Citation: Pinilla-Buitrago G, Martínez-Morales MA, González-García F, Enríquez PL, Rangel-Salazar JL, Guichard Romero CA, Navarro-Sigüenza AG, Monterrubio-Rico TC, Escalona-Segura G (2014) CracidMex1: a comprehensive database of global occurrences of cracids (Aves, Galliformes) with distribution in Mexico. ZooKeys 420: 87–115. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.420.7050 GBIF key: http://www.gbif.org/dataset/d912f677-e998-4beb-a61f-b68406c2b66b
Resource citation: El Colegio de la Frontera Sur (2014 -). CracidMex1: a comprehensive database of global occurrences of cracids (Aves, Galliformes) with distribution in Mexico. 23896 records. Contributed by Pinilla-Buitrago G, Martínez-Morales MA, González-García F, Enríquez PL, Rangel-Salazar JL, Guichard Romero CA, Navarro-Sigüenza AG, Monterrubio-Rico TC, Escalona-Segura G. Online at http://ipt.pensoft.net/ipt/resource.do?r=cracidmex1, released on 10-03-2014, version 7 (last updated on 19-04-2014). GBIF key: http://www.gbif.org/dataset/d912f677-e998-4beb-a61f-b68406c2b66b. Data Paper ID: doi: 10.3897/zookeys.420.7050
Cracids are among the most vulnerable groups of Neotropical birds. Almost half of the species of this family are included in a conservation risk category. Twelve taxa occur in Mexico, six of which are considered at risk at national level and two are globally endangered. Therefore, it is imperative that high quality, comprehensive, and high-resolution spatial data on the occurrence of these taxa are made available as a valuable tool in the process of defining appropriate management strategies for conservation at a local and global level. We constructed the CracidMex1 database by collating global records of all cracid taxa that occur in Mexico from available electronic databases, museum specimens, publications, “grey literature”, and unpublished records. We generated a database with 23, 896 clean, validated, and standardized geographic records. Database quality control was an iterative process that commenced with the consolidation and elimination of duplicate records, followed by the geo-referencing of records when necessary, and their taxonomic and geographic validation using GIS tools and expert knowledge. We followed the geo-referencing protocol proposed by the Mexican National Commission for the Use and Conservation of Biodiversity. We could not estimate the geographic coordinates of 981 records due to inconsistencies or lack of sufficient information in the description of the locality.
Given that current records for most of the taxa have some degree of distributional bias, with redundancies at different spatial scales, the CracidMex1 database has allowed us to detect areas where more sampling effort is required to have a better representation of the global spatial occurrence of these cracids. We also found that particular attention needs to be given to taxa identification in those areas where congeners or conspecifics co-occur in order to avoid taxonomic uncertainty. The construction of the CracidMex1 database represents the first comprehensive research effort to compile current, available global geographic records for a group of cracids. The database can now be improved by continuous revision and addition of new records. The CracidMex1 database will provide high quality input data that could be used to generate species distribution models, to assess temporal changes in species distributions, to identify priority areas for research and conservation, and in the definition of management strategies for this bird group. This compilation exercise could be replicated for other cracid groups or regions to attain a better knowledge of the global occurrences of the species in this vulnerable bird family.
Ortalis, Penelope, Penelopina, Oreophasis, Crax, Cracidae, Aves, chachalacas, guans, curassows, Mexico, Neotropic, geographic record, Darwin Core
Cracids are a primitive family of Neotropical Galliformes. They are mainly frugivorous birds that inhabit primary forests, and may play an important role in regenerating and structuring forests through the dispersion and predation of seeds (
Cracids are one of the most vulnerable groups of Neotropical birds because almost half of the 54 recognized species (
The lack of up to date, high quality data on the presence and abundance of cracids in many regions of their distribution prevents the definition and implementation of appropriate management strategies for their conservation (
To tackle this imperative need for information, we constructed the CracidMex1 database that embodies an exhaustive, high quality, and updated compilation of the global geographic records of the eight cracid species with distribution in Mexico. The collation of records from numerous sources required a thorough process of quality control in terms of consolidation and elimination of record redundancies, completion of missing data, verification of record localities and their spatial precision, and validation of taxa identity. This involved an iterative process of automatized tasks and the use of expert knowledge in terms of species and regions.
The CracidMex1 database will provide high quality, input data that could be used to identify areas where more research is needed, generate species distribution models, assess temporal changes in species distribution, identify priority areas for cracid conservation, and even in the definition of management strategies for this avian group. This compilation exercise could be replicated for other groups of cracids or regions to achieve a more complete knowledge of the global occurrences of the species of this vulnerable bird family.
This open access database will be continuously reviewed and supplemented with additional records, and all contributions to the database are very welcome.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
Order: Galliformes
Family: Cracidae
Genera: Ortalis, Penelope, Penelopina, Oreophasis, Crax
Species: Ortalis vetula (Wagler, 1830), Ortalis wagleri Gray, 1867, Ortalis poliocephala (Wagler, 1830), Ortalis leucogastra (Gould, 1843), Penelope purpurascens Wagler, 1830, Penelopina nigra (Fraser, 1852), Oreophasis derbianus Gray, 1844, Crax rubra Linnaeus, 1758 (Table 1).
Conservation and endemic features of the cracid taxa included in the CracidMex1 database.
| Species/Subspecies | Common name | CITES |
IUCN |
NOM-059 |
Endemicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ortalis vetula | Plain Chachalaca | III |
Least Concern | Not endemic | |
| Ortalis vetula vetula | • E Mexico to Costa Rica | ||||
| Ortalis vetula mccalli | • SE USA, E Mexico | ||||
| Ortalis vetula pallidiaventris | • Yucatan Peninsula (Mexico) | ||||
| Ortalis vetula deschauenseei | • Utila Island (Honduras) | ||||
| Ortalis vetula intermedia | • S Mexico, Guatemala, Belize | ||||
| Ortalis wagleri | Rufous-bellied Chachalaca | Least Concern | North western Mexico | ||
| Ortalis poliocephala | West Mexican Chachalaca | Least Concern | Central western Mexico | ||
| Ortalis leucogastra | White-bellied Chachalaca | Least Concern | Special protection | Northern Central America (Pacific slope) | |
| Penelope purpurascens | Crested Guan | III |
Least Concern | Threatened | Not endemic |
| Penelope purpurascens purpurascens | • Threatened | • Not endemic | |||
| Penelope purpurascens aequatorialis | • Not endemic | ||||
| Penelope purpurascens brunnescens | • N Colombia, N Venezuela | ||||
| Penelopina nigra | Highland Guan | III |
Vulnerable | Endangered | Northern Central America |
| Oreophasis derbianus | Horned Guan | I | Endangered | Endangered | S Mexico, Guatemala |
| Crax rubra | Great Curassow | III |
Vulnerable | Threatened | Not endemic |
| Crax rubra rubra | • Threatened | • Not endemic | |||
| Crax rubra griscomi | • Endangered | • Cozumel Island (Mexico) |
1 Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora <http://www.cites.org/eng/app/appendices.php>.
2 The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species <http://www.iucnredlist.org>.
3 Mexican environmental legislation (
4 Guatemala and Honduras.
5 Honduras.
6 Guatemala.
7Guatemala, Honduras, Costa Rica, and Colombia.
Common names: Chachalacas, Guans, and Curassows
The CracidMex1 database comprises 23, 896 global records of 12 taxa of cracid species and subspecies with distribution in Mexico. This includes eight cracid species distributed in Mexico, out of the 54 recognized species in the Neotropical region (
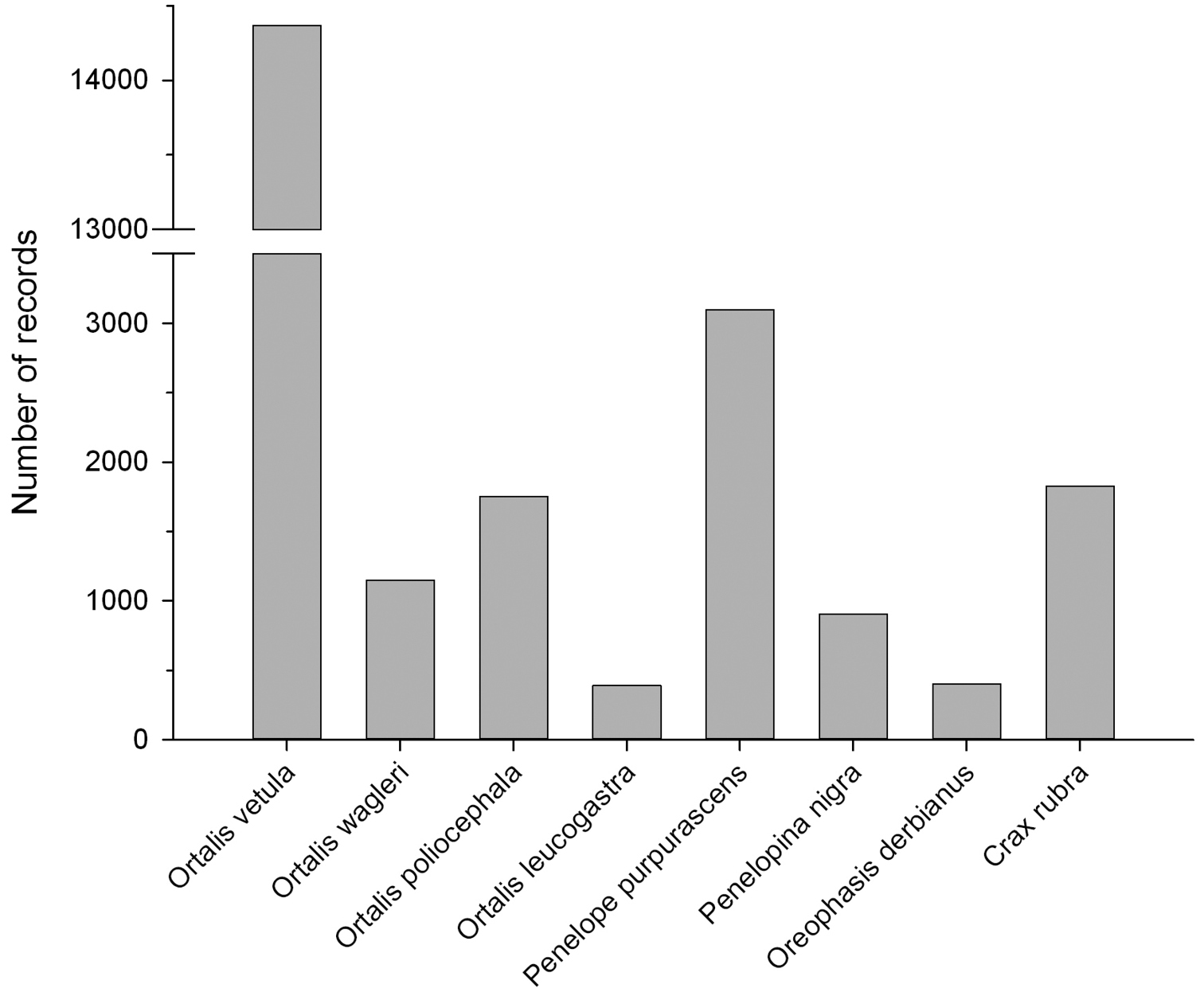
Distribution of the 23, 896 records by species in the CracidMex1 database.
Number of records in the CracidMex1 database by genus, species, and subspecies.
| Genus/Species/Subspecies | Records | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ortalis | 17, 663 | 73.9 |
| Ortalis vetula | 14, 366 | 60.1 |
| Ortalis vetula vetula | 193 | 0.8 |
| Ortalis vetula mccalli | 291 | 1.2 |
| Ortalis vetula pallidiventris | 119 | 0.5 |
| Ortalis vetula deschauenseei | 4 | 0.0 |
| Ortalis vetula intermedia | 58 | 0.2 |
| Ortalis wagleri | 1, 151 | 4.8 |
| Ortalis poliocephala | 1, 754 | 7.3 |
| Ortalis leucogastra | 392 | 1.6 |
| Penelope | 3, 100 | 13.0 |
| Penelope purpurascens | 3, 100 | 13.0 |
| Penelope purpurascens purpurascens | 1, 152 | 4.8 |
| Penelope purpurascens aequatorialis | 164 | 0.7 |
| Penelope purpurascens brunnescens | 29 | 0.1 |
| Penelopina nigra | 907 | 3.8 |
| Oreophasis derbianus | 401 | 1.7 |
| Crax | 1, 825 | 7.6 |
| Crax rubra | 1, 825 | 7.6 |
| Crax rubra rubra | 1, 797 | 7.5 |
| Crax rubra griscomi | 28 | 0.1 |
General spatial coverage
Valid distributional records (22, 731), based on the native distribution of taxa, cover distributions from southern Texas, USA, in the north, to Loja, Ecuador, in the south, including Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, and Peru (Table 3, Figures 2 and 3). These records are labelled as presente (present) in the “occurrenceStatus” field of the database. Other records corresponded to zoo specimens (49), records with spatial inconsistencies or ambiguities (143), and records for which coordinates could not be calculated due to insufficient information in the description of the locality (981). These records are labelled as ausente (absent) or dudoso (doubtful) in the “occurrenceStatus” field. In this case a label of “absent” (186 records) means that the record is out of the distributional range of the species (e.g., zoo records), and “doubtful” (979) means that the species could be present in the area, but the ambiguity in the description of the locality prevents an unequivocal assertion of the spatial validity of the record (e.g., Locality: Mexico).
Geographic distribution of the 22, 731 valid distributional records of cracids in the CracidMex1 database. Grey shadeing represents the area where the species occurrence is expected based on
Distribution of cracid genera by country for the 22, 731 valid distributional records in the CracidMex1 database.
Number of valid distributional records of cracid species by country in the CracidMex1 database.
| Country | Ortalis vetula | Ortalis wagleri | Ortalis poliocephala | Ortalis leucogastra | Penelope purpurascens | Penelopina nigra | Oreophasis derbianus | Crax rubra | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 9, 904 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9, 904 |
| Mexico | 2, 938 | 1, 113 | 1, 675 | 124 | 642 | 533 | 145 | 430 | 7, 600 |
| Belize | 533 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 175 | 0 | 0 | 112 | 820 |
| Guatemala | 408 | 0 | 0 | 87 | 176 | 145 | 210 | 115 | 1, 141 |
| Honduras | 134 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 42 | 0 | 16 | 225 |
| El Salvador | 1 | 0 | 0 | 78 | 10 | 29 | 0 | 10 | 128 |
| Nicaragua | 17 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 21 | 73 | 0 | 17 | 161 |
| Costa Rica | 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1, 410 | 0 | 0 | 769 | 2, 236 |
| Panama | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 141 | 0 | 0 | 59 | 200 |
| Colombia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 128 | 0 | 0 | 43 | 171 |
| Venezuela | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 |
| Ecuador | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 103 |
| Peru | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 13, 992 | 1, 113 | 1, 675 | 322 | 2, 868 | 822 | 355 | 1, 584 | 22, 731 |
Coordinates
-4.3327 to 31.1707 Latitude; -109.4433 to -61.1382 Longitude. This range includes the location of only the 22, 731 valid distributional records (Figure 2).
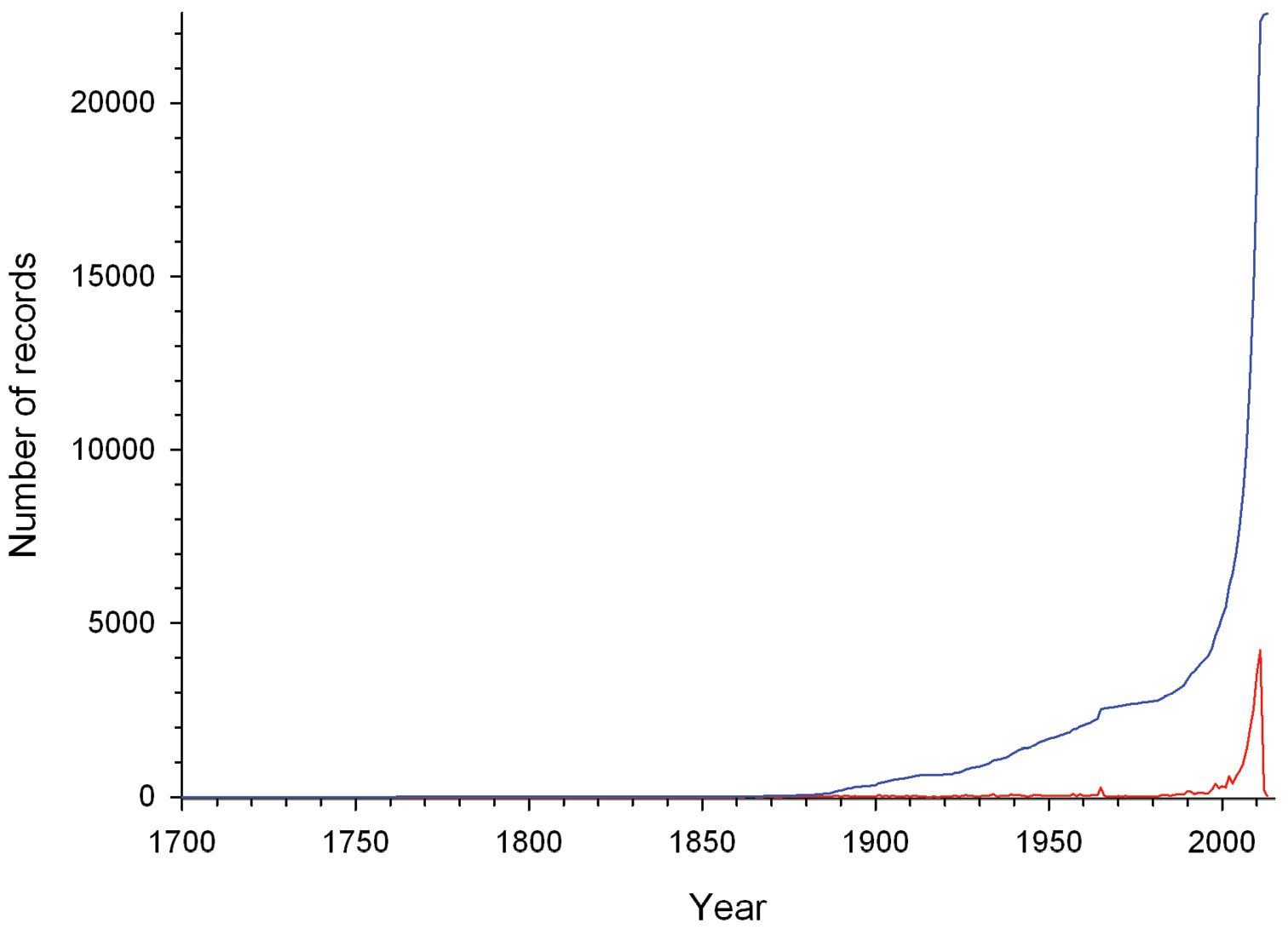
The date of occurrence records (year-month-day) encompasses from 1700-01-01 to 2013-10-25. However, of the 22, 731 valid distributional records, 854 lack information on recording date. Although temporal coverage spans more than 300 years, most of the records were generated in the last decades (Figure 4). A boom in reporting or generating species records started at the end of the last century, most probably due to the emergence of the Internet and technological advancement in field survey equipment. Additionally, this observed pattern might be due to an increased interest in studying this bird group. Information gathered through years of research and observation of the species’ natural history led to the publication in 1973 of the first edition of the inspiring book “Curassows and related birds” by Delacour and Amadon. Added to which the First International Symposium on the Family Cracidae was organized in 1981, which may also have triggered an exponential increase in the interest for studying this avian group, and thus, an increase in reporting species occurrences.
Number of cracid records gathered per year (red line) and the cumulative number of cracid records gathered from 1700 to 2013 (blue line).
Title: Present and future distribution models of cracids occurring in Mexico.
Personnel: Miguel Angel Martínez-Morales (Project Coordinator, Resource Contact, Resource Creator), Gonzalo Enrique Pinilla-Buitrago (Database Manager, Metadata Provider), Fernando González-García, Paula L. Enríquez, José Luis Rangel-Salazar, Carlos Alberto Guichard Romero, Adolfo G. Navarro-Sigüenza, Tiberio César Monterrubio-Rico, Griselda Escalona-Segura (Data Contributors).
Funding: National Commission for Knowledge and Use of Biodiversity (CONABIO), Mexico, under the agreement FB1585/JM024/12.
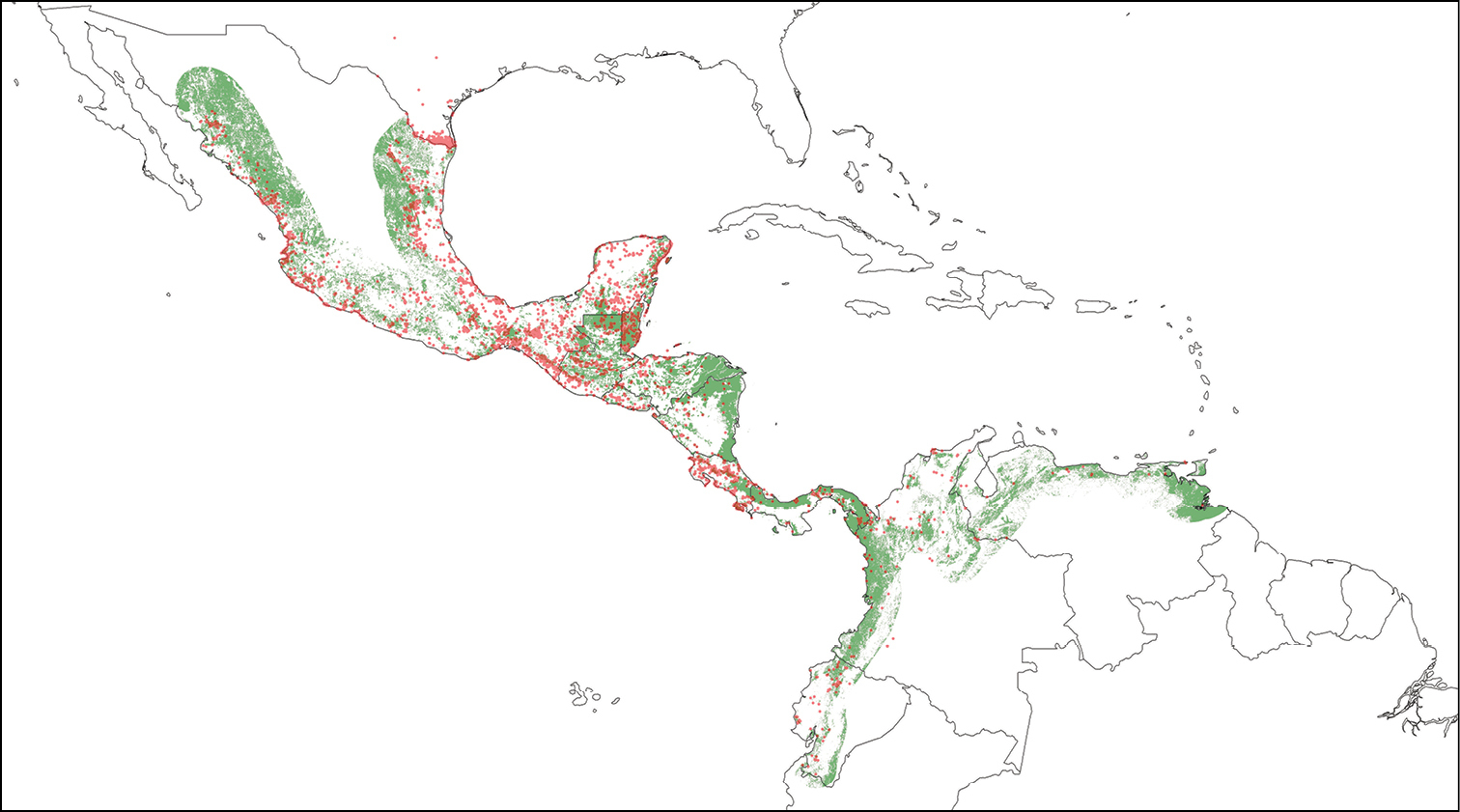
Study area descriptions/descriptor: Valid distribution records are located in the northern portion of the Neotropical region, including the transitional zone with the Nearctic region (Figure 5). Native vegetation in this area ranges from tropical dry to humid forests, and from lowlands to montane forests. However, a large proportion of the native vegetation has been converted to pasture and agricultural areas. The expansion of human settlements, infrastructure, and mining have also contributed to forest degradation and deforestation in the region. Tropical forests have the largest net loss of forested area compared to other forest types in the world (
Geographic distribution of the 22, 731 valid distributional records of cracids in the CracidMex1 database. Present pattern of forest cover is depicted in green shading. Forest cover was obtained from
Given the current pattern of forest cover in the region, and the temporal coverage of records in the CracidMex1 database, many records, particularly older records, are now located outside of currently forested areas (Figure 5). This suggests a substantial reduction in the distribution of cracid species, particularly for those species restricted to primary forests (Penelope purpurascens, Penelopina nigra, Oreophasis derbianus, and Crax rubra). Habitat loss and hunting pressure are the main drivers of cracid population declines and distribution contractions, the synergy of which has caused the endangerment of these species (
Design description: The construction of the CracidMex1 database aimed to gather most of the globally available records of cracids which are distributed in Mexico, in order to generate global species distribution models. We initiated the construction of the database by collating records from six electronic databases available through the Internet: GBIF <http://data.gbif.org>, ORNIS <http://www.ornisnet.org>, REMIB <http://www.conabio.gob.mx/remib/doctos/remib_esp.html>, UNIBIO <http://unibio.unam.mx>, SpeciesLink <http://splink.cria.org.br>, and IBC <http://ibc.lynxeds.com>. Additionally, we obtained records from the National System of Information on Biodiversity (SNIB) database at CONABIO and from museum specimen records contained in the Bird Atlas of Mexico database at the Facultad de Ciencias of the National Autonomous University of Mexico. We also obtained records from published papers through searches in BioOne <http://www.bioone.org>, EBSCO <http://search.ebscohost.com>, JSTOR <http://www.jstor.org>, ScienceDirect <http://www.sciencedirect.com>, Springer Link <http://www.springerlink.com>, Web of Science <http://apps.webofknowledge.com>, Wiley Online Library <http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com>, Zoological Record <http://thomsonreuters.com/zoological-record/>, Redalyc <http://www.redalyc.org>, SciELO <http://www.scielo.org>, and Google Scholar <scholar.google.com>. We also reviewed the bulletins of the Cracid Group of the Galliformes Specialists Group <http://www.cracids.org>. Added to which, we gathered records from “grey literature” through searches in technical reports and theses. These searches included the electronic portal of CONABIO and the repositories OpenDOAR <http://opendoar.org> and the Registry of Open Access Repositories <http://roar.eprints.org>. Finally, we gathered records from our own and unpublished databases of colleagues through personal contacts. After the GBIF, these personal unpublished databases were the second most important source of records, followed by records gathered from the SNIB and published papers (Table 4).
Relative contribution of records of cracid species by the different sources used in the construction of the CracidMex1 database. Numbers represent non-duplicate records. GBIF was the main source of records, but its relative contribution is magnified in this table because in the consolidation process we considered this source as the reference database.
| Source | Ortalis vetula | Ortalis wagleri | Ortalis poliocephala | Ortalis leucogastra | Penelope purpurascens | Penelopina nigra | Oreophasis derbianus | Crax rubra | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GBIF | 13, 479 | 982 | 896 | 279 | 2, 751 | 734 | 233 | 1, 524 | 20, 878 |
| ORNIS | 180 | 19 | 11 | 64 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 279 |
| REMIB | 86 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 98 |
| UNIBIO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SpeciesLink | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| IBC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| SNIB | 209 | 1 | 435 | 8 | 17 | 26 | 9 | 12 | 717 |
| Bird Atlas Mex | 120 | 95 | 31 | 1 | 57 | 34 | 2 | 51 | 391 |
| Published papers | 235 | 47 | 77 | 37 | 131 | 56 | 40 | 90 | 713 |
| “Grey literature” | 37 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 20 | 4 | 2 | 16 | 91 |
| Unpublished DB | 19 | 4 | 298 | 0 | 116 | 52 | 115 | 116 | 720 |
| Total | 14, 366 | 1, 151 | 1, 754 | 392 | 3, 100 | 907 | 401 | 1, 825 | 23, 896 |
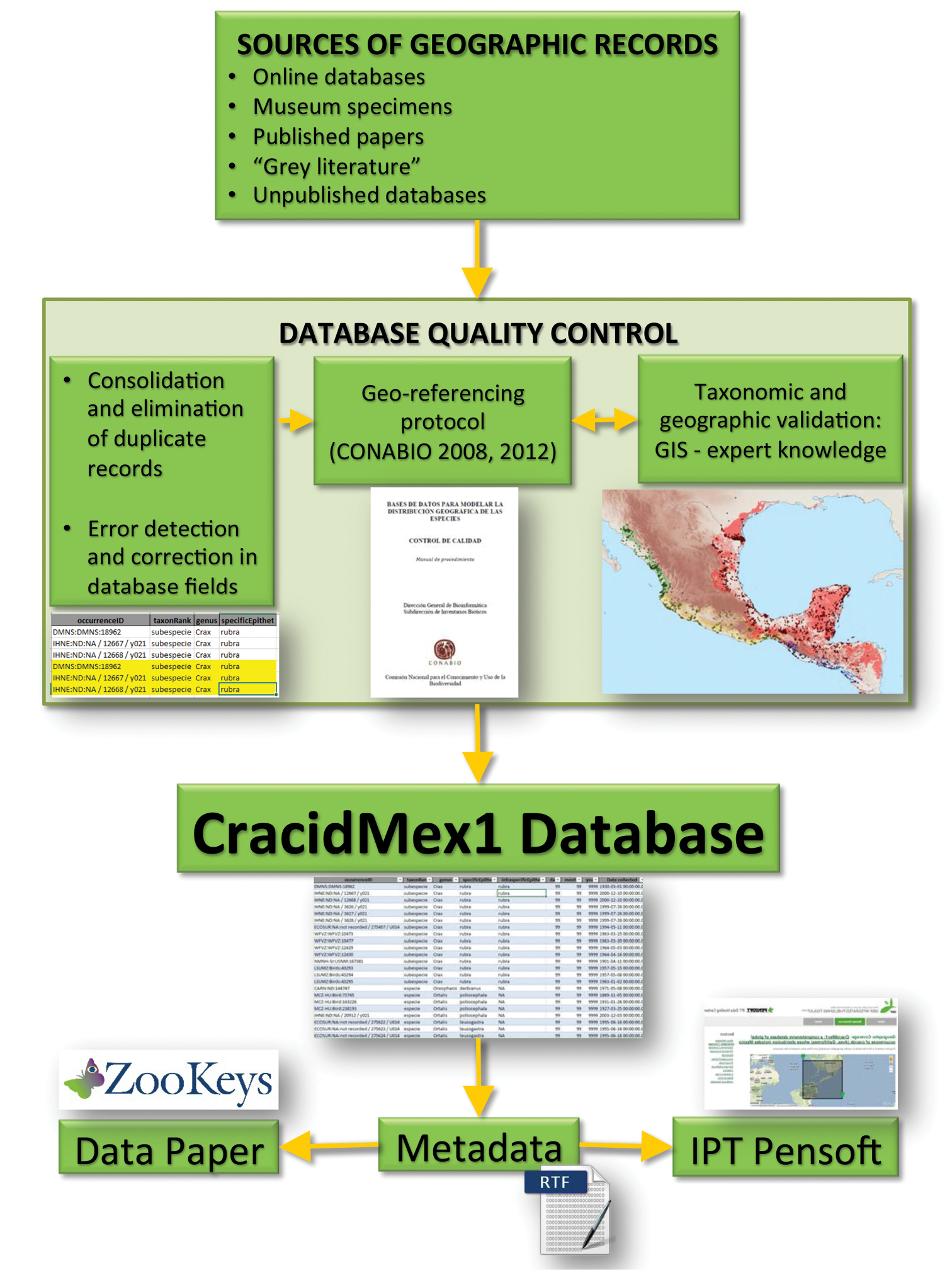
Database quality control, based on the standards described in
Flowchart depicting the iterative process for the construction of the CracidMex1 database up to publication.
The CracidMex1 database has 41 fields based on the standard Darwin Core version 1.4 (Table 5).
Definition of fields included in the CracidMex1 database based on the standard Darwin Core version 1.4.
| Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| institutionCode | The name (or acronym) in use by the institution having custody of the object(s) or information referred to in the record. In the case of personal records, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). |
| collectionCode | The name, acronym, code, or initials identifying the collection or data set from which the record was derived. If the record was not held in a collection, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). If the collection name was not known, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| datasetName | The name identifying the data set from which the record was derived. If the data set name was not known, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| basisOfRecord | The specific nature of the data record. • Ejemplar preservado (Preserved specimen). Denoting a preserved specimen in a collection. • Observación (Human observation). Denoting an observation made by one or more people. • Observación con aparato (Machine observation). Denoting an observation made by a machine. • Ocurrencia (Occurrence). Denoting a case where no information is available on how the record was obtained. |
| occurrenceID | A uniform resource name as a unique identifier for the record. In the absence of a persistent global unique identifier, this was constructed in the form: “[institutionCode]: [collectionCode]: [catalogNumber]”. If the record lacked a value in one of these fields (NA or ND) a sequential number was assigned at the end. |
| catalogNumber | An identifier for the record within the data set or collection. If the record did not have a catalogue number, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). If we did not know the catalogue number, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| recordNumber | An identifier given to the occurrence at the time it was recorded. This often serves as a link between field notes and an occurrence record, such as a specimen collector’s number. If the record did not have a record number, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). If we did not know the record number, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| recordedBy | A list (concatenated and separated) of names of people, groups, or organizations responsible for recording the original occurrence. The primary collector or observer, especially one who applies a personal identifier (recordNumber), is listed first. If we did not know the name of the collector, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| individualCount | The number of individuals recorded at the time of the occurrence. We left the value empty if individualCount was unknown. |
| occurrenceStatus | A statement about the presence or absence of a taxon at a location. • Presente (Present). There is at least one well documented record of the taxon’s presence in the area. • Ausente (Absent). There is evidence to document the absence of a taxon in the area. • Dudoso (Doubtful). The taxon is presumed present in the area, but there is doubt over the evidence, including taxonomic or geographic imprecision in the records. |
| associatedReferences | A list (concatenated and separated) of identifiers (publication, bibliographic reference, global unique identifier) of literature associated with the occurrence. If no reference was associated, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). |
| year | The four-digit year in which the event occurred, according to the Common Era Calendar. If we did not know the year, we used “9999”. |
| month | The ordinal month in which the event occurred. If we did not know the month, we used “99”. |
| day | The integer day of the month on which the event occurred. If we did not know the day, we used “99”. |
| country | The name of the country or major administrative unit in which the location occurs. If we did not know the name, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| stateProvince | The name of the next smaller administrative region below country (state, province, canton, department, region, etc.) in which the location occurs. If we did not know the name, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| county | The full, unabbreviated name of the next smaller administrative region below stateProvince (county, shire, department, municipality) in which the location occurs. If this administrative region does not apply, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). If we did not know the name, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| locality | The specific description of the place. This term may contain information modified from the original to correct perceived errors or standardize the description. If we did not know the description, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| decimalLatitude | The geographic latitude (in decimal degrees, using the spatial reference system given in geodeticDatum) of the geographic centre of a location. Positive values are north and negative values are south of the Equator. We left the value empty if decimalLatitude was unknown. |
| decimalLongitude | The geographic longitude (in decimal degrees, using the spatial reference system given in geodeticDatum) of the geographic centre of a location. Positive values are east and negative values are west of the Greenwich Meridian. We left the value empty if decimalLongitud was unknown. |
| geodeticDatum | The ellipsoid, geodetic datum, or spatial reference system upon which the geographic coordinates given in decimalLatitude and decimalLongitude are based. We used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined) when no data was available in decimalLatitude and decimalLongitude. |
| coordinateUncertaintyInMeters | The horizontal distance (in meters) from the given decimalLatitude and decimalLongitude describing the smallest circle containing the entire location. We left the value empty if the uncertainty was unknown, could not be estimated, or was not applicable (because there are no coordinates). |
| georeferencedBy | A list (concatenated and separated) of names of people, groups, or organizations who determined the geo-reference for the location. |
| georeferenceProtocol | A description or reference for the methods used to determine the spatial footprint, coordinates, and uncertainties. |
| georeferenceSources | A list (concatenated and separated) of maps, gazetteers, or other resources used to geo-reference the location. |
| identifiedBy | A list (concatenated and separated) of names of people, groups, or organizations who assigned the taxon to the subject. If we did not know the name, we used the value “ND” No determinado (Not determined). |
| dateIdentified | The date on which the subject was identified as representing the taxon. Format yyyy-mm-dd. If we did not know the date, we used “9999”. |
| typeStatus | A list (concatenated and separated) of nomenclatural types applied to the subject. If the nomenclatural type did not apply, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). |
| scientificName | The full scientific name of the lowest taxonomic rank determined. |
| originalNameUsage | The taxon name, as it originally appeared when first determined. |
| kingdom | The full scientific name of the kingdom in which the taxon is classified. |
| phylum | The full scientific name of the phylum in which the taxon is classified. |
| class | The full scientific name of the class in which the taxon is classified. |
| order | The full scientific name of the order in which the taxon is classified. |
| family | The full scientific name of the family in which the taxon is classified. |
| genus | The full scientific name of the genus in which the taxon is classified. |
| specificEpithet | The name of the species epithet of the scientificName. |
| infraspecificEpithet | The name of the lowest or terminal infraspecific epithet of the scientificName. If the infraspecific epithet did not apply, we used the value “NA” No aplica (Not applicable). |
| taxonRank | The taxonomic rank of the most specific name in the scientificName. |
| scientificNameAuthorship | The authorship information for the scientificName formatted according to the conventions. |
| taxonomicStatus | The status of the use of the scientificName as a label for a taxon. |
Object name: Darwin Core Archive CracidMex1: a comprehensive database of global occurrences of cracids (Aves, Galliformes) with distribution in Mexico
Character encoding: UTF-8
Format and storage mode: xlsx; ASCII csv, tab-delimited; decimal separator: ‘.’
Distribution: http://ipt.pensoft.net/ipt/resource.do?r=cracidmex1
Publication date of data: 2014-03-10
Language: Spanish.
Metadata language: English.
Date of metadata creation: 2014-01-08
Hierarchy level: Dataset
We are thankful to the many colleges that contribute with records at specific localities, particularly Adrián Maldonado, Alan Monroy Ojeda, Alejandro Salinas Melgoza, Alma Patricia Degante González, Barbara MacKinnon de Montes, David Molina Tovar, Epifanio Blancas Calvas, Erik González, Fernando Ayerbe Quiñones, Gonzalo Merediz Alonso, Gustavo A. Bravo, Hernaldo Padilla, James Rodríguez, Javier Rivas, José Raúl Vázquez Pérez, Juan Freile Ortiz, Juan Quiñones, Karla Patricia Parra Noguez, Mario C. Lavariega, Paola Nicté Cotí Lux, Robert Ridgely, Román Díaz Valenzuela, and Santiago Guallar. Alejandro Gordillo (MZFC) coordinated the geolocation of specimen data for the Atlas of the Birds of Mexico. The manuscript was improved thanks to the appropriate comments of Katherine Renton and two anonymous reviewers. CONABIO provided financial support (project JM024).