|
||
|
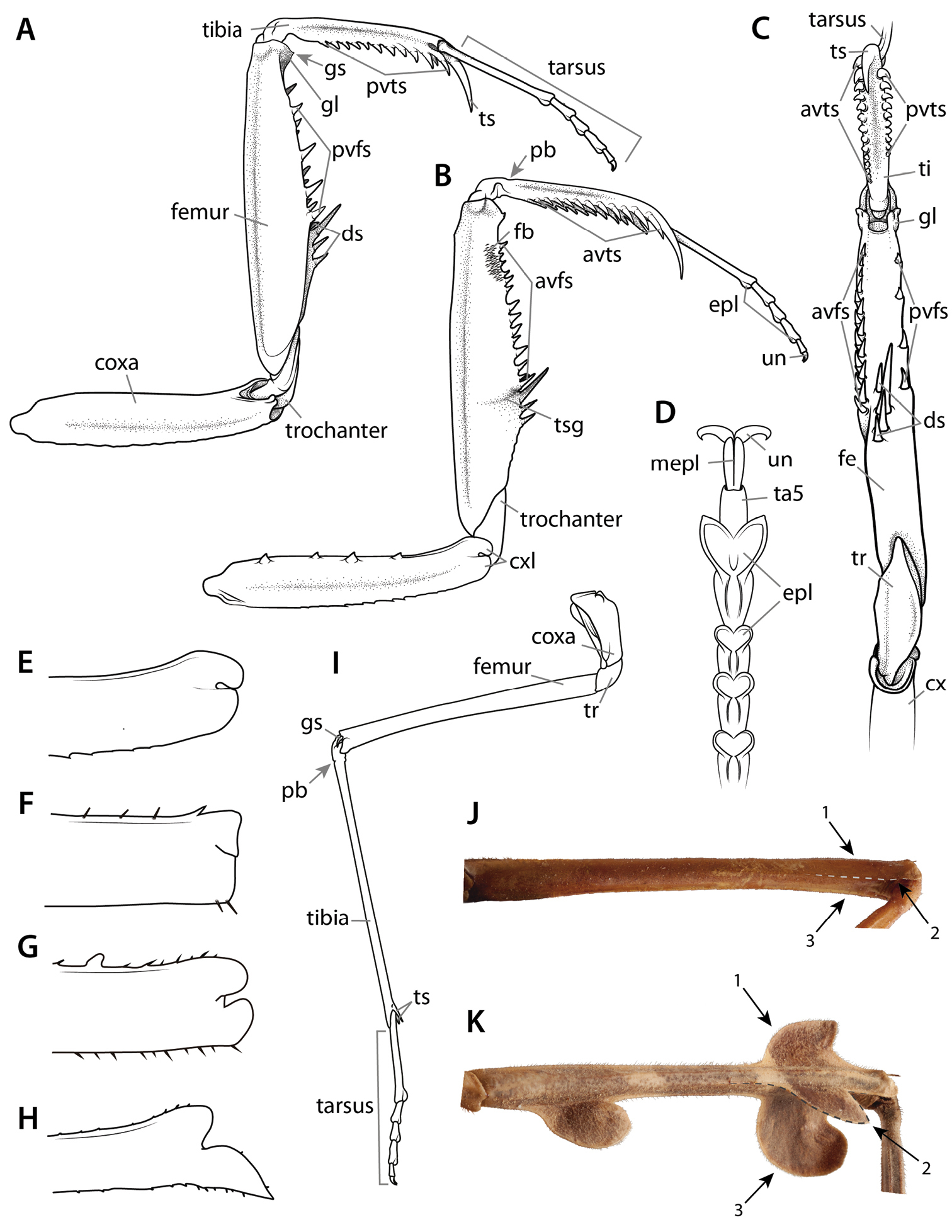
Annotated illustrations of leg structures. Generalized mantodean foreleg A dorsal view; B ventral view; C interior view. Generalized tarsus D ventral view. Examples of convergent coxal lobes: E Sphodromantissp. ♂; F Paramorphoscelis gondokorensis Werner, 1907 ♀. Example of parallel coxal lobes G Acromantis insularis Giglio-Tos, 1915 ♀. Example of divergent coxal lobes H Gongylus gongylodes Linné, 1758 ♂. Generalized metathoracic leg I ventral view. Examples of carinae that can be present on the meso- and metathoracic femora and tibiae J Stagmatoptera Burmeister, 1838 ♀: ventral view 1 = anterodorsal metafemoral carina; 2 = anteroventral metafemoral carina; 3 = posteroventral metafemoral carina. Example of the cuticular lobes that can project from leg carinae K Alangularis multilobata (Chopard, 1910) ♀: ventral view 1 = anterodorsal metafemoral lobe; 2 = anteroventral metafemoral lobe; 3 = posteroventral metafemoral lobe. Dashed lines demarcate anteroventral carinae (J) and associated lobes (K). Abbreviations: avfs = anteroventral femoral spines; avts = anteroventral tibial spines; cx = coxa; cxl = coxal lobes; ds = discoidal spines; epl = euplantulae; fb = femoral brush; fe = femur; gl = genicular lobe; gs = genicular spur; mepl = medial euplantula; pb = proximal bend in the tibia; pvfs = posteroventral femoral spines; pvts = posteroventral tibial spines; ta5 = tarsomere 5; ti = tibia; tr = trochanter; ts = tibial spur; tsg = tibial spur groove; un = unguis. |