(C) 2012 Alexei V. Abramov. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 (CC-BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
For reference, use of the paginated PDF or printed version of this article is recommended.
Karyotypes of Hapalomys delacouri (Rodentia, Muridae) and Typhlomys cinereus (Rodentia, Platacanthomyidae) from Vietnam are described for the first time. The diploid karyotype of Hapalomys delacouri is 38 (NFa=48), consisting of six pairs of bi-armed and 12 pairs of acrocentric autosomes decreasing in size; plus a large metacentric X chromosome and Y chromosome, also metacentric, that is equal in size to the largest pair of acrocentric autosomes. The newly described karyotype differs significantly from that reported for Hapalomys delacouri from northern Thailand. The latter record very likely represents a different species of Hapalomys, possibly the taxon Hapalomys pasquieri described from north-central Laos.The diploid karyotype of Typhlomys cinereus is 38 (NF=48), consisting of five pairs of meta- to submetacentric and 14 pairs of acrocentric chromosomes varying in size from large to small; sex chromosomes were not defined.
karyotypes, Hapalomys delacouri, Hapalomys pasquieri, Typhlomys cinereus, Vietnam
According to the recent checklist by
It is well known that karyological data can be useful for tackling problems of rodent taxonomy and evolution (
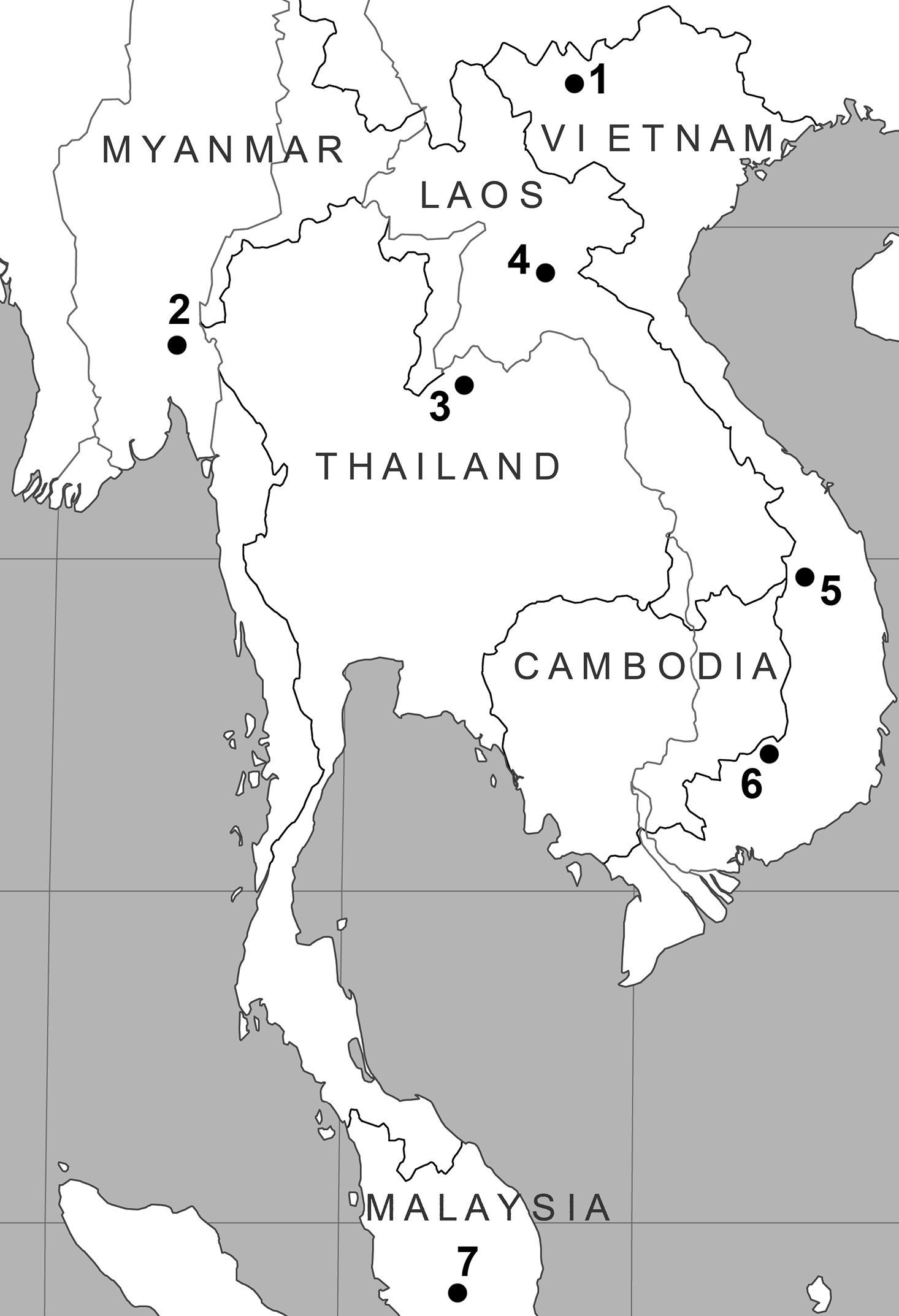
A number of rare and poorly-known mammal species were collected during a biodiversity surveys carried out by the Joint Vietnam-Russian Tropical Research and Technological Centre in 2010. Voucher specimens are deposited in the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (ZIN), Saint-Petersburg, Russia. Five specimens of the marmoset rat Hapalomys delacouri Thomas, 1927 were collected in southern Vietnam, NE of Bu Gia Map Village, Binh Phuoc Province (12°12'N, 107°12'E; ZIN 98922, 99486-99488, 100410). A specimen of the soft-furred tree mouse Typhlomys cinereus Milne-Edwards, 1877 was collected in northern Vietnam, near Tram Ton Station of Hoang Lien National Park, W of Sa Pa Village, Lao Cai Province (22°21'N, 103°46'E; ZIN 100411). The collecting localities are shown in Fig.1.
The rodents were caught alive using locally made cage traps. The specimens were immediately brought to the laboratory where they were karyotyped. Chromosome analysis was carried out on preparations obtained from bone marrow following the standard colchicines method (
The marmoset rats have very distinct external and cranial characteristics which preclude an incorrect generic identification (
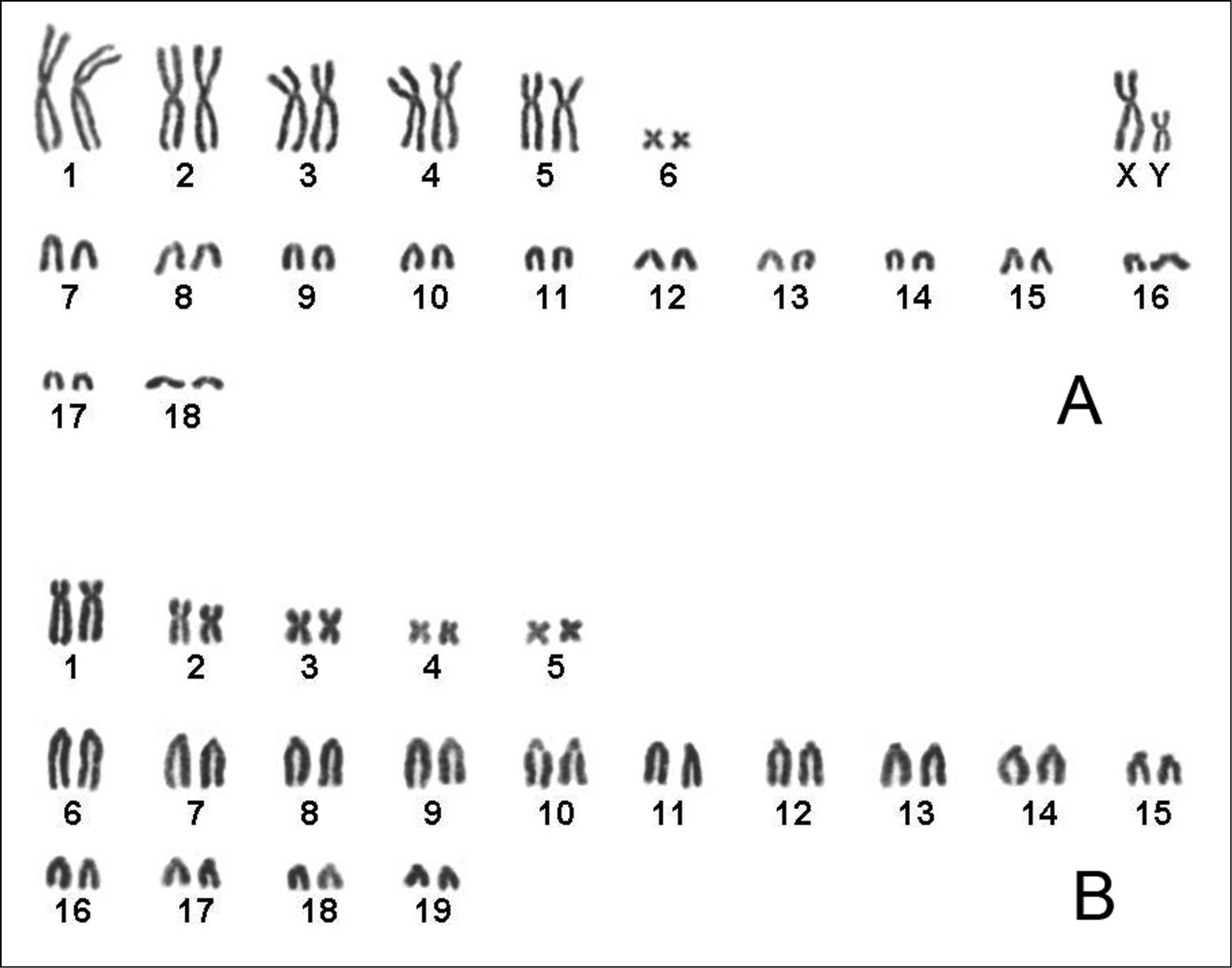
The diploid chromosome number is 2n=38, NFa=48 (Fig. 3A). This karyotype consists of six pairs of bi-armed and 12 pairs of acrocentric autosomes decreasing in size, with a large metacentric X chromosome and with Y chromosome, also metacentric, which is equal in size to the largest pair of acrocentric autosomes.
The observed karyotype differs significantly from that described by
According to recent taxonomic studies (
| Measurements | Hapalomys longicaudatus (from |
Hapalomys delacouri (from |
Hapalomys delacouri Bu Gia Map, n=4 |
Hapalomys pasquieri (from |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of head and body | 162-165 (163.5) | 123-136 (131.0) | 130-146 (136.7) | 121.0 |
| Length of tail | 193-202 (198.3) | 140-160 (149.2) | 155-165 (160.0) | 171.0 |
| Greatest length of skull | 39.7-41.5 (40.47) | 33.6-34.2 (34.00) | 34.6-35.7 (35.10) | 32.0 |
| Length of nasals | 11.5-12.6 (12.25) | 11.7-12.0 (11.87) | 11.7-11.9 (11.72) | 10.5 |
| Length of rostrum | 9.7-10.2 (9.93) | 9.3-9.7 (9.47) | 9.4-10.0 (9.66) | 8.3 |
| Height of brain case | 11.2-12.0 (11.63) | 9.1-9.5 (9.33) | 9.1-9.7 (9.49) | 9.0 |
| Palatal length | 18.1-22.3 (20.78) | 16.9-18.0 (17.48) | 17.4-18.2 (17.83) | 15.8 |
| Maxillary tooth-row* | 7.9-8.0 | ca. 6.3 | 6.3-6.6 (6.4) | ca. 5.9 |
Map of localities. 1 sampling locality of Typhlomys cinereus 2 type locality of Hapalomys longicaudatus 3 locality from
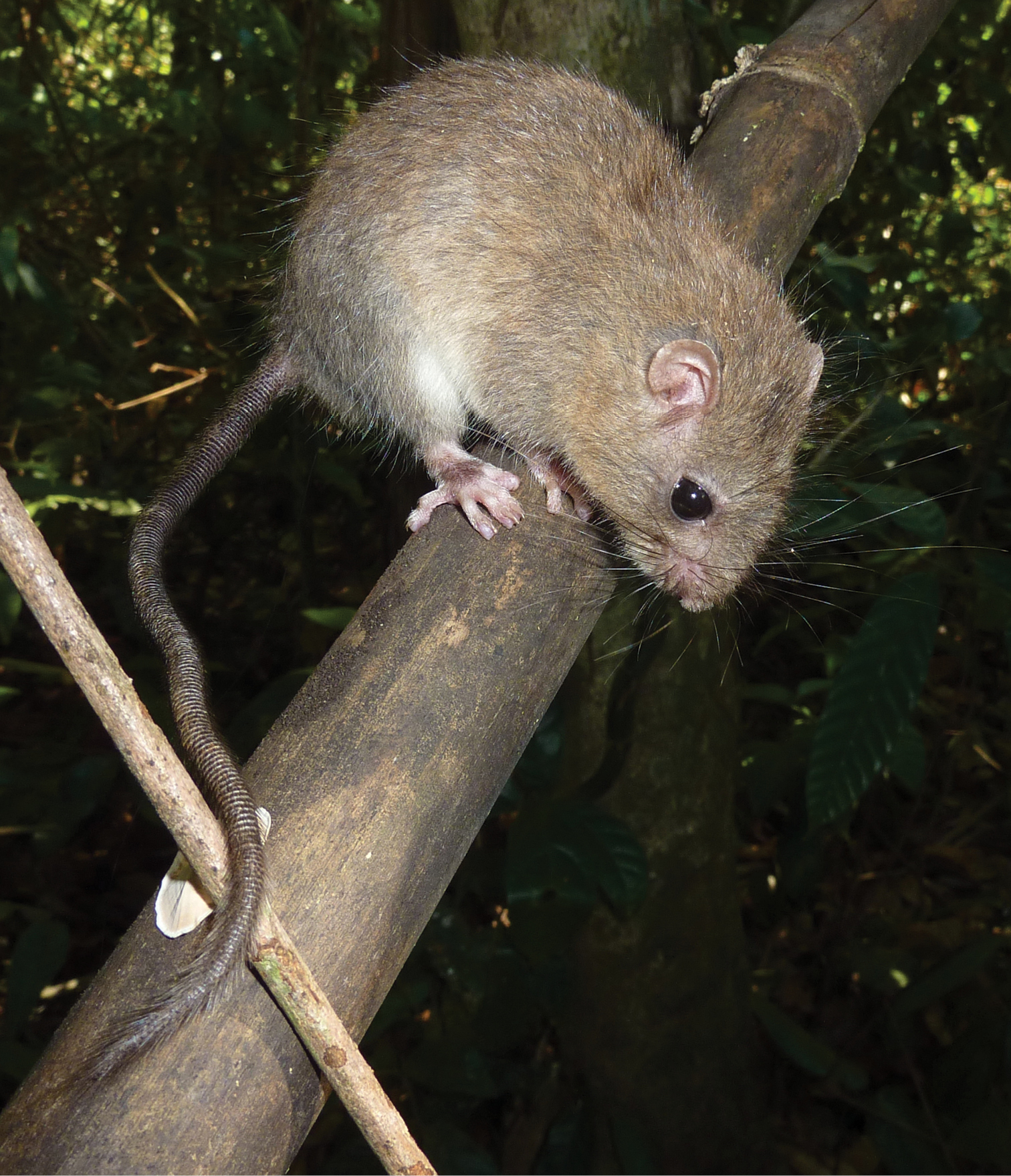
Hapalomys delacouri. Adult male from Bu Gia Map, Binh Phuoc Province, southern Vietnam. Photographed by Alexei V. Abramov.
A Karyotype of male Hapalomys delacouri (ZIN 100410), 2n=38, NFa=48 B Karyotype of female Typhlomys cinereus (ZIN 100411), 2n=38, NF=48.
The diploid chromosome number is 2n=38, NF=48 (Fig. 3B), consisting of five pairs of meta- to submetacentric and 14 pairs of acrocentric chromosomes varying in size from large to small. Sex chromosomes of Typhlomys cinereus have not defined, as the female only was karyotyped in this study. It is the first karyotype described for a representative of the genus Typhlomys.
The soft-furred tree mouse, or pygmy dormouse, Typhlomys cinereus (Fig. 4) belongs to the enigmatic family Platacanthomyidae, the earliest phylogenetic offshoot within Muroidea (
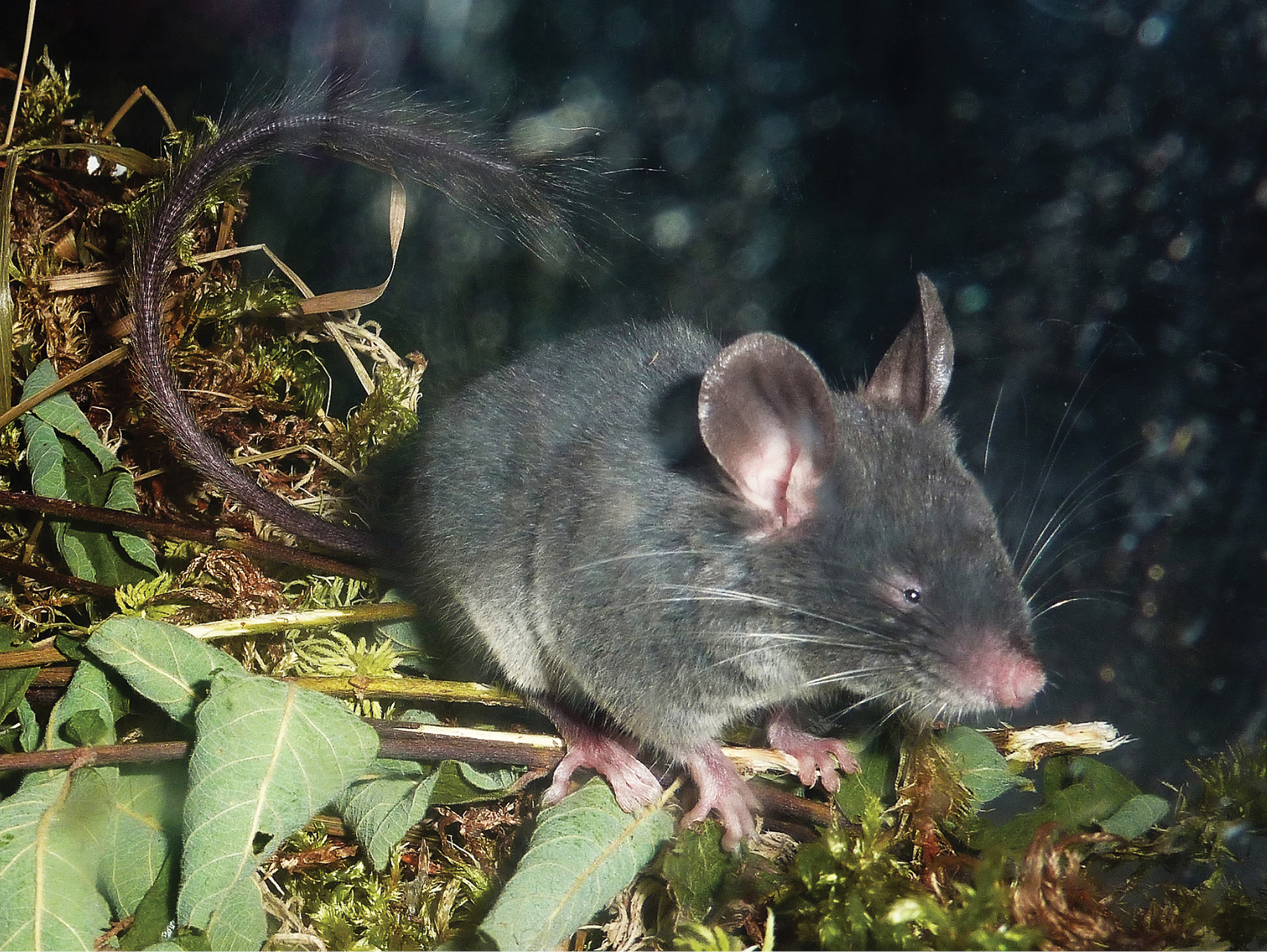
Typhlomys cinereus. Adult female from Sa Pa, Lao Cai Province, northern Vietnam. Photographed by Alexei V. Abramov.
We are grateful to the administration of the Bu Gia Map Nature Reserve and Hoang Lien National Park for providing us with an opportunity to carry out field surveys. We would like to express our sincere thanks to A.V. Shchinov, S.V. Kruskop and all expedition members of the Joint Vietnam-Russian Tropical Research and Technological Centre for their great help and scientific expertise during the field works. We are obliged to Dmitri Logunov (Manchester, UK) for assistance with English language. We are grateful to Ken Aplin and anonymous reviewer for useful comments on an earlier draft. This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Education and Science of Russian Federation.