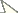(C) 2011 J. Paretas-Martínez. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
The Australian Thrasorinae are revised and Mikeius is transferred to Mikeiinae Paretas-Martínez & Pujade-Villar, subfam. n., and Mikeius clavatus Pujade-Villar & Restrepo-Ortiz, sp. n., is described. Two new genera of Thrasorinae are erected: Cicatrix Paretas-Martínez, gen. n., including Cicatrix pilosiscutum(Girault), comb. n. from Amblynotus, Cicatrix schauffi (Buffington), comb. n. from Mikeius, and Cicatrix neumannoides Paretas-Martínez & Restrepo-Ortiz, sp. n.; and Palmiriella Pujade-Villar & Paretas-Martínez, gen. n., including Palmiriella neumanni (Buffington), comb. n. from Mikeius, Thrasorus rieki Paretas-Martínez & Pujade-Villar, sp. n., is also described. A phylogenetic analysis of 176 morphological and biological characters, including all these new taxa and all genera previously included in Thrasorinae, was conducted. All subfamilies were recovered as monophyletic, with the following relationships: Parnipinae (Euceroptrinae (Mikeiinae (Plectocynipinae (Thrasorinae)))). A worldwide key to the subfamilies of Figitidae is provided that includes the new subfamily, as well as a key to genera Thrasorinae.
Australia, Figitidae, Mikeiinae, Cicatrix, Mikeius, Palmiriella, Thrasorus
Figitidae (Hymenoptera: Cynipoidea) are parasitoids of the larvae of other insects, principally cyclorraphous Diptera (
Thrasorinae is a stem group of figitids (
Following the examination of many undetermined specimens of Thrasorinae in the Australian National Insect Collection (ANIC) and the Queensland Museum (QM), as well as the type material of all species included in Mikeius Buffington, new questions arose regarding the taxonomy of Thrasorinae. First, an undescribed species of Mikeius was discovered (described herein); second, two species originally described in Mikeius were determined to render the genus polyphyletic, and new generic assignments are required; and third, phylogenetic analyses determined that the inclusion of Mikeius within Thrasorinae renders the subfamily paraphyletic with respect to Plectocynipinae. In response to these discoveries, Mikeiinae is described as a new subfamily to accommodate Mikeius, and species previously described in Mikeius are moved into other genera. In two cases, no current genus concept could accommodate these species, and the two new genera Cicatrix, gen. n., and Palmiriella, gen. n., are herein described. The goal of this study is to bring clarity to the taxonomic and phylogenetic relationships of these unusual groups of figitid wasps.
Material and methodsList of Repositories
QM - Queensland Museum, Brisbane, Australia (C. Burwell).
ANIC - Australian National Insect Collection, CSIRO, Canberra, Australia (J. LaSalle).
Specimen illustration and observation.
Environmental scanning electron micrographs (ESEM) were obtained at
Barcelona University with the FEI Quanta 200 ESEM without any coating at
15 KV. Additional ESEM images were obtained either with a Hitachi
TM3000 E-SEM, or an Amray 1810 SEM under a vacuum, using a lanthanum
hexaboride electron source (LaB6) at 10 Kv, both housed at the National
Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution. Images were edited
using Adobe CS4 Software (Adobe, Inc). The terminology for
morphological structures comes from
Phylogenetic analysis. Twenty-two taxa were included in the phylogenetic analysis (Table 1), representing all genera previously and currently included in Thrasorinae,
and all new taxa and combinations described in this work. Three
species of each genus were included (except for monotypic genera or
those with less than three species), so as to capture the morphological
diversity of each genus. Parnips nigripes (Barbotin, 1964) was chosen as an out-group based on
Table 1. Taxa included in the phylogenetic analysis. OG: outgroup.
| Higher taxon | Species |
|---|---|
| Parnipinae (OG) | Parnips nigripes (Barbotin, 1964) |
| Euceroptrinae | Euceroptres primus Ashmead, 1896 |
| Euceroptres whartoni Buffington & Liljeblad, 2008 | |
| Euceroptres montanus Weld, 1926 | |
| Thrasorinae | Scutimica flava Ros-Farré & Pujade-Villar, 2007 |
| Scutimica transcarinata Ros-Farré & Pujade-Villar, 2007 | |
| Myrtopsen platensis Diaz, 1975 | |
| Myrtopsen luederwaldti Dettmer, 1928 | |
| Myrtopsen mimosae Weld, 1926 | |
| Palmiriella neumanni (Buffington, 2008) | |
| Thrasorus pilosus Weld, 1944 | |
| Thrasorus schmidtae Buffington, 2008 | |
| Thrasorus rieki sp. n. | |
| Cicatrix pilosiscutum (Girault, 1929) | |
| Cicatrix schauffi (Girault, 1929) | |
| Cicatrix neumannoides sp. n. | |
| Plectocynipinae | N. gen., n. sp. plectocynipine |
| Plectocynips pilosus Díaz, 1976 | |
| Mikeiinae, subfam. n. | Mikeius hartigi (Girault, 1930) |
| Mikeius grandawi Buffington, 2008 | |
| Mikeius clavatus sp. n. | |
| Mikeius berryi Buffington, 2008 |
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:9A0F4DEB-C4CE-44E2-BAAC-D86A88DC25CE
http://species-id.net/wiki/Mikeiinae
Fig. 1Mikeius Buffington, 2008.
Differs from Thrasorinae by the absence of a circumtorular impression (Fig. 1A; compare with Figs 2A, D, 3A, 4A, 9A-B), and the absence of a distinctly projected pronotal plate (Fig. 1C and G) (Table 2). Differs from Plectocynipinae by lacking an extremely long posterior metatibial spur (Fig. 6F;
Ros-Farre and Pujade-Villar 2007), a laterally compressed metasoma in
females (Ros-Farre and Pujade-Villar 2007), and a long, exposed
hypopygium (7th sternite) in females (Ros-Farre and Pujade-Villar 2007).
Differs from Euceroptrinae by lacking an areolet in the forewing, a lateral pronotal carinae (ARE, Fig. 6D;
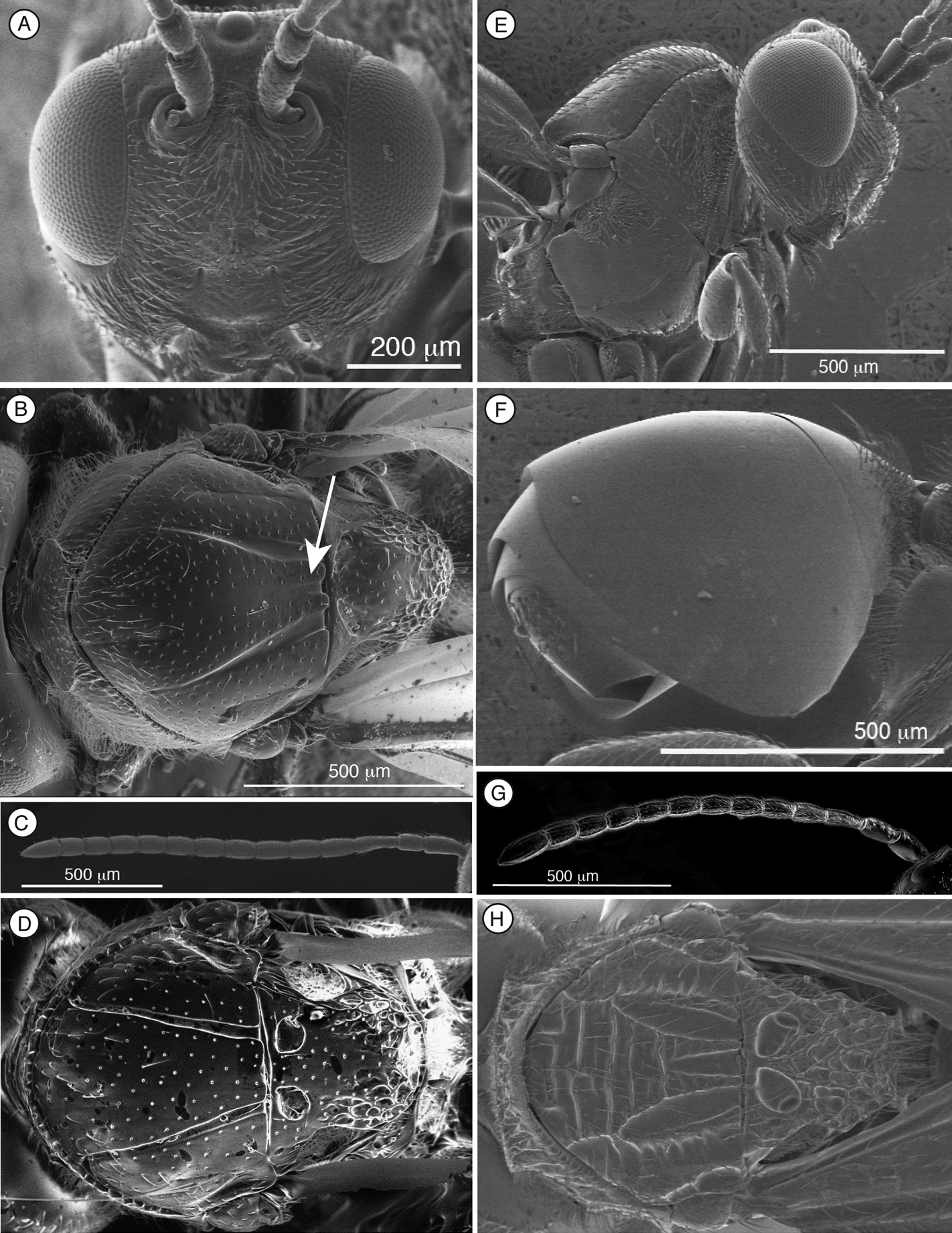
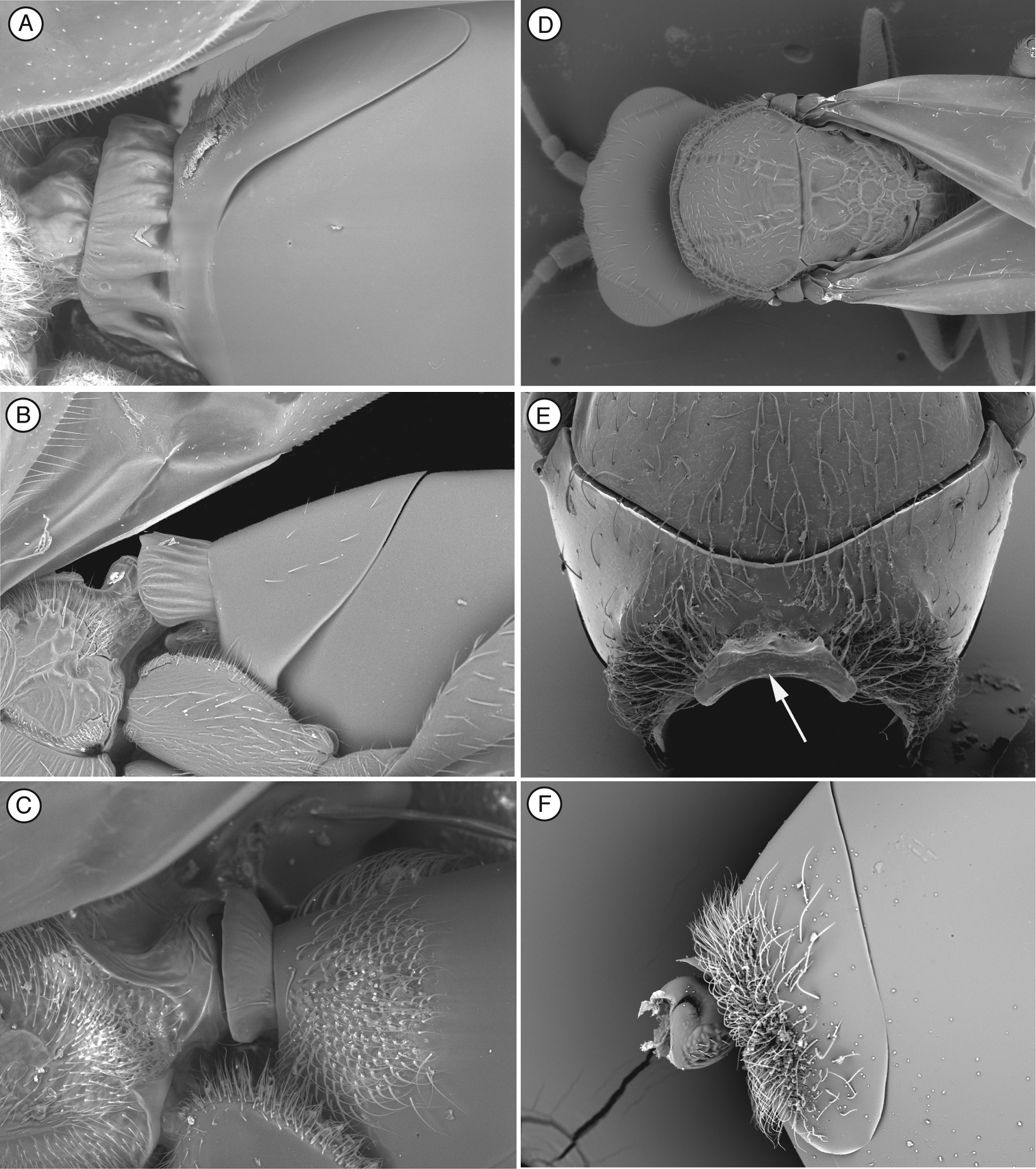
Figure 1. Diagnostic characters of Mikeius sp. (Mikeiinae), female. A–D, F and G: Mikeius hartigi; E, Mikeius clavatus A head, anterior view B mesosoma, lateral view C mesosoma, antero-dorsal view D–E antenna, medial view F mesosoma, dorsal view G pronotum (mesosoma), antero-dorsal view.
Length. 2 – 3.5 mm.
Coloration. Head and mesosoma dark brown to black, antenna and legs yellowish to brown. Metasoma light brown to black.
Head. (Fig. 1A) Frons and face with abundant setae. Transverse carinae or strigae on face absent. Clypeus distinctly projected ventrally, curved ventrally, clypeopleurostomal lines well developed. Malar furrow absent; malar space coriaceous, striate. Occiput and genae smooth without carinae. Circumtorular impression absent.
Antenna. (Fig. 1D, E) Filiform or clavate with 10–11 flagellomeres in females (last one larger, possibly fusion of two), 12 in males. Males with F1 curved.
Mesosoma. (Fig. 1B, C, F, G) Lateral margins of posterior part of pronotal plate short, not reaching scutum, not forming projected plate; lateral pronotal depressions open laterally. Mesoscutum horizontally striate. Notauli complete, uniformly wide along entire length, or gently widening posteriorly. Parascutal sulcus marked only in basal half. Lateral basal impressions weak. Antero-admedian lines absent or weak. Median mesoscutal line present, short or long. Scutellum striate anteriorly and in center, rugose posteriorly; scutellar foveae round subtriangular or subquadrate, sometimes not delimited posteriorly; interfoveal carina absent. Mesopleural furrow absent or present. Propodeal carinae wide, almost straight. Pronotum, mesoscutum, scutellum, mesopleural triangle and metapleura all covered with sparse/dense setae.
Forewing. Short setae present on wing surface and along margins. Radial cell closed along anterior margin, 2 to 2.5 times longer than wide, R2 almost straight; areolet absent.
Legs. Metatibia with two spurs, sub-equal in length, not exceeding one-third the length of tarsomere 1.
Metasoma. Base of T3 with a complete or incomplete ring of setae. Tergite 3 smaller than T4; T4 large, covering almost entire metasomal surface; remaining terga short, telescoped within T4; entire metasoma shiny and smooth.
In the original description of Mikeius,
Associated with Chalcidoidea (Hymenoptera: Apocrita) that induce galls on species of Acacia (Fabaceae)and Eucalyptus (Myrtaceae), although most of these host records await verification through isolated rearing (Buffington, 2008).
Australia.
Mikeius Buffington, 2008.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:8D74319A-2A25-48A6-B857-80E6ABB2BE9C
http://species-id.net/wiki/Mikeius_clavatus
Fig. 1EDiffers from all the other species of Mikeius in having the antenna strongly clavate with the six terminal segments 1.5 times wider than previous segments (Fig. 1E); further distinguished from Mikeius berryi and Mikeius grandawi by the absence of a mesopleural carina.
As in subfamily description (see above) with the following specific characters.
Length. Female 2.8 - 3 mm. Male unknown.
Coloration. Head and mesosoma black, antenna yellowish, except scape, brown, metasoma pale brown. Legs pale yellow, except coxae, brown.
Antenna. (Fig. 1E) Female. Strongly clavate, 11 flagellomeres, antennal formula: 8(4): 4(4): 5(3): 3(3): 3(3): 3(3.5): 4(5): 5(6): 5(6): 6(5): 5(6): 5(6): 7(4). Placoid sensillae from F7 to terminal segment.
Mesosoma. Mesoscutum slightly striate. Notauli complete of uniform width. Antero-admedian lines weak. Median mesoscutal line very short. Scutellar foveae round to subquadrate, not delimited posteriorly. Mesopleural furrow absent.
Forewing. Radial cell 2.4 times longer than wide.
Metasoma. Base of T3 with an almost complete hairy ring.
HOLOTYPE ♀ (ANIC) with the following label data: “AUSTRALIA: Vict. Mt. Donna Buang, 1200m 11–17.i. 80, Eucalyptus-Nothofagus forest, A. Newton, M. Thayer” (white label), “flight intercept window/trough trap” (white label), “AUST. NAT. INS. COLL.” (green label), “Holotype Mikeius clavatus P-V & R-O” (red label). PARATYPE ♀ (ANIC) with the following labels: “W side Cobungra Hill 20km WbyN, Omeo Vic. 27 Feb. 1980, I.D. Naumann J. C. Cardale” (white label), “ex alcohol collection” (white label), “AUST. NAT. INS. COLL.” (green label), “Paratype Mikeius clavatus P-V & R-O” (red label).
Unknown.
Victoria, Australia.
The specific name refers to the strongly clavate antenna.
Thrasorus Weld, 1944.
Distinguished from other figitids by the presence of a circumtorular impression (Figs 2A, D, 3A, 4A, 9A, B) (Table 2); further distinguished from Euceroptrinae by the absence of an areolet in the forewing and the absence of a lateral pronotal carina. Additional characters that distinguish Thrasorinae from other Figitidae can be found in the key to subfamilies below.
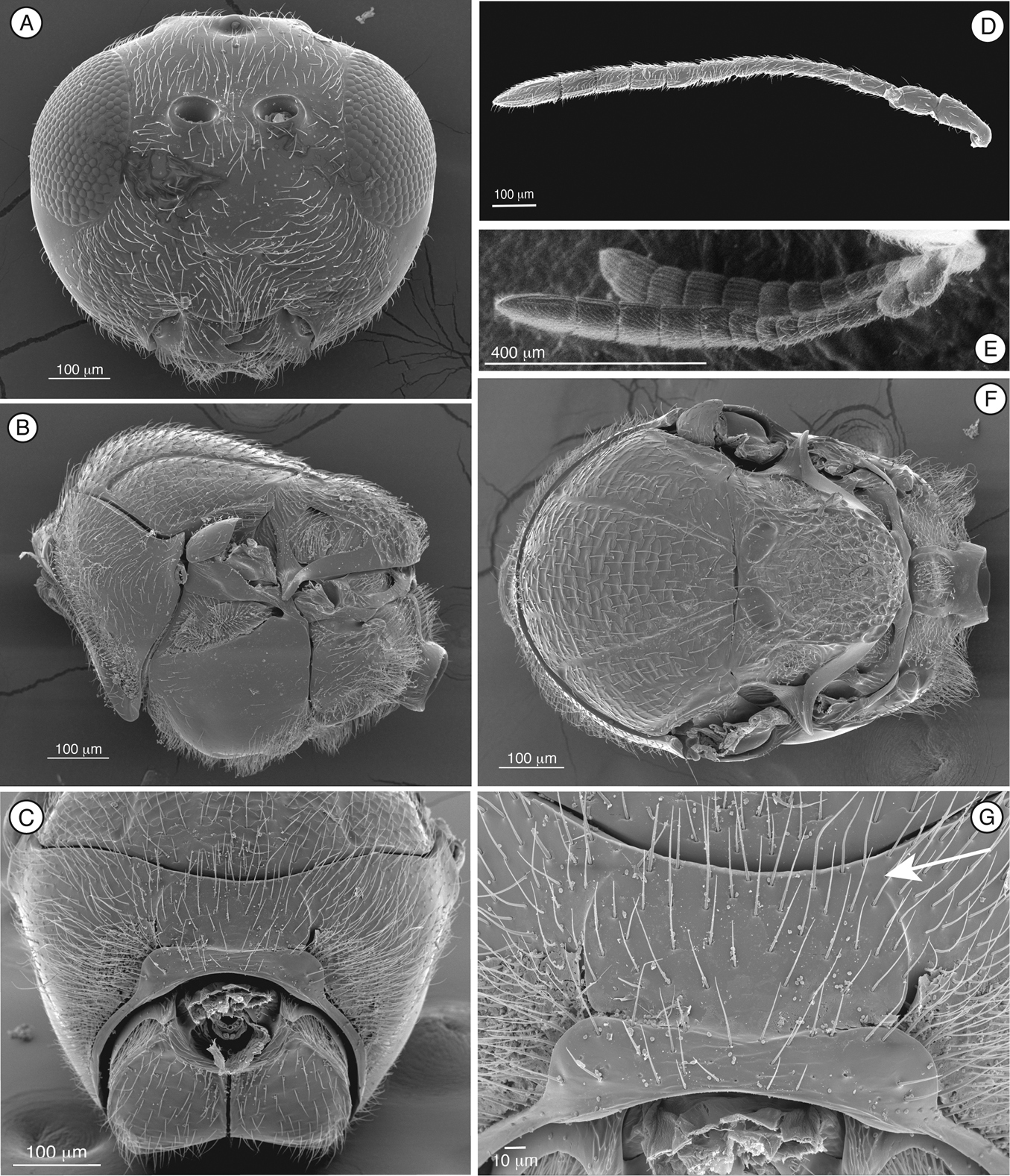
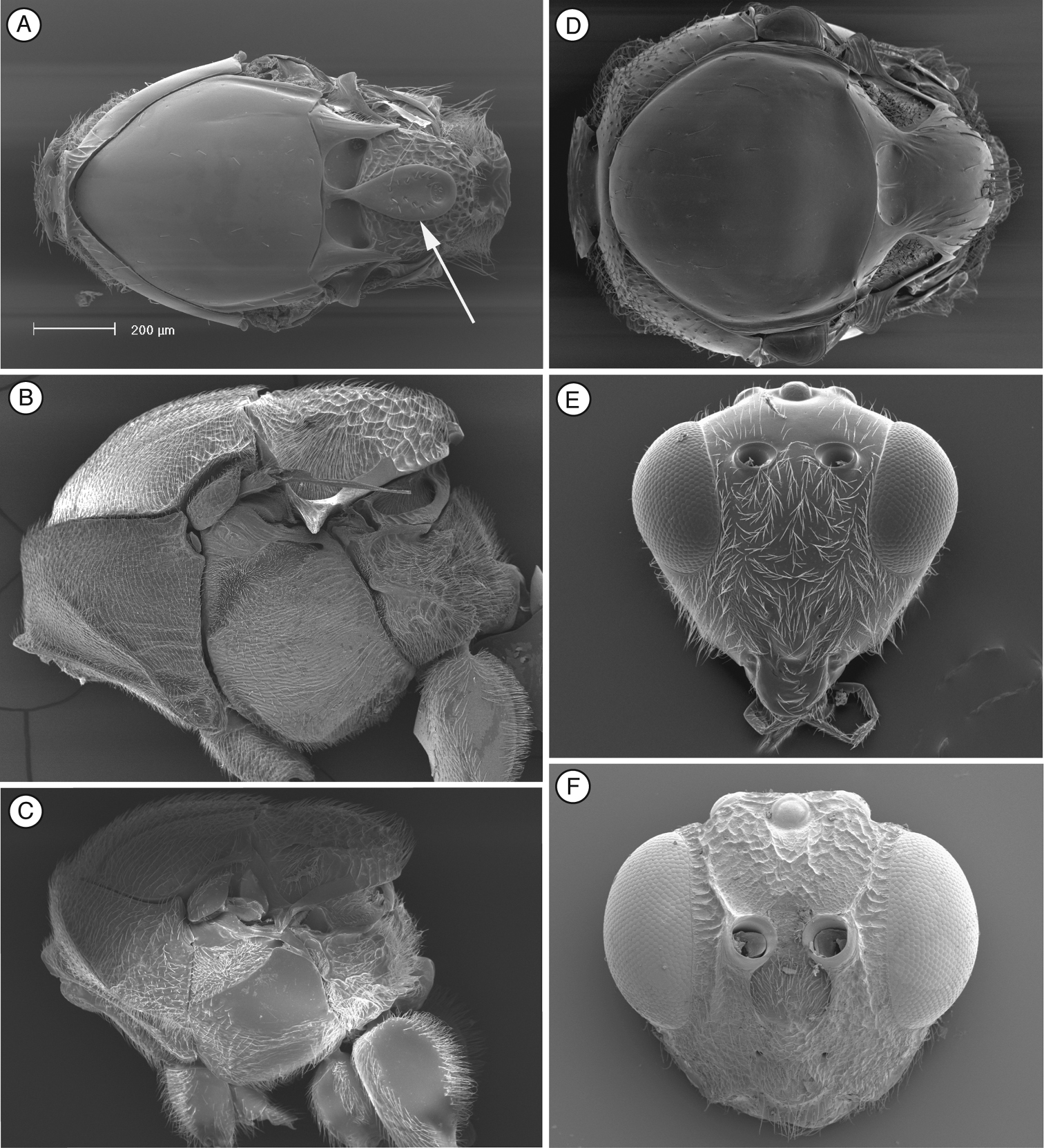
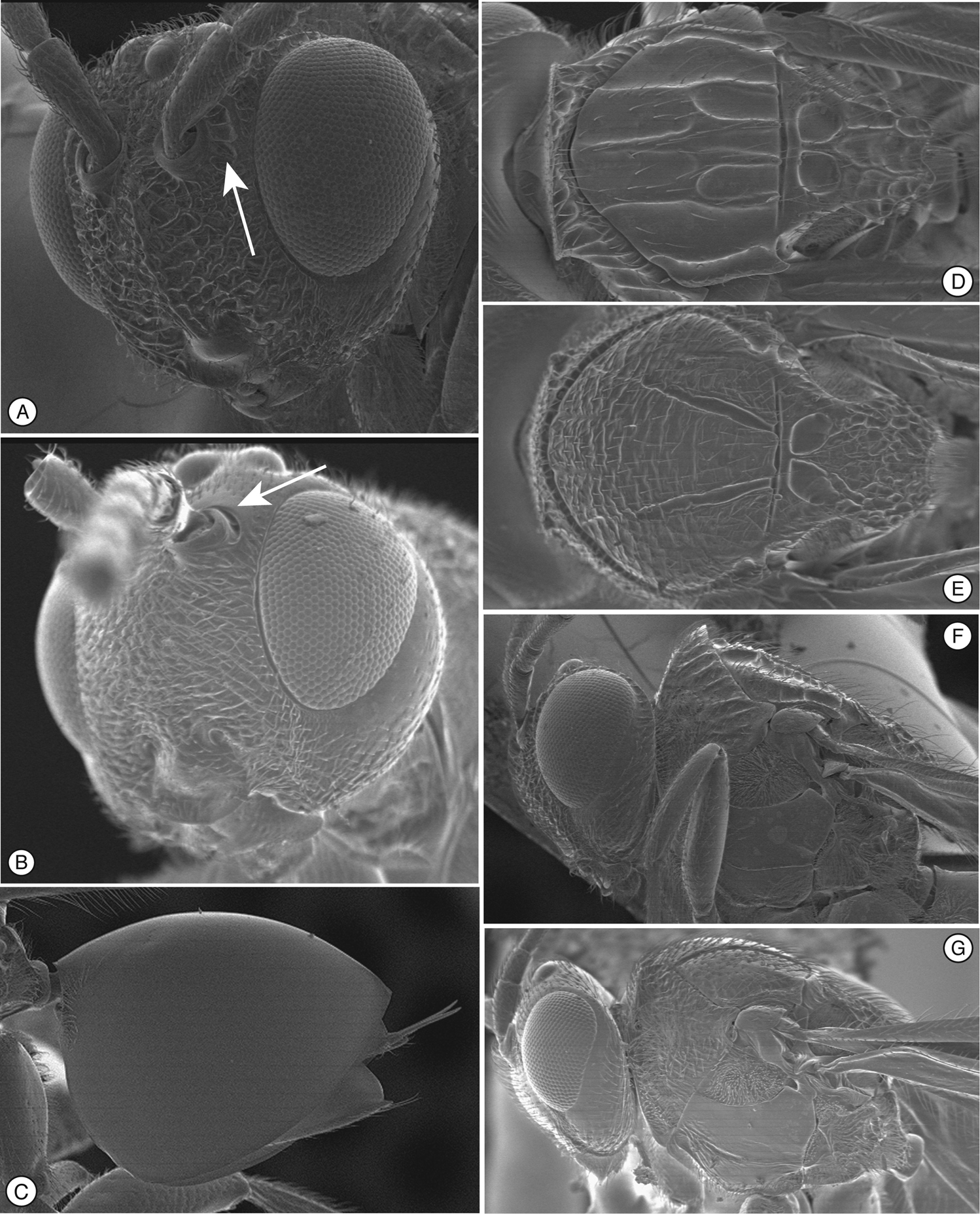
Figure 2. Diagnostic characters of Cicatrix sp. (Thrasorinae): A Cicatrix pilosiscutum; B–D and F Cicatrix schauffi; E, Cicatrix neumannoides A head, anterior view B mesosoma, dorsal view C metasoma, lateral view D head, anterior view E mesosoma, dorsal view Ffemale antenna, dorsal view. CI, circumtorular impression.
In the redescription of Thrasorus,
Unknown.
Australia, South America and North America.
Cicatrix, gen. n.; Myrtopsen Rübsaamen, 1908; Palmiriella, gen. n., Scutimica Ros-Farré, 2007; Thrasorus Weld, 1944.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:F831C129-F846-4A87-A668-524A2EA64E19
http://species-id.net/wiki/Cicatrix
Fig. 2Cicatrix pilosiscutum (Girault), comb. n.
Cicatrix neumannoides, sp. n., Cicatrix pilosiscutum (Girault), Cicatrix shauffi (Buffington), comb. n.
(Table 2) Cicatrix, gen. n., is distinguished from Myrtopsen, Palmiriella, gen. n., and Scutimica by having T3 and T4 as separate sclerites (Fig. 2C); in these latter three genera, T3 and T4 are fused into a syntergum (Fig. 3F, 9C). Cicatrix is distinguished from Thrasorus having horizontally striate microsculpture on the mesoscutum (Fig. 2B, E); Thrasorus has a smooth mesoscutum (Fig. 4B).
Table 2. Diagnostic table for Mikeius (Mikeiinae, n. subf.) and genera of Thrasorinae.
| Mikeiinae | Thrasorinae | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mikeius | Thrasorus | Cicatrix | Palmiriella | Scutimica | Myrtopsen | |
| Circumtorular impression | absent | present | present | present | present | present |
| Lateral margins of posterior part of pronotal plate | not reaching scutum, not forming an upraised plate | reaching scutum, forming an upraised plate | reaching scutum, forming an upraised plate | reaching scutum, forming an upraised plate | reaching scutum, forming an upraised plate | reaching scutum, forming an upraised plate |
| Mesoscutum sculpturing | microsculpture horizontally striate | absent, smooth | microsculpture horizontally striate | microsculpture horizontally striate | smooth or with parapsides | microsculpture horizontally striate |
| T3-T4 | T4 2x length of T3 | T4 2x length of T3 | T4 2x length of T3 | fused, syntergum not covering the entire metasoma | fused, syntergum covering the entire metasoma | fused, syntergum covering the entire metasoma |
| Face sculpturing | absent | carinae on lower face | carinae on lower face | absent | irregularly wrinkled/carinate | irregularly wrinkled/carinate |
| Posterior margin of scutellum | rounded | rounded | rounded | rounded | emarginate | truncate/emarginate |
| Pronotum sculpturing | absent | absent | absent | absent | carinate | carinate/ microsculpture |
| Notauli | complete | complete | complete | complete | incomplete, each forming a large cell | complete |
Length. Female2.5 – 4.5 mm.Male unknown.
Coloration. The entire body with the same coloration, light brown or chestnut depending on the specimen.
Head (Fig. 2A, D). Face and frons with abundant setae . Face with transverse carinae, strong across entire face, or only marked at lateral sides of face, smoother, tending towards strigae. Clypeus distinctly projected anteriorly, curved ventrally, clypeopleurostomal lines well developed. Malar furrow coriaceous. Occiput and genae smooth without carinae. Circumtorular impression present.
Antennae (Fig. 2F). Female.Filiform, with 10 or 11 flagellomeres.
Mesosoma (Fig. 2B and E). Pronotal carinae reaching anterior margin of mesoscutum, forming small plate, conspicuous but not projected, concave dorsomedially. Mesoscutum horizontally striate. Notauli complete, of uniform width to slightly wider posteriorly. Parascutal sulcus wide only in basal half. Lateral basal impressions conspicuous. Antero-admedian lines weak. Median mesoscutal line absent, short or long. Scutellum rugose; scutellar foveae round, subtriangular or subquadrate; interfoveal carina absent. Mesopleural furrow conspicuous. Propodeal carinae wide, curved. Pronotum, mesoscutum, scutellum, mesopleural triangle and metapleura all covered with sparse/dense setae.
Forewing. Short setae present on wing surface and along margins. Radial cell closed along anterior margin, two times longer than wide, R2 almost straight; areolet absent.
Legs. Metatibia with two spurs, sub-equal in length, not exceeding one-half length of tarsomere 1.
Metasoma (Fig. 2C). Petiole short. Base of T3 with patches of setae or an almost complete hairy ring. Tergite 3 smaller than T4; T4 four large, covering almost entire metasomal surface; remaining terga short, telescoped within T4; entire metasoma shiny, smooth. Hypopygium and ventral spine visible.
Unknown.
Australia.
From the Latin word cicatrix, meaning “scar”, refering to the carinae that resemble a scar through the face. Gender is masculine.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Cicatrix_pilosiscutum
Fig. 2ADiffers from Cicatrix neumannoides and Cicatrix schauffi by having female antenna with 11 flagellomeres (these two species having female antenna with 10 flagellomeres, (Fig. 2F, Cicatrix schauffi)), much stronger carinae crossing the entire face (Fig. 2A) (only marked at lateral sides of the face in the other two species, and being smoother, more like strigae), and by lacking a median mesoscutal impression (present and long in Cicatrix schauffi comb. n. (Fig. 2B), short in Cicatrix neumannoides sp. n. (Fig. 2E)).
As in generic description (see above) with the following specific characters: Length. Female 4.4 mm. Male unknown.
Coloration. Completely light brown except mesosoma, which is dorsally dark.
Head. (Fig. 2A) Frons and face with piliferous punctures; strong transverse carinae crossing the entire face.
Antenna. Female. 11 flagellomeres, antennal formula: 9(4): 5(3): 10(3): 9(2.5): 8.5(2.5): 8(3): 8(3): 8(3): 7(3): 5(3): 5(3): 4.5(3): 7.5(3). Placoid sensillae absent on basal half of F1 to F4, scarce on dorsal half; abundant from F5 to F11.
Mesosoma. Median mesoscutal impression absent. Scutellar foveae subtriangular.
HOLOTYPE ♀ (QM) with the following labels: “25. 10. 23, National Pk., Q. H. Hacker.” (white label), “HOLOTYPE” (pink label), “Amblynotus pilosiscutum ♀, Type Girault” (white label, handwritten), “Xyalophoroides pilosiscutum (Gir), E. F. Riek det 1953” (white label, handwritten), QM Reg. No. T99348” (yellow label), “Cicatrix pilosiscutum P-M det-2009” (white label).
Unknown.
Australia. Label data suggest the single specimen was taken in Royal National Park in Sydney.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Cicatrix_schauffi
Fig. 2B–D and FSimilar to Cicatrix neumannoides, sp. n., in having female antenna with 10 flagellomeres (Fig. 2F) and a face horizontally striate only on the lateral areas (Fig. 2D) (Cicatrix pilosiscutum, comb. n., has female antenna with 11 flagellomeres and much stronger carinae crossing the entire face), but differs from Cicatrix neumannoides sp. n. by having a long median mesoscutal impression and subtriangular scutellar foveae (Fig. 2B).
As in generic description (see above) with the following specific characters: Length. Female: 3.9 mm. Male unknown.
Coloration. Completely light brown.
Head. (Fig. 2D) Frons with piliferous punctures, face horizontally striate only on lateral areas.
Antenna. (Fig. 2F) Female. 10 flagellomeres, antennal formula: 6(2): 4(3): 5(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4.2(3.1): 4.2(3.1): 4.3(3.3): 5.2(3.3): 4.6(3.3): 3.5(3.3): 6(4). Placoid sensillae present from F4, abundant from F6 through terminal segment.
Mesosoma. (Fig. 2B) Median mesoscutal impression long, one-third length of scutum. Scutellar foveae irregular, subquadrate and not delimited posteriorly.
Type material. HOLOTYPE ♀ (ANIC) with the following label data: “23.36S 133.35E 32 km WNW of Alice Springs, NT 8 Oct. 1978 J:C: Cardale” (white label), “ex alcohol collection” (white label), “AUST. NAT. INS. COLL.” (green label). “HOLOTYPE, Mikeius schauffi, Buffington” (red label), “Cicatrix schauffi P-M det-2009” (white label).
Unknown
Central Australia.
The circumtorular impression present in this species indicates that it belongs in Thrasorinae, not in Mikeiinae. We transfer this species to Cicatrix gen. n., because it possesses all the diagnostic characters of that genus.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:1A6D286B-94AF-43F8-945B-D9AF124EEC57
http://species-id.net/wiki/Cicatrix_neumannoides
Fig. 2ESimilar to Cicatrix schauffi, comb. n., having female antenna with 10 flagellomeres and a face with horizontal strigae only on the lateral areas (Cicatrix pilosiscutum comb. n. has female antenna with 11 flagellomeres and much stronger carinae crossing the entire face), but differs from Cicatrix schauffi comb. n. by having short median mesoscutal impression and rounded scutellar foveae (Fig. 2E).
As in generic description (see above) with the following specific characters.
Length. Female: 2.9 to 3.0 mm. Male unknown.
Coloration. Shiny chestnut, scutum darker in center.
Head. Frons and face with piliferous punctures; face with a few carinae from internal margin of eye reaching center of face.
Antenna. Female. 10 flagellomeres, antennal formula: 6(2): 4(2.8): 6(2.5): 4.1(2.8): 4.1(2.8): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4.8(3.1): 3.8(3.3): 3.5(3.3): 5.6(4). Placoid sensillae starting from F4, F4 to F6 are scarce, abundant from F7-F10.
Mesosoma. (Fig. 2E) Median mesoscutal impression short, only indicated basally, not reaching one-fifth length of scutum. Scutellar foveae rounded.
The specific name neumannoides means “related to neumanni”, referring to the fact that the specimens used to describe this species were previously included in the type series of Mikeius neumanni.
HOLOTYPE ♀ (ANIC) with the following labels:
“AUSTRALIA: NSW Peak Hill Range, Braidwood, Cooma Road, At top of
pass. 30 December 1994. A. Sundholm & R de keyzer. On Acacia dealbata” (white label), “AUST. NAT. INS. COLL.” (green label), “Mikeius neumanni Det. M. L.
Unknown; label data suggests an association with Acacia.
New South Wales and Western Australia, Australia.
Although
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:5F540007-4494-49BF-A619-F0A54F5CE41E
http://species-id.net/wiki/Palmiriella
Fig. 3Palmiriella neumanni (Buffington), comb. n., by present designation and monotypy.
(Table 2) Palmiriella, gen. n., can be distinguished from other thrasorines by having the face smooth, without any sculpturing (Fig. 3A); in Scutimica and Myrtopsen, the face is irregularly sculptured (Fig. 9A, B); in Cicatrix and Thrasorus, strong transverse carinae are present crossing the entire face or on lateral areas (Fig. 3A, D, 4A). Palmiriella is further differentiated from other thrasorines by having metasomal T3 and T4 fused into a syntergum, but not covering the entire metasomal surface (Fig. 3F); in Scutimica and Myrtopsen, a syntergum covering the entire metasomal surface is present (Fig. 9C); in Cicatrix and Thrasorus, T3 and T4 are separate sclerites (syntergum absent) (Fig. 2C, 4F). Additionally, Palmiriella is distinguished from Scutimica and Myrtopsen by having the scutellum posteriorly rounded (Scutimica and Myrtopsen have an emarginate/truncate scutellum, Fig. 9D, E), and pronotum not sculptured nor projected (strongly carinate and projected in Scutimica (Fig. 9F), with microsculpture or carinate in Myrtopsen (Fig. 9G)); from Thrasorus by having horizontally striate microsculpture on the mesoscutum (Fig. 3B) (mesoscutum smooth in Thrasorus, Fig. 4B).
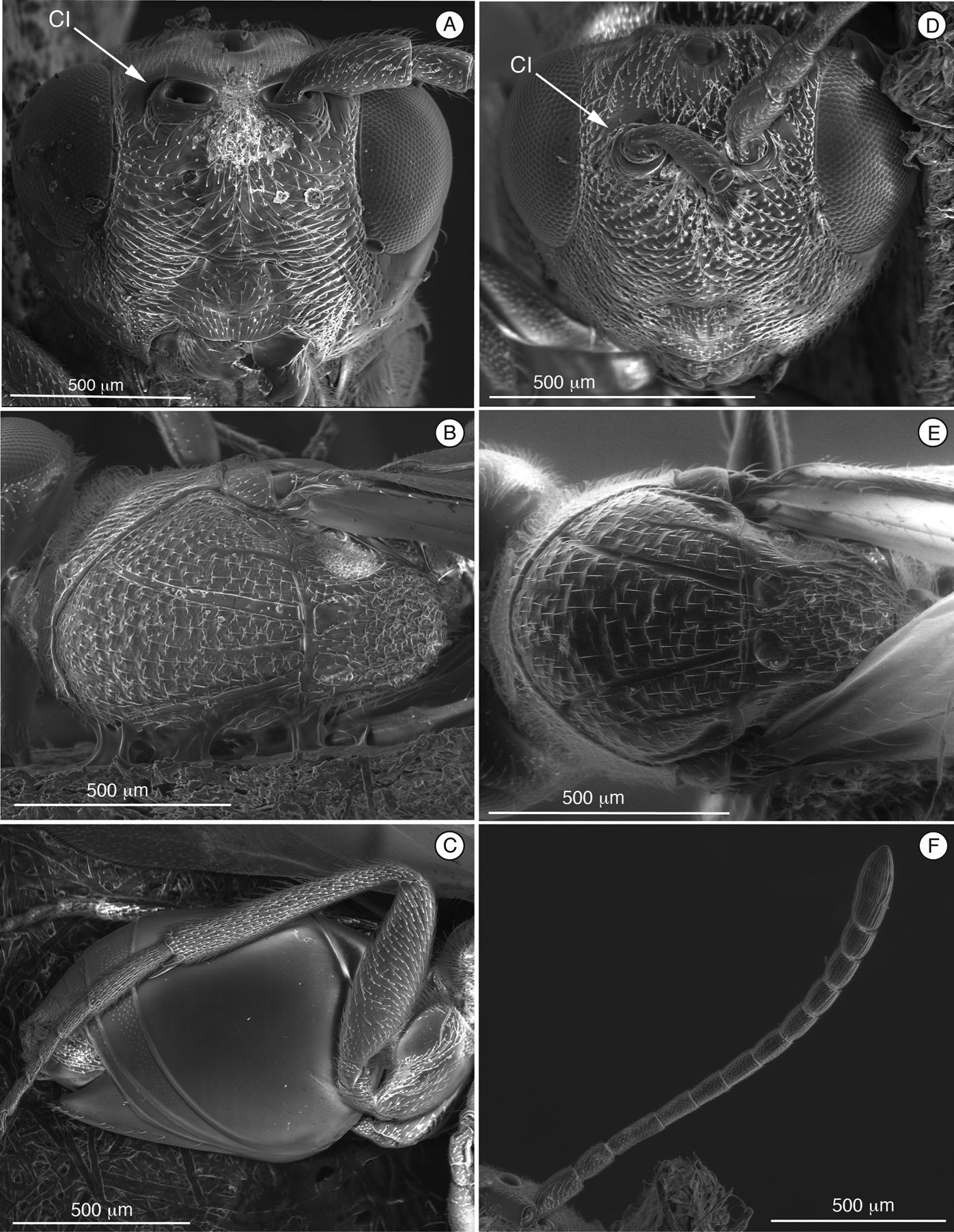
Figure 3. Diagnostic characters of Palmiriella neumanni (Thrasorinae), female Ahead, anterior view B mesosoma, dorsal view C mesosoma, lateral view D antenna, dorsal view E head and mesosoma, antero-dorsal view F metasoma, lateral view. CI, circumtorular impression.
See description, biology and distribution of type species below.
The new genus is dedicated to our colleague and good friend Palmira Ros-Farré, who has helped us for many years with our little wasps. Gender is feminine.
The holotype of Mikeius neumanni Buffington, unlike the other species included in Mikeius, does have the circumtorular impression diagnostic for Thrasorinae. For this reason, this species is transferred from Mikeius to the new thrasorine genus Palmiriella. Characters summarized in the diagnosis below and phylogeny in Fig. 5 justify the erection of the new genus.
http://species-id.net/wiki/Palmiriella_neumanni
Fig. 3A–FLength. Female 3.2 mm. Male unknown.
Coloration. Head and mesosoma black, antennae yellowish except scape, brown, metasoma medium brown. Legs light yellow except tibia and metatarsi, brown.
Head (Fig. 3A, F). Frons and face with piliferous punctures and abundant setae. No transverse carinae or strigae on face. Clypeus distinctly projected anteriorly, curved ventrally, clypeopleurostomal lines well developed. Malar space with conspicuous, coriaceous, striate band. Vertex in dorsal view with small piliferous punctures. Occiput and genae smooth without carinae. Circumtorular impression present.
Antenna (Fig. 3D). Female. 11 flagellomeres; antennal formula: 7(4): 4(4): 4(3): 4.5(3): 4.5(3): 4.5(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 3(3): 3(3): 3(3): 5(4). Placoid sensillae from F7 to terminal segment.
Mesosoma (Fig. 3B, C, E). Pronotal carinae reaching scutum, forming small plate, conspicuous but not projected, concave dorsomedially. Mesoscutum horizontally striate. Notauli complete of uniform width. Parascutal sulcus wide only in basal half. Lateral basal impression conspicuous. Antero-admedian lines weak, reaching anterior one-third of mesoscutum. Median mesoscutal impression short and weak. Scutellum rugose; scutellar foveae triangular; interfoveal carina absent. Mesopleural furrow present. Propodeal carinae present. Pronotum, mesoscutum, scutellum, mesopleural triangle and metapleura all covered with sparse/dense setae.
Forewing. Short setae present on wing surface and along margins. Radial cell closed, 2.3 times longer than wide; R2 almost straight, basal vein distally widening; areolet absent.
Legs. Metatibia with two spurs, sub-equal in length, not exceeding one-half length of tarsomere 1.
Metasoma (Fig. 3F). Petiole very short, almost not visible. T3 and T4 fused into a syntergum, not covering the entire metasomal surface; remaining terga short, telescoped within T4; entire metasoma shiny and smooth. Hypopygium and ventral spine visible. Base of syntergum with only some scattered setae.
HOLOTYPE ♀ (ANIC) with the following labels: “Mt Nebo, S. E. Qld, 24. Xi. 1970, S. R. Monteith” (white label), “AUST. NAT. INS. COLL.” (green label). “HOLOTYPE, Mikeius neumanni, Buffington” (red label), “Palmiriella neumanni P-V & P-M det-2009” (white label).
Unknown.
Queensland, Australia.
Thrasorus pilosus Weld, 1944.
Thrasorus pilosus Weld, Thrasorus rieki, sp. n., Thrasorus schmitdae Buffington.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:BCD3677F-EA0D-4D37-B62B-F093CEDF7B02
http://species-id.net/wiki/Thrasorus_rieki
Fig. 4BDiffers from other species of Thrasorus by having small scutellar foveae not clearly defined in posterior margin (Fig. 4B); other species of Thrasorus have scutellar foveae clearly delimited in the entire circumference (Fig. 4D). Further differs from other Thrasorus species by having a well-defined median mesoscutal impression (arrow, Fig. 4B); in other Thrasorus, the impression is not present, or at most, a very small incision can be seen (Fig. 4D).
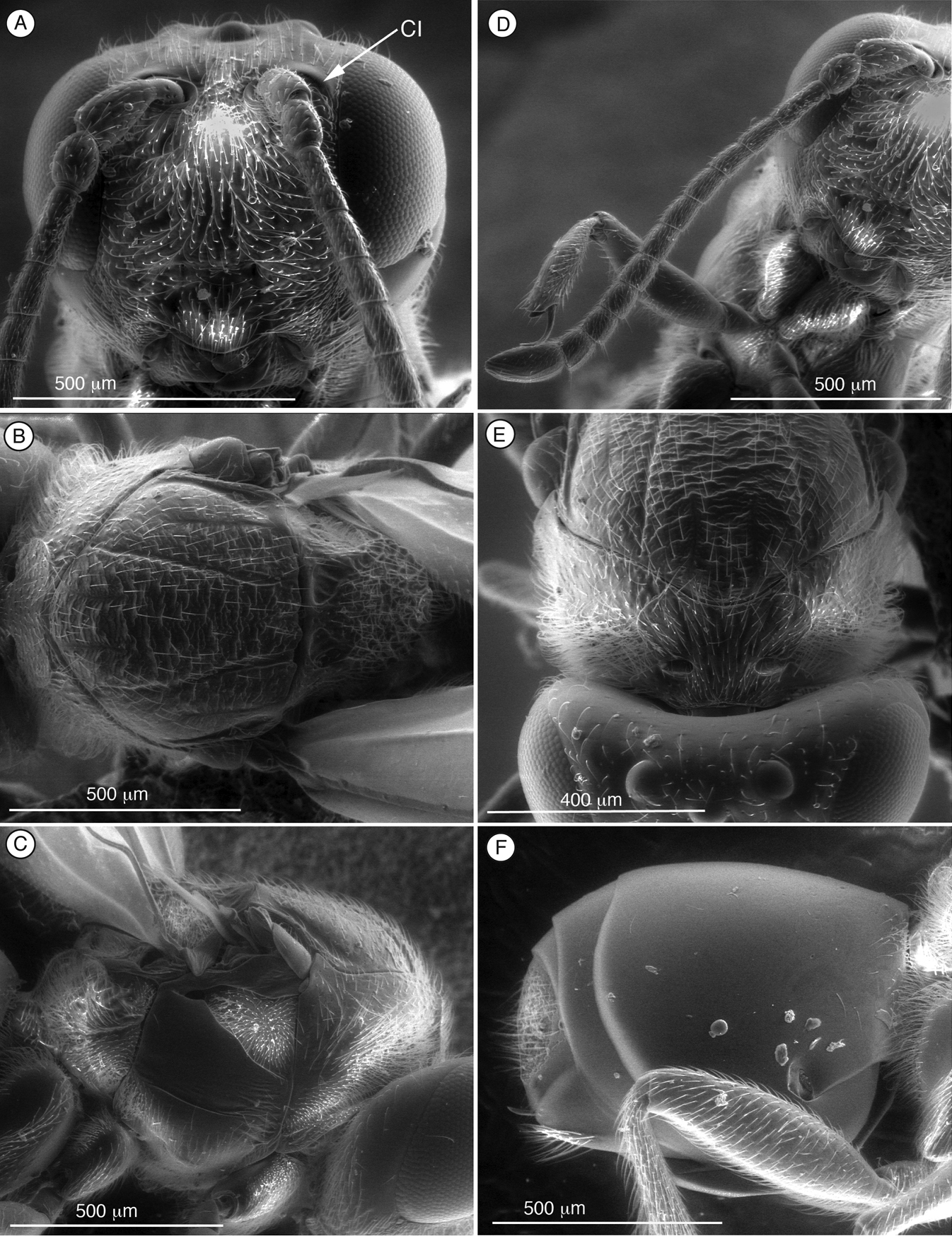
Figure 4. Characters of Thrasorus (A–G) and Scutimica (H) A head, anterior view B mesosoma, dorsal view, Thrasorus rieki C antenna, male, medial view D mesosoma, dorsal view, Thrasorus schmidtae E head and mesosoma, lateral view F metasoma, lateral view G antenna, female, medial view H mesosoma, dorsal view, Scutimica transcarinata.
Length. Female: 3.0–3.2 mm; males: 3.2–3.3 mm.
Coloration. Head and mesosoma black, antennae brown, and metasoma pale brown. Legs pale yellow except coxae, brown.
Head. (Fig. 4A) Frons and face with abundant setae and piliferous punctures; space between clypeus and compound eye with carinae. Malar furrow conspicuous, coriaceous and striate. Occiput smooth; genae with strong striae. Vertex in dorsal view with small piliferous punctures. Circumtorular impression present.
Antenna. Female. (Fig. 4G) 11 flagellomeres, antennal formula: 6(3): 2(2): 5(2): 4(2): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 3(3): 3(3): 3(3): 5(4). Placoid sensillae from F4 to terminal segment. Male. (Fig. 4C) 12 flagellomeres, antennal formula: 7(3): 3(2): 5(2): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 4(3): 5(3). Placoid sensillae starting from F1.
Mesosoma (Fig. 4B, E). Lateral margins of pronotal plate reaching the scutum, forming a small plate conspicuous but not projected, concave dorsomedially, with piliferous punctures. Mesoscutum smooth and shiny, with piliferous punctures. Notauli complete, very narrow anteriorly and much wider posteriorly. Parascutal sulcus wide only in basal half. Lateral basal impressions weak. Antero-admedian lines very weak. Median mesoscutal impression well defined but not clearly delimited anteriorly. Scutellum smooth on anterior falf and centre, rugose posteriorly; scutellar foveae small subtriangular, not clearly delimited posteriorly; interfoveal carina absent. Mesopleural furrow present but not conspicuous. Propodeal carinae present. Pronotum, mesoscutum, scutellum, mesopleural triangle and metapleura not very pubescent, only some sparse setae.
Forewing. Short setae present on wing surface and along margins. Radial cell closed, 1.9 times longer than wide; R2 almost straight; areolet absent.
Legs. Metatibia with two spurs, sub-equal in length, not exceeding one-half length of tarsomere 1.
Metasoma. (Fig. 4F) Petiole short. Base of T3 with an almost complete hairy ring. Tergite 3 smaller than T4; T4 four large, covering almost entire metasomal surface; remaining terga short, telescoped within T4; entire metasoma shiny and smooth.
HOLOTYPE ♀ (ANIC; marked by a red spot, on a pinned card with six other specimens of the same taxon) with the following labels: “Out of large galls on mullee acacia On 18–1-16” (handwritten below the label with the insects), “Thrasorus berlesei (Grlt) Riek det” (white label, handwritten), “sp 7 (berlesei) det ML Buffington 2006” (white label), “Holotype Thrasorus rieki P-M & P-V det-2009” (red label). PARATYPES: 4 ♂ and 1 ♀ (on the same pinned card as the holotype) with the same data as the holotype, “Paratype Thrasorus rieki P-M & P-V det-2009” (red label); 1 ♂ and 5 ♀ (ANIC) (on a pinned card together with 6 Chalcidoidea specimens) with the following labels: “Out of Acacia galls ???? 19.1.16 QLD” (handwritten below the label with the insects), “AUST. NAT. INS. COLL.” (green label), “Paratype Thrasorus rieki P-M & P-V det-2009” (red label); 1 ♀ (QM) with the following labels: “Amblynotus berlesei ♀ Girault types” (white label handwritten), “HOLOTYPE” (pink label), “Thrasorus berlesei (Gir) EF Riek det 1953” (white label handwritten), “QM reg. No. T99347” (yellow label), “Paratype Thrasorus rieki P-M & P-V det-2009” (red label).
Unknown host on Acacia galls (based on label data).
Australia, Queensland.
Named after E.F. Riek, who worked before us on Australian Cynipoidea.
In the QM, there is one specimen labelled as ‘Amblynotus berlesei’
by Girault. In ANIC, there are six specimens on one large card with a
determination label placed by Riek, stating that taxon is ‘Thrasorus berlesei (Grlt)’. But as
Mikeius, described by
The morphology of the metasoma is a very important character and is frequently used in all Figitidae subfamilies to separate different genera. Within Thrasorinae, there are two main metasomal morphologies: T3-T4 free (Thrasorus, Cicatrix), and T3-T4 fused into a syntergum (Palmiriella, Scutimica, Myrtopsen). The primary difference between Thrasorus and Cicatrix is the sculpturing of the mesoscutum. Though the sculpturing on the mesoscutum can be variable in other groups of Figitidae, in the ‘pool’ of genera treated in this paper, mesoscutal sculpture is useful and unique character. Thrasorus is the only genus, not only among Thrasorinae but also among all the genera previously included in this subfamily (Plectocynips, Pegascynips, Euceroptres, Mikeius), that aside from notauli, lacks sculpturing of any kind (microsculpture, carinae or parapsides) in the mesoscutum; we believe that this character is enough to justify the separation of Thrasorus from Cicatrix and the other thrasorines.
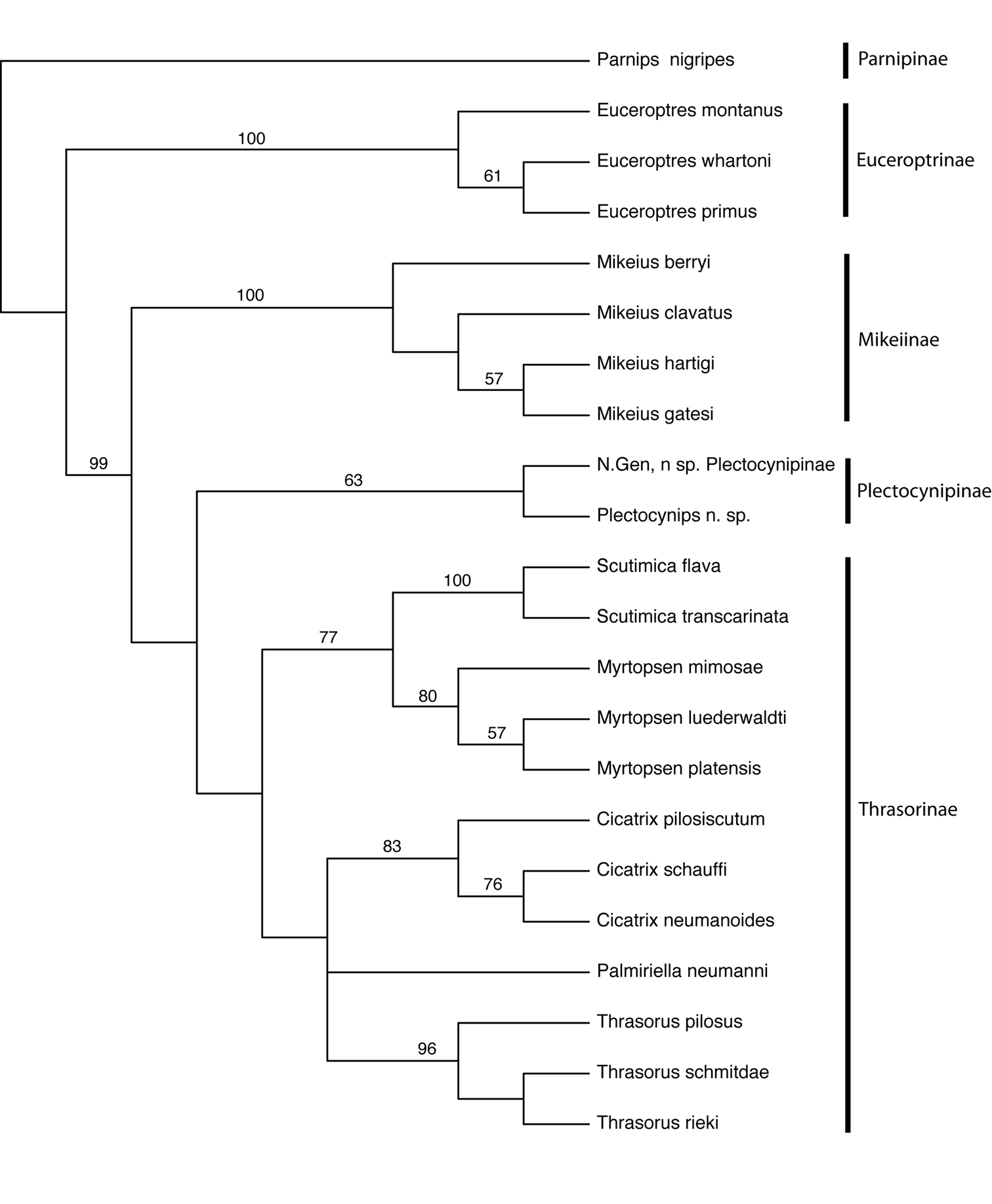
Figure 5. Cladogram of Euceroptrinae, Mikeiinae, Plectocynipinae, and Thrasorinae. Numbers above branches indicate bootstap support. CI=0.58; RI=0.73; RC=0.43. Strict consensus of 2 trees, L=190.
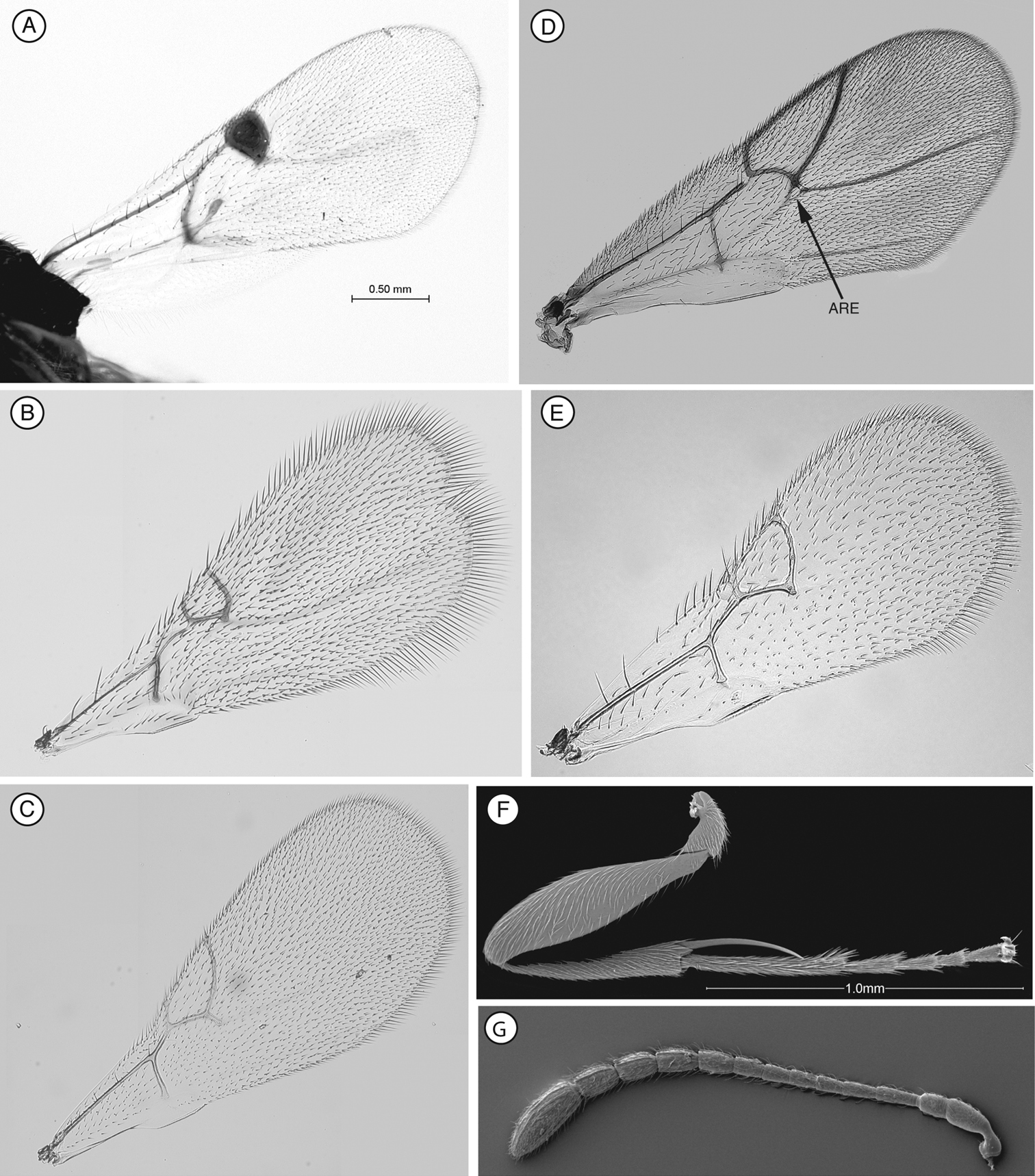
Figure 6. Characteristics of Figitidae: forewing, leg and antenna A Pycnostigmus rostratus (Pycnostigminae) B Emargo sp. (Emargininae) C Phaenoglyphis sp. (Charipinae) D Euceroptres montanus (Euceroptrinae) E Agrostrocynips diastrophus (Eucoilinae) F hindleg, Plectocynips pilosus (Plectocynipinae) G female antenna, Lonchidia sp. (Figitinae).
Figure 7. Characteristics of Figitidae: mesosoma and head A Trybliographa rapae (Eucoilinae) B Parnips nigripes (Parnipinae) C Euceroptres montanus (Euceroptrinae) D Phaenoglyphis sp. (Charipinae) E Anacharis sp. (Anacharitinae) F Aspicera sp. (Aspicerinae).
Figure 8. Characteristics of Figitidae: mesosoma and metasoma A metasomal tergum 2 and 3, Callaspidia sp. (Aspicerinae) B metasomal tergum 2 and 3, Figites sp. (Figitinae) C metasomal tergum 2 and 3, Melanips opacus (Figitinae) D head and mesosoma, Xyalaspis sp. (Anacharitinae) E pronotum, antero-dorsal view, Lonchidia sp. (Figitinae), arrow indicating anterior half of pronotal plate F metasomal tergum 2 and 3 Mikeius hartigi (Mikeiinae).
Figure 9. Characters of Scutimica and Myrtopsen A head, Scutimica transcarinata B head, Myrtopsen luedervaldti C metasoma, Myrtopsen sp. D mesosoma in dorsal view, Scutimica flava E mesosoma in dorsal view, Mikeius mimosae F mesosoma in lateral view, Scutimica transcarinata G mesosoma in lateral view, Mikeius punctuatus.
The characters that differentiate Palmiriella from Scutimica and Myrtopsen are detailed in the diagnosis of the genus (see above). The combination of the smooth face (Palmiriella being the only genus among Thrasorinae
and genera previously included in the subfamily lacking any kind of
sculpture on face), shape of syntergum T3-T4, shape of scutellum,
shape of pronotum, and absence of sculpturing on pronotum, distinguish
Palmiriella from Scutimica and Myrtopsen. The differences between Scutimica and Myrtopsen have already been remarked and discussed in
The results of the phylogenetic analysis are summarized in Fig. 5. Two trees of length 190 were recovered, with a CI of 0.58, RI of 0.73, and RC of 0.43. All subfamilies treated here were recovered as monophyletic, with following pattern of relationship: Parnipinae (Euceroptrinae (Mikeiinae (Plectocynipinae (Thrasorinae)))). It is clear that Mikeius renders the Thrasorinae paraphyletic, supporting the description of Mikeiinae, and that Cicatrix and Palmiriella are distinct clades. Erecting a new subfamily for a single genus is not desirable, but the only alternative to this while respecting the clades recovered in the phylogenetic analysis would be grouping together Mikeius, Palmiriella, Thrasorus, Cicatrix, Scutimica, Myrtopsen, Plectocynips and Pegascynips in a single subfamily; we feel this grouping is undesirable from the standpoint of predictability, since these genera contain species possessing markedly different biological and morphological attributes, and still would lack a single common diagnostic character for all of them. As currently defined, each of the subfamilies recognized here has its own diagnostic character: long metatibial spur for Plectocynipinae, circumtorular impression for Thrasorinae and two carinae in median area of pronotum not forming a projected pronotal plate for Mikeiinae.
The Thrasorinae from Australia are one of the most poorly known groups of figitids. More field data and specimens would help to clarify the status of this group and some taxa described here. However, there is no single researcher in Australia dedicated to the study of Cynipoidea, and workers on Figitidae wanting to study the systematics of this group must rely on ‘rare’ specimens coming from non-target collections while pursuing the sampling of other groups. The study we present here has been done with all the thrasorines and Mikeius that have been collected, curated, and deposited in museums worldwide.
Key to figitid subfamilies of the World| 1 | Radial cell secondarily sclerotized forming a pseudostigma (Fig. 6A); Afrotropical and southwestern Palaearctic regions, rarely collected | Pycnostigminae |
| – | Radial cell (Fig. 6 B–E) not sclerotized, forming a typical wing cell | 2 |
| 2 | Scutellum with an oval, tear-drop shaped, or elongate elevated plate dorsally (arrow, Fig. 7A); scutellar plate equipped with a glandular release pit medially or posteriorly; parasitoids of Diptera: Cyclorrhapha; Cosmopolitan | Eucoilinae |
| – | Scutellum different or occasionally with raised carinae defining a central area but never with an elevated plate equipped with a glandular release pit dorsally (Figs 7 B–D and 8D) | 3 |
| 3 | Metatibial spur at least half the length of metatarsomere 1 (Fig. 6F); associated with hymenopteran galls in Nothofagus forests in the Neotropical Region | Plectocynipinae |
| – | Metatibial spur at most 1/4 length of metatarsomere 1 | 4 |
| 4 | Apex of forewing deeply bilobed (Fig. 6B); Pantropical, rarely collected | Emargininae |
| – | Apex of forewing rounded (Fig 6 C–D) | 5 |
| 5 | Areolet present on forewing (Fig. 6D); base of metasoma always glabrous | 6 |
| – | Areolet absent on forewing (Fig. 6 C, E); base of metasoma setose or glabrous | 7 |
| 6 | Mesopleuron completely strigose, with no indication of a distinct mesopleural furrow (Fig. 7B); parasitoids of Barbotinia (Cynipidae) in Papaver (Papaveraceae); Palaearctic, Mediterranean Region | Parnipinae |
| – | Mesopleuron dorsally smooth, ventrally striate along the mesopleural furrow, mesopleural furrow distinct (Fig. 7C); parasitoids of Andricus (Cynipidae) in Quercus (Fagaceae) in the Nearctic Region | Euceroptrinae |
| 7 | Head triangular in anterior view (Fig. 7E), always wider than the mesosoma (in dorsal view; Fig. 8D); mouth region small, with mandibles broadly overlapping (Fig. 7E); parasitoids of Neuroptera; Cosmopolitan | Anacharitinae |
| – | Head squared or rounded in anterior view (Figs 1A, 2 A & D, 7F), wider, equal to, or narrower than the mesosoma; mouth region broadened, mandibles larger and not overlapping as extensively (Figs 1A & 7F) | 8 |
| 8 | Facial impression present (Fig. 7F); third metasomal tergum distinctly saddle shaped with posterolateral margin concave and central part almost tongue-like (Fig. 8A); parasitoids of Diptera: Syrphidae; Cosmopolitan | Aspicerinae |
| – | Facial impression absent (Fig. 1A); third abdominal tergum rounded, not saddle-shaped, with the posterolateral margin usually convex, rarely concave (Figs 3F, 4F, 8B–C, F) | 9 |
| 9 | Body lacking transversally carinate sculpture, generally shiny and smooth (Fig. 7D) (Lytoxysta is exceptional in havingfine reticulate sculpturing on the head and mesosoma; some species of Phaenoglyphis have fine imbricate sculpture on the mesoscutum and scutellum ( |
Charipinae |
| – | Mesoscutum usually with some transversal macro or microcarinate sculpture (Figs 1F, 2 B & E, 3B, 4D & H, 8D), sometimes smooth or at most piliferous (Fig. 4B); mesopleural triangle always present (Fig. 1B, 3C, 4E); notauli partially to fully present (Fig. 1F, 2B & E, 3B, 4B & D & H, 8D); larger insects, typically greater than 2mm in length | 10 |
| 10 | Circumtorular impression present (CI, Fig. 2A & D, 3A, 4A) | Thrasorinae |
| - | Circumtorular impression absent (Fig. 1A) | 11 |
| 11 | Second metasomal segment modified into either a collar with strong carinae (Fig. 8A), a carinate sheath (Fig. 8B) or carinate flange Fig. 8C), obscuring part of the petiole in lateral and dorsal view; parasitoids of Diptera: Cyclorrhapha; Cosmopolitan | Figitinae |
| – | Second metasomal segment small, not heavily sclerotized, typically obscured by the anterior margin of tergite 3 (Fig. 8F); Australian Region, parasitoids of gall inducing Hymenoptera | Mikeiinae, subfam. n. |
| 1 | Metasomal syntergum absent (post-petiolar terga free) (Fig. 2C) | 2 |
| – | Metasomal syntergum present (post-petiolar terga fused) (Figs 3F, 9C) | 3 |
| 2 | Mesoscutum with horizontal microsculpture (Fig. 2B, E); face with strong or weak transverse strigae (Fig. 2A, D) | Cicatrix gen. n. |
| – | Mesoscutum smooth, at most with some piliferous punctures (Fig. 4B, D); face without transverse strigae; if present, strigae are weak (Fig. 4A) | Thrasorus Weld |
| 3 | Metasomal syntergum not covering the entire metasomal surface (Fig. 3F); face without transversal strigae (Fig. 3A) | Palmiriella, gen. n. |
| – | Metasomal syntergum covering the entire metasoma (Fig. 9C); face with strigae (Fig. 9A, B) | 4 |
| 4 | Mesoscutum smooth or with parapsides; notauli incomplete, not reaching pronotum, each one forming a large cell (Figs 4H, 9D). Pronotum sometimes projected, with very strong longitudinal carinae (Figs 4H, 9F) | Scutimica Ros-Farré |
| – | Mesoscutum with microsculpture (only one species with transverse carinae); notauli complete, even if being much larger at the base than close to pronotum (Fig. 9E). Pronotum not projected, striate or with strong irregular carinae (Fig. 9G) | Myrtopsen Rübsaamen |
We are very grateful to John La Salle and Nicole Fisher (CSIRO/ANIC, Canberra, Australia) for sending the undetermined specimens and to Chris Burwell and Susan Wright (QM, Brisbane, Australia) for sending the Girault types. We also thank Palmira Ros-Farré (University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain) for her very valuable comments on this work. MB thanks Smithsonian Institution intern Stephanie Bailey for providing SEM images of Mikeius hartigi. John Brown and Thomas Henry (Systematic Entomology Laboratory, ARS/USDA, Washington DC), and John La Salle (CSIRO, Canberra, Australia), and two anonymous reviewers, dramatically improved earlier drafts of this manuscript.
List of morphological and biological characters used in analysis
Note: The list of morphological and biological characters is available on the ZooKeys website as a Microsoft Word file (.doc), doi: 10.3897/zookeys.108.829.app.1).
Data matrix which includes 79 parsimony-informative characters.
Note: The data matrix is available on the ZooKeys website as a Microsoft Word file (.doc), doi: 10.3897/zookeys.108.829.app.2).