|
||
|
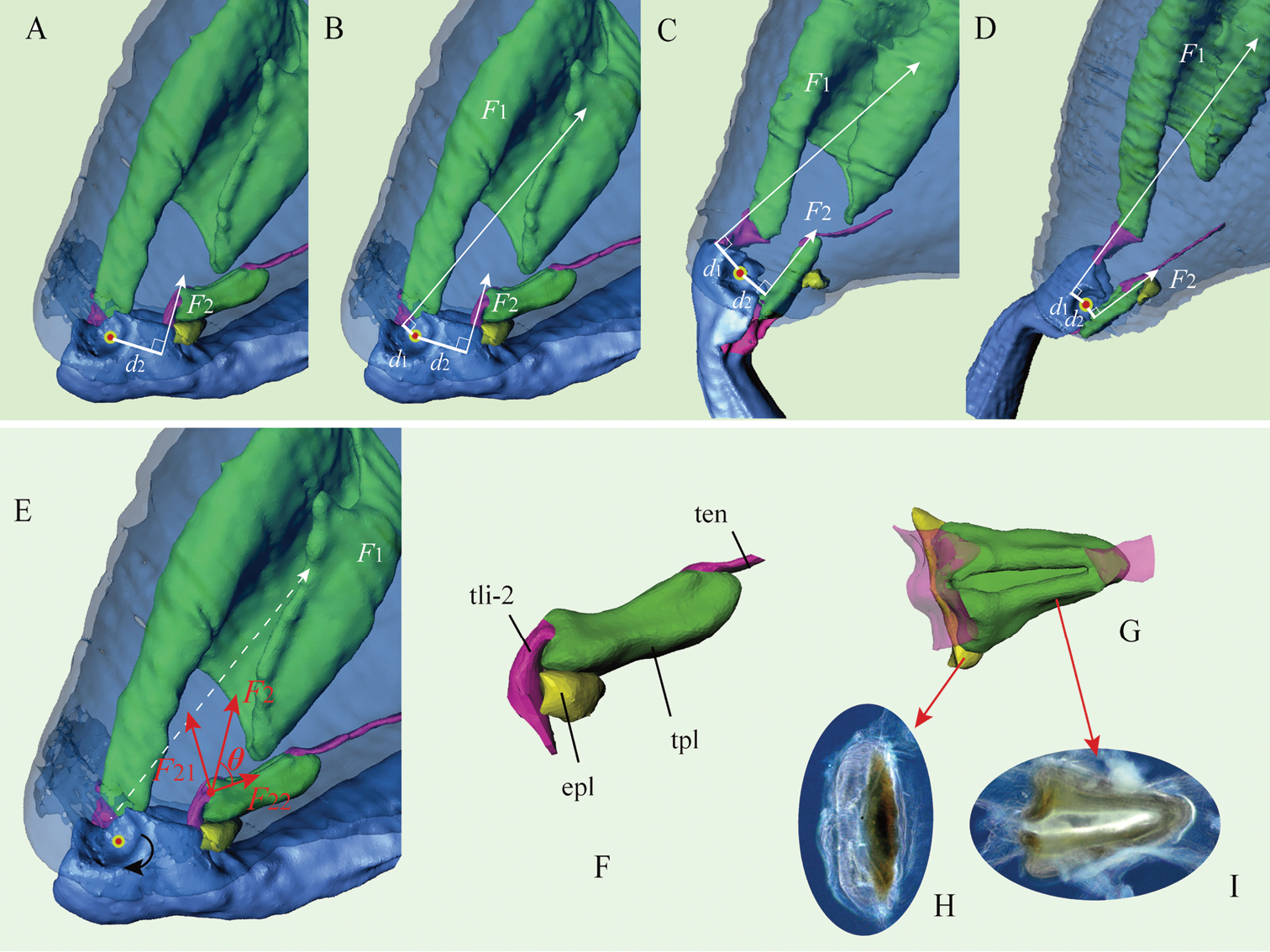
The dynamics of the catapult mechanism of the flea beetle hind leg powered by the elastic plate (Asiophrida xanthospilota, micro-CT 3D reconstructions from four different phases of the jumping leg). (F1 indicates the force generated by tibial extensor muscles responsible for extension of the tibia; F2 indicates the force responsible for flexion of the tibia which is indirectly generated by tibial flexor muscles). A–D 3D reconstructions of four hind legs through each of the four phases of the jump, indicating variable d1 (moment arm of F1) and d2 (moment arm of F2). d1 is at its minimal length at the start of the hind leg extension and at its maximal length during the middle; by contrast, d2 is at its maximal length at the start of the hind leg extension and at its minimal at the end A phase I B phase II C phase III D phase IV E the positive feedback mechanism in the take-off process. F2 comprises F21, which is the constrained force generated by the elastic plate, and F22, which is generated by the tibial flexor muscle F the triangular plate – elastic plate complex (lateral view) G the triangular plate – elastic plate complex (dorsal view) H the elastic plate (dorsal view, under light microscope, dark-field microscopy) I the triangular plate (dorsal view, under light microscope, dark-field microscopy). Abbreviations: epl: elastic plate; tli-2: secondary tibial ligament; tpl: triangular plate; ten: tendon of tibial flexor. |