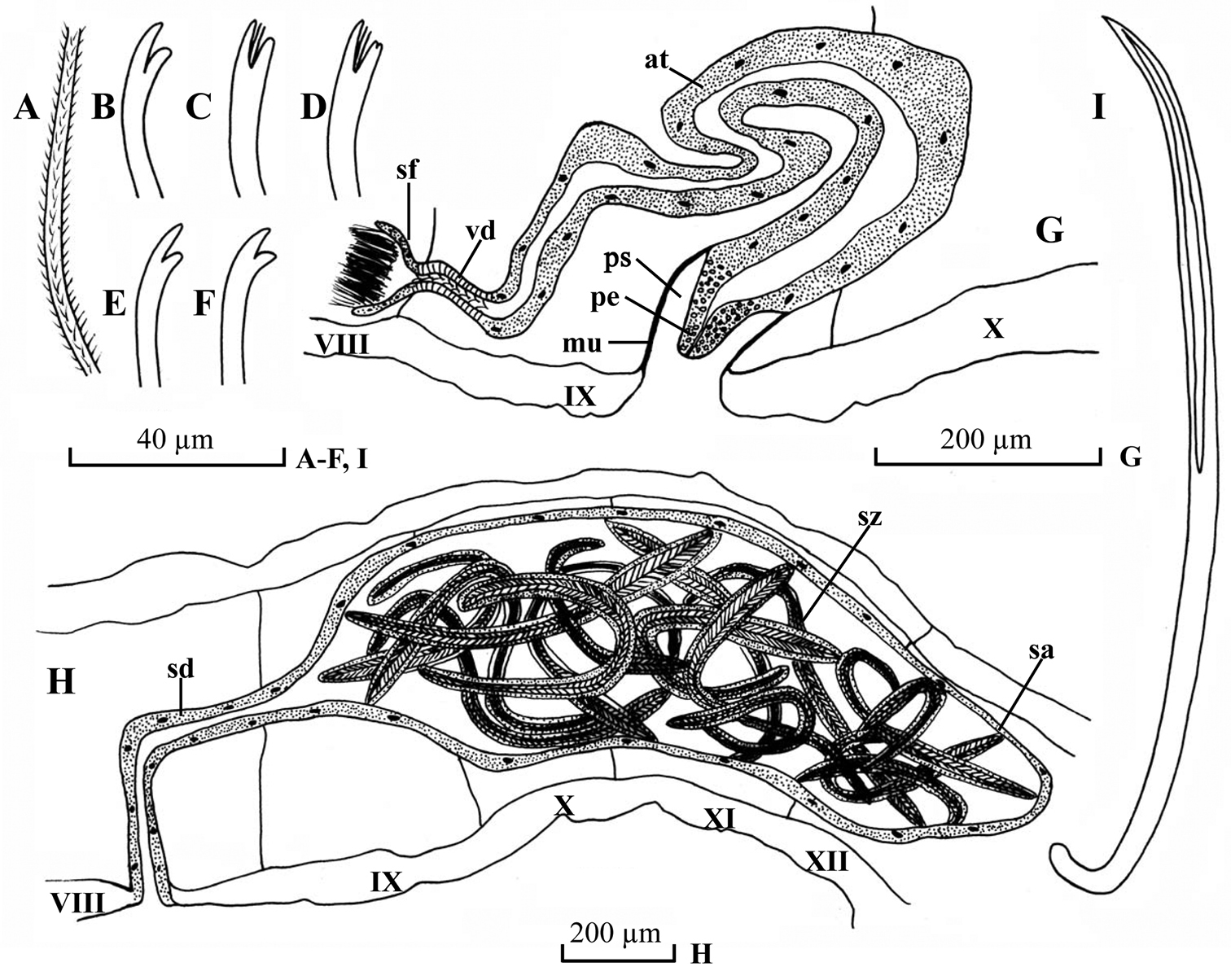
Dorsal chaetae (Fig. 3B) of II (II–IV) bifid only, 7–8 per bundle, 100–145 µm long, 2.8–3.0 µm thick, upper tooth longer and thicker than lower. Dorsal bundle of III (V)-IX 4–8 hair chaetae and 5–8 bifid chaetae per bundle; plumose hair chaetae (Fig. 3A), 250–300 µm long, 2.8–3.2 µm thick basally; pectinate bifid chaetae (Fig. 3C–D), 140–150 µm long, 2.8–3.2 µm thick, with 1–3 intermediate teeth, upper tooth slightly longer and thinner than lower (usually bifurcated), or equally long. Dorsal bundles of posterior segments 2–4 hair chaetae and 3–4 bifid chaetae per bundle, shorter and thinner than those of anterior segments, hair chaetae 200–240 µm long, bifid chaetae 100–120 µm long, 2.6–2.8 µm thick. Ventral chaetae (Fig. 3E–F) bifid, 6–10 per bundle anteriorly, 100–150 µm long, 2.8–3.0 µm thick; 3–5 per bundle in postclitellar segments, 100–125 µm long, 2.4–2.6 µm thick, all with tooth similar to dorsal chaetae in II–IV. Spermathecal chaetae (Fig. 3I) one per bundle in middle to posterior of VIII or IX, entally embedded in glandular sacs, about 125–140 µm long, 4.0 µm thick, ental end strongly curved, with ectal part grooved. Penial chaetae absent. Male pores paired in line with ventral chaetae, middle to posterior of IX or X. Spermathecal pores paired in line with ventral chaetae, middle of X, immediately anterior to spermathecal chaetae.
Pharyngeal glands in II. Chloragogen cells from IV or V onwards. No coelomocytes. Male genitalia (Fig. 3G) paired. Vasa deferentia (Fig. 3G, vd) 45–70 µm long, 18–24 µm wide, entering atria apically. Atria (Fig. 3G, at) 880 µm long, 44–80 µm wide, tubular and rather homogenous throughout, with thin outer muscular layer and thick inner epithelium. Prostate gland absent. Soft part of penis (Fig. 3G, pe) cylindrical and tapering ectally, 80–100 µm long, basally 45–60 wide, ectally 25–36 wide, enclosed in penial sacs. Penial sac (Fig. 3G, ps) 80–130 µm long, 72–92 µm wide, with muscular layer 2–4 µm thick.
Spermathecae (Fig. 3H) in VIII–XIII or VIII, ducts (Fig. 3H, sd) 500–568 µm long, 74–95 µm wide, ampullae (Fig. 3H, sa) elongated, 470–1280 µm long, maximally 320–442 µm wide. Spermatozeugmata (Fig. 3H, sz) 10–25 in each ampulla, about 400–860 µm long.
Potamothrix paprbedoti sp. n., A hair B–D distal end of dorsal bifids (VI, VII, XX, respectively)E–F distal end of ventral chaetae (II, XV, respectively) G lateral view of male duct in segments VIII–X H lateral view of spermatheca in segments VIII–XII I spermathecal chaeta. Scale bars: A–F, I 40 µm; G–H200 µm.
Known only from its type locality, Yunnan Province, China; freshwater lake, 70–110 m depth, water temperature less than 15 °C, fine clay.
According to short vasa deferentia, long tubular atria and lack of ejaculatory ducts, the new species fits more closely the definition of Potamothrix Vejdovský and Mrázek, 1902 than that of any other described tubificine genus (
The new speciesresembles Potamothrix bedoti (Piguet, 1913)in some aspects of reproductive organ (
The new species are distinguishable from other species from Yunnan Lakes in that of the position of their reproductive organs and the characteristic of some somatic chaetae. For instance, the reproductive organs are move to VIII–X in Potamothrix parabedoti sp. n. but that were in X–XIII in other species; the hair and pectinate bifids are absent in Potamothrix rhytipeniatus and Potamothrix paramoldaviensis sp. n., but present in other four species.
The principal distinguishable characteristics of the species of Potamothrix are given in Table 1 and Table 2. Nineteen previous species (Table 1) were divided into two groups, considered as subgenera, by lacking or possessing the prostate gland, respectively: Potamothrix Potamothrix Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902 (type species: Potamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovský & Mrázek, 1902) and Potamothrix Euilyodrilus Brinkhurst, 1963 (type species: Potamothrix hammoniensis (Michaelsen, 1901) (
In the genus of Potamothrix, the histological structure of the epithelium of the atrium is taxonomically useful (
In addition, the presence of pectinate bifid chaetae accompanied with hair chaetae in the Yunnan lake species could be a special feature, but their position is variable. For instance, the hairs and pectinate bifids begin from segments V, VI, VII, III or V, respectively in Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n., Potamothrix scleropenis Cui & Wang, 2005, Potamothrix aductus Cui & Wang, 2012, and Potamothrix parabedoti sp. n. The position of spermathecal pores of Potamothrix always lies in lateral line; however, in species from the Yunnan lakes, they were ventral instead of lateral.
As for habitat and distribution, the five species of Potamothrix from Fuxian Lake are well adapted to low dissolved oxygen concentrations, only found in the profundal region, to water depths lower than 70 m, water temperatures less than 16 °C, and they are found in sediments always clayey and sandy. Another species, Potamothrix rhytipeniatus Cui & Wang, 2012 was found in Xingyun Lake, in water depth of about 5 m, water temperature around 18 °C, and muddy sediments.
Lastly, according to some specific features, such as hair and pectinate bifid chaetae, spermathecal pore position, atrium histological structure, and their habitat, the species from Yunnan lakes maybe one new taxonomical group, the systematic placement of which needs further confirmation from more work.
Key to the genus of Potamothrix Vejdovský and Mrázek, 1902| 1 | Prostate glands present | 2 |
| – | Prostate glands absent | 15 |
| 2 | Hair chaetae present | 3 |
| – | Hair chaetae absent | 11 |
| 3 | With plumose hair chaetae | 4 |
| – | Without plumose hair chaetae | 5 |
| 4 | Prostate glands small, proximally attached to atria | Potamothrix aductus Cui & Wang, 2012 |
| – | Prostate glands small, proximally attached to atria and far from vasa deferentia | Potamothrix praeprostatus sp. n. |
| 5 | Dorsal bifid chaetae pectinated | 6 |
| – | Dorsal chaetae bifid | 9 |
| 6 | Spermathecal chaetae present | 7 |
| – | Spermathecal chaetae absent | Potamothrix postojnae Karaman, 1974 |
| 7 | Histological atria tripartite | 8 |
| – | Histological atria bipartite | Potamothrix hammoniensis (Michaelsen, 1901) |
| 8 | Length ratio of vasa deferentia to atria about 1:33–35 | Potamothrix alatus Finogenova, 1972 |
| – | Length ratio of vasa deferentia to atria about 1:20 | Potamothrix thermalis (Pop, 1968) |
| 9 | Spermathecal chaetae present and modified | 10 |
| – | Spermathecal chaetae absent or 1–2 bifid chaetae | Potamothrix ochridanus (Hrabĕ, 1931) |
| 10 | Upper tooth of ventral chaetae just shorter or equal the lower | Potamothrix vejdovskyi (Hrabĕ, 1941) |
| – | Upper tooth of ventral chaetae reduced | Potamothrix svirenkoi Lastočkin, 1937 |
| 11 | Spermathecal chaetae present and modified | 12 |
| – | Spermathecal chaetae absent or 1–3 bifid chaetae | 14 |
| 12 | Penes present | 13 |
| – | Penes absent | Potamothrix paramoldaviensis sp. n. |
| 13 | Ventral chaetae 5–6 per bundle | Potamothrix danubialis (Hrabĕ, 1941) |
| – | Ventral chaetae 8–10 per bundle | Potamothrix isochaetus (Hrabĕ, 1931) |
| 14 | Upper tooth of bifid chaetae longer and thinner than the lower | Potamothrix caspicus (Lastočkin, 1937) |
| – | Upper tooth of bifid chaetae equal the lower | Potamothrix marzeki (Hrabĕ, 1941) |
| 15 | Hair chaetae present | 16 |
| – | Hair chaetae absent | 23 |
| 16 | With plumose hair chaetae | 17 |
| – | Without plumose hair chaetae | 18 |
| 17 | Male genitalia in X–XI, with penial sheath | Potamothrix scleropenis Cui & Wang, 2005 |
| – | Male genitalia in VIII–IX, without penial sheath | Potamothrix parabedoti sp. n. |
| 18 | Dorsal bifid chaetae pectinated | 20 |
| – | Dorsal chaetae bifid | 9 |
| 19 | Upper tooth of ventral chaetae slightly longer and thinner than the lower | Potamothrix orientalis (Černosvitov, 1938) |
| – | Tooth of ventral chaetae equal in length | Potamothrix prespaensis (Hrabĕ, 1931) |
| 20 | Histological atria homogeneous | Potamothrix tudoranceai Šporka, 1994 |
| – | Histological atria bipartite | Potamothrix rhytipeniatus Cui & Wang, 2012 |
| – | Histological atria tripartite | 21 |
| 21 | Male genitalia in X–XI | 22 |
| – | Male genitalia in VIII–IX | Potamothrix bedoti (Piguet, 1931) |
| 22 | Length ratio of vasa deferentia to atria about 1:20 | Potamothrix heuscheri (Bretscher, 1900) |
| – | Length ratio of vasa deferentia to atria about 1:8–9 | Potamothrix bavaricus (Oschmann, 1913) |
| 23 | Spermathecal chaetae present and modified | 24 |
| – | Spermathecal chaetae absent or 4–5 bifid chaetae | Potamothrix cekanovskajae Finogenova, 1972 |
| 24 | Histological atria bipartite | Potamothrix manus Finogenova, 1972 |
| – | Histological atria tripartite | Potamothrix moldaviensis Vejdovský and Mrázek, 1902 |
We are indebted to Dr. Xueqin Liu, Dr. Jianhui Qin and Dr. Sixin Li (Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for their kind assistance in the field work. We also want to especially thank Prof. Yanling Liang (Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Prof. Tarmo Timm (Centre for Limnology, Tartumaa, Estonia), Dr. Patrick Martin (Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences) and Dr. Mark J. Wetzel (Illinois Natural History Survey) for their inspiring comments on the manuscript. The financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30470205) and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.